Indian Society and Social Issues: August 2023 UPSC Current Affairs | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
World Tribal Day 2023
Today, August 9, 2023, is World Tribal Day. This day is observed by the United Nations to promote and protect the rights of the world’s indigenous peoples. It is also a day to celebrate the achievements and contributions that indigenous peoples make to society.
There are over 476 million indigenous peoples living in over 90 countries around the world. They make up about 5% of the world’s population, but they account for more than 15% of the world’s poorest people. Indigenous peoples are often marginalized and discriminated against, and they face many challenges, such as poverty, lack of access to education and healthcare, and environmental degradation.
World Tribal Day 2023 Theme
This year’s theme for World Tribal Day is “Indigenous Youth as Agents of Change for Self-determination.” This theme highlights the important role that indigenous youth play in their communities and in the world. Indigenous youth are often at the forefront of social and environmental movements, and they are leading the way in shaping the future of their cultures and traditions.
World Tribal Day 2023 Significance
The significance of World Tribal Day is to raise awareness of the challenges faced by indigenous peoples around the world, such as discrimination, poverty, and lack of access to education and healthcare. It is also an opportunity to celebrate the cultures and contributions of indigenous peoples.
World Tribal Day is an important day to celebrate the diversity of indigenous cultures and to raise awareness of the challenges they face. It is also a day to commit to working towards a better future for indigenous peoples around the world.
Here are some ways to celebrate World Tribal Day:
- Learn about the indigenous peoples in your community.
- Support indigenous businesses and organizations.
- Get involved in advocacy work for indigenous rights.
- Educate others about the challenges faced by indigenous peoples.
- Celebrate indigenous cultures and traditions.
World Tribal Day is a day to come together and show our support for indigenous peoples around the world. Let’s make this year’s celebration a meaningful one!
World Tribal Day History
The International Day of the World’s Indigenous Peoples, also known as World Tribal Day, was first proclaimed by the United Nations General Assembly in December 1994. The date of August 9 was chosen to mark the day of the first meeting of the UN Working Group on Indigenous Populations of the Sub-Commission on the Promotion and Protection of Human Rights in 1982.
The purpose of World Tribal Day is to raise awareness of the challenges faced by indigenous peoples around the world, such as discrimination, poverty, and lack of access to education and healthcare. It is also an opportunity to celebrate the cultures and contributions of indigenous peoples.
Barrier to Women’s Labor Force Participation
Why in News?
Recently, the Tamil Nadu government has launched the Kalaignar Magalir Urimai Thogai Thittam, a women's basic income scheme, recognizing Women's Unpaid Labor. The scheme will provide Rs 1,000 per month to women in eligible households
- In Marriages, the wife bears and rears children and minds the home, and therefore bears the brunt of unpaid care and domestic work, hindering their Participation in Labor Force.
What are the Causes of Lower Women Participation in the Labour Force?
- Patriarchal Social Norms:
- Deep-rooted patriarchal norms and traditional gender roles often limit women's access to education and employment opportunities.
- Societal expectations may prioritize women's roles as caregivers and homemakers, discouraging their active participation in the labor force.
- Gender Wage Gap:
- Women in India often face wage disparities compared to men for similar work.
- According to World Inequality Report, 2022 , men in India capture 82% of labour income, while women earn just 18%.
- This wage gap can discourage women from seeking formal employment opportunities.
- Unpaid Care Work:
- The burden of unpaid care and domestic work falls disproportionately on women, limiting their time and energy for paid employment.
- Married women in India spend over 7 hours per day on unpaid care and domestic work, while men spend less than 3 hours.
- This trend is consistent across income levels and caste groups, leading to a significant Gender Disparity in domestic responsibilities.
- This unequal distribution of household responsibilities can be a significant barrier to women's participation in the labor force.
- Social and Cultural Stigma:
- In some communities, there may be stigma or resistance associated with women working outside the home, leading to lower labor force participation rates.
What are the Statistics Regarding Unpaid Care of Women?
- Female Labor Force Participation Rate (LFPR):
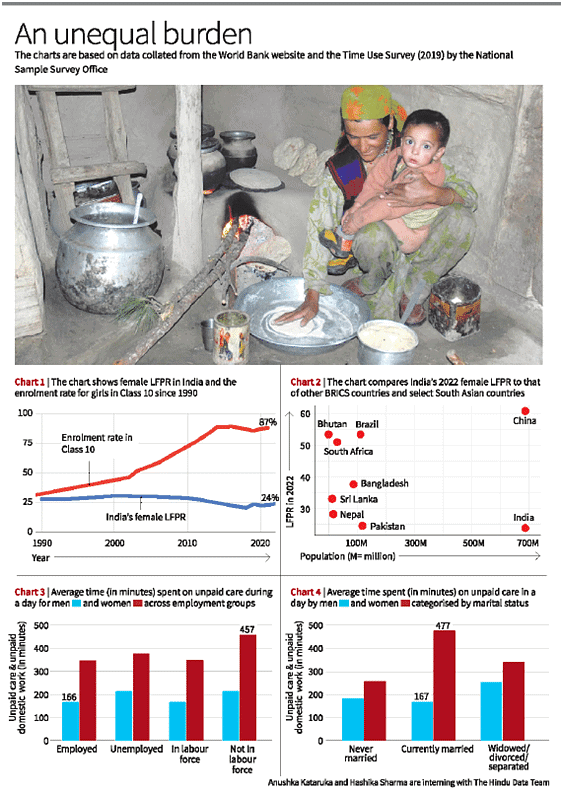
- Despite a surge in the enrollment rate for girls in Class 10, India's Female LFPR has declined from 30% to 24% over the past two decades.
- The burden of domestic work is a key factor contributing to lower female LFPR, even among educated women.
- India's female LFPR (24%) is the lowest among BRICS countries and select South Asian countries.
- China, with the highest female population, boasts the highest female LFPR at 61%.
- Impact on Women's Employment:
- Women not in the labor force spend the most time on unpaid domestic/care work, averaging 457 minutes (7.5 hours) per day.
- Employed women follow closely, spending 348 minutes (5.8 hours) per day on such chores, impacting their ability to engage in paid work.
How can Higher Women Labor Participation Impact the Society at Large?
- Economic Growth:
- Women's participation in the labor force is directly linked to economic growth. When a significant portion of the female population remains underutilized, it results in a loss of potential productivity and economic output.
- Increased women's labor force participation can contribute to higher GDP (Gross Domestic Product) and overall economic prosperity.
- Poverty Reduction:
- When women have access to income-generating opportunities, it can lift households out of poverty, leading to better living standards and improved well-being for families.
- Human Capital Development:
- Educated and economically active women can positively influence the education and health outcomes of their children, leading to intergenerational benefits.
- Gender Equality and Empowerment:
- Higher women's participation in the labor force can challenge traditional gender roles and norms, promoting gender equality.
- Economic empowerment enables women to have greater control over their lives, decision-making power, and autonomy.
- Fertility and Population Growth:
- Studies have shown that as women's labor force participation increases, fertility rates tend to decline.
- This phenomenon, known as the "fertility transition," is associated with improved access to education, healthcare, and family planning, leading to more sustainable population growth.
- Reduced Gender-Based Violence:
- Economic empowerment can enhance women's bargaining power and reduce their vulnerability to gender-based violence and abusive relationships.
- Labor Market and Talent Pool:
- Increasing women's participation in the labor force can help address skill shortages and labor market imbalances, leading to a more efficient allocation of talent and resources.
Way Forward
- Gender equality discussions should move beyond compartmentalizing women's lives into work and life and recognize the comprehensive valuation of all kinds of work, both formal and informal, that women do.
- Policy solutions must be derived from women's own negotiations within their cultural context, focusing on increasing autonomy and flexible work options.
- Promoting and supporting higher women's labor force participation is not only a matter of gender equality but also a crucial driver of societal progress and development.
- By unlocking the full potential of women in the workforce, societies can reap the benefits of economic growth, poverty reduction, improved human capital, and more inclusive and equitable communities.
Organ Donation in India
Context
Presently, India is suffering from high shortage of organ donations and this has led to a situation, where thousands of patients are waiting for transplants.
More about the news
- Recently, the central government has modified National Organ Transplantation Guidelines, allowing those above 65 years of age to receive an organ for transplantation from deceased (dead) donors.
- Basically, Transplantation of Human Organs Act, 1994 provides various rules and regulations for the removal of human organs and their storage. This act also regulates the transplantation of human organs.
Key provisions of the Transplantation of Human Organs Act, 1994 include
- Regulation of Organ Transplants: The act regulates the removal, storage, and transplantation of human organs and tissues for therapeutic purposes. It establishes a framework for the legal and ethical aspects of organ transplantation.
- Authorized Hospitals and Medical Practitioners: The act designates hospitals as "authorized hospitals" that are permitted to conduct organ transplantation procedures. Similarly, it designates medical practitioners as "authorized medical practitioners" who are qualified to perform organ transplantation procedures.
- Requirement of Authorization Committee: The act mandates the establishment of ‘authorization committees’ at the state and central levels. These committees are responsible for reviewing and granting approvals for organ transplantations. They ensure that the transplantation is conducted in accordance with the law and ethical standards.
- Categories of Relatives: The act specifies the categories of relatives who can legally donate organs to patients. For instance, organs can be donated by parents, siblings, children, and other near relatives.
- Prohibition of Commercial Dealing: One of the main objectives of the act is to prevent the commercial trade of human organs. It prohibits the sale and purchase of organs, making commercial organ trafficking illegal.
- Preservation of Organs: The act mentions procedures for the preservation of donated organs to maintain their viability and increase the chances of successful transplantation.
- Penalties for Violations: The act defines penalties for violations, including unauthorized removal of organs, contravention of the act's provisions, and illegal commercial dealings. Penalties can include imprisonment and fines.
- Consent and Authorization: The act emphasizes the importance of informed consent from the donor or their relatives for organ transplantation. It also requires that the authorization for transplantation be obtained in a prescribed manner.
About the status of organ donation in India
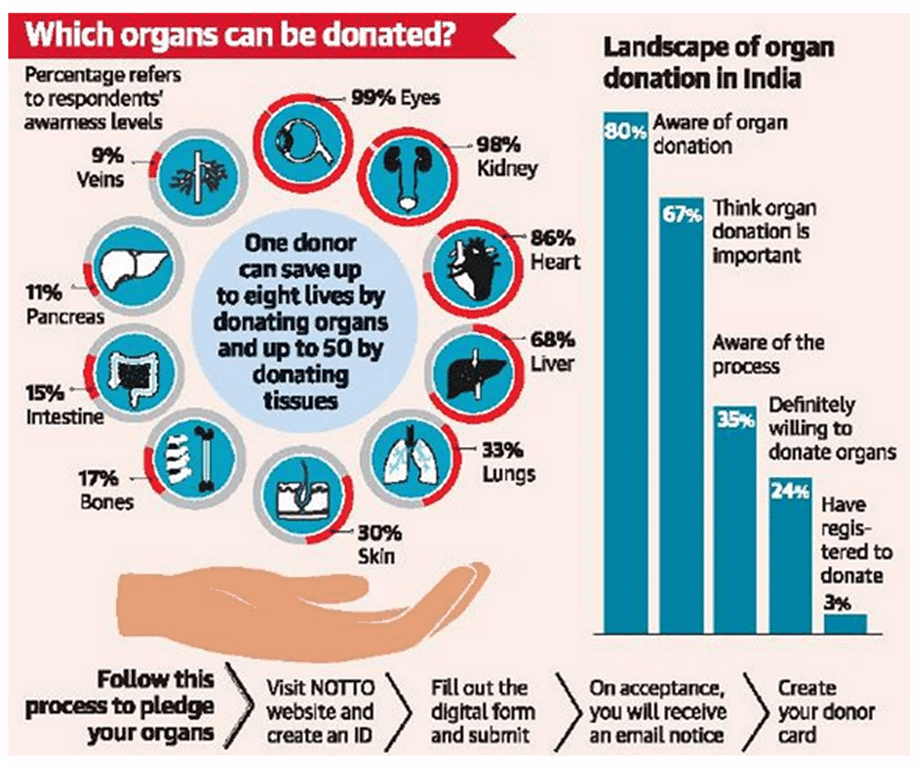
- Presently, almost 3 lakh patients are on the waiting list for organ donations in India and the supply of organ donors is very less as compare to demand.
- Around 20 people die daily due to shortage of organs.
- The number of donors including both living and deceased, have shown very slow growth over the years. From 6,916 donors in 2014, the number has increased to around 16,041 donors in 2022.
- Living donors forms the majority in India as they account for almost 85% of all donors in India.
- States like Telangana, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Gujarat and Maharashtra are on the top in terms of deceased organ donors, while Delhi-NCR, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Maharashtra, and West Bengal are on the top in case of living donors.
Challenges regarding organ donation in India are
- Lack of Awareness: A significant challenge is the lack of awareness about organ donation and its importance. Many people are not fully informed about the benefits of organ donation.
- Myths and Misconceptions: There are various myths and misconceptions surrounding organ donation in India, such as fears that organ donation could impact one's afterlife or lead to bodily disfigurement. Addressing these misconceptions is essential to increase public acceptance.
- Religious and Cultural Beliefs: India is a diverse country with a multitude of religious and cultural beliefs. Some of these beliefs may be opposed to organ donation, posing challenges in promoting the concept across all communities.
- Trust in the Healthcare System: A lack of trust in the healthcare system can deter potential donors from participating. Concerns about misuse of organs, organ trafficking, and unethical practices can make people hesitant to donate.
- Family Consent: In India, family consent is often required for organ donation, even if the deceased had expressed a desire to donate their organs. If family members are not aware of the deceased's wishes or are unwilling to give consent, it can hinder organ donation.
- Infrastructure and Resources: Adequate infrastructure and resources are essential for organ transplantation procedures. Many hospitals lack the necessary facilities, trained medical staff, and equipment for successful organ transplant surgeries.
- Legal and Regulatory Challenges: While the Transplantation of Human Organs Act, 1994, and subsequent amendments provide a regulatory framework, there can still be challenges related to enforcement and interpretation of the law.
- Shortage of Organ Procurement Organizations (OPOs): Organ Procurement Organizations are responsible for identifying potential donors, obtaining consent, and coordinating the organ retrieval process. The limited number of OPOs in India can hinder the efficient collection of organs from deceased donors.
- Organ Trafficking and Commercialization: Despite legal provisions, cases of illegal organ trafficking and commercialization still exist. These activities can deter individuals from participating in organ donation due to concerns about exploitation.
Conclusion
Addressing these challenges requires a multi-faceted approach that involves raising awareness, improving healthcare infrastructure, enhancing legal enforcement, collaborating with religious and community leaders, and promoting a culture of organ donation that prioritizes ethical practices and the well-being of both donors and recipients.
World Breastfeeding Week 2023
Context
The United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF) and the World Health Organization (WHO) lauded the progress made by several countries in increasing exclusive breastfeeding rates on the occasion of World Breastfeeding Week 2023. They also pointed out the potential for further advancements if breastfeeding is protected and supported, particularly in the workplace.
World Breastfeeding Week
- In the commemoration of the 1990 Innocenti Declaration, it is observed on an annual basis during the first week of August.
- The Innocenti Declaration was signed by the policymakers, UN health agencies, and other organizations for protecting, promoting, and supporting breastfeeding in 1990.
- The World Alliance for Breastfeeding Action (WABA) was formed in 1991 as a global network, and since 1992, on an annual basis, the world has marked Breastfeeding Week.
- WBW has been aligned with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) since 2016. It helps in achieving many 17 SDGs comprising goals on poverty, hunger, health, education, gender equality, and sustainable consumption.
- UNICEF and WHO urged the governments, donors, civil society and the private sector for speeding up efforts in order to help in eliminating barriers women and families face in achieving their breastfeeding goals and reaching the global 2030 target of 70%.
Progress in Exclusive Breastfeeding Rates
- It comprises feeding babies only on breast milk and excluding all other foods, liquids, infant formula, or water, barring necessary medications or vitamin and mineral supplements.
- It proffers very crucial health benefits to infants, comprising protection against common infectious diseases and bolstering their immune systems, ensuring they receive essential nutrients for optimal growth and development.
- The global rate of exclusive breastfeeding has increased by an impressive 10% points, reaching 48% over the past decade.
Indian Policy Measures Relating to Breastfeeding
- MAA is a nationwide program of the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare to promote breastfeeding.
- Vatsalya – Maatri Amrit Kosh
- MAA - "Mothers Absolute Affection"
- In collaboration with the Norwegian government, National Human Milk Bank and Lactation Counselling Centre named Vatsalya has been established.
SC Allows Termination of Pregnancy for Rape Survivor
Why in News?
Observing that pregnancy outside marriage, especially in cases of sexual assault, is injurious and a cause of stress, the Supreme Court of India allowed a rape survivor from Gujarat to terminate her 27-week pregnancy.
- The court overruled the Gujarat High Court’s order that denied her request and directed the hospital to carry out the procedure without any delay.
- Under the Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) Amendment Act 2021, the upper limit for termination of pregnancy is 24 weeks.
What are the Legal Provisions Related to Abortion in India?
- Until the 1960s, abortion was prohibited in India, and violating this led to imprisonment or fines under Section 312 of the Indian Penal Code.
- The Shantilal Shah Committee was set up in the mid-1960s to investigate the need for abortion regulations.
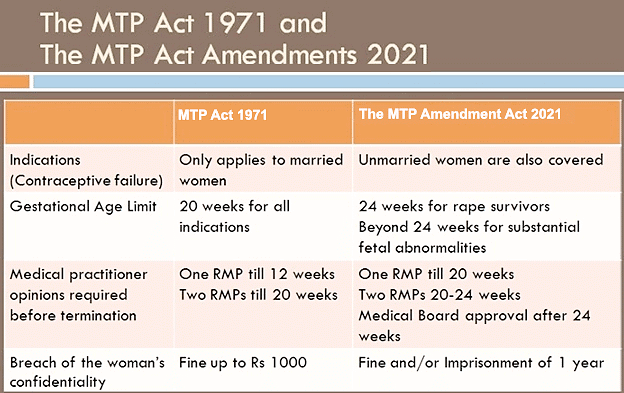
- Based on its findings, the Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) Act, 1971 was enacted, allowing safe and legal abortions, safeguarding women's health, and reducing maternal mortality.
- The MTP Act, 1971, allows abortion up to 20 weeks of gestation, with the consent of the woman and on the advice of one registered medical practitioner (RMP). However, the law was updated in 2002 and 2021.
- The 2021 amendment permits abortion from 20 to 24 weeks of gestation for specific cases like rape survivors, with approval from two doctors.
- It sets up state level Medical Boards to decide if a pregnancy may be terminated after 24 weeks in cases of substantial fetal abnormalities.
- The 2021 amendment permits abortion from 20 to 24 weeks of gestation for specific cases like rape survivors, with approval from two doctors.
- It extends the failure of contraceptive clauses to unmarried women( initially only married women), allowing them to seek abortion services on grounds of their choice, irrespective of their marital status.
- Consent requirements vary based on age and mental state, ensuring medical practitioner oversight.
- Recent Supreme Court judgments reaffirm women's bodily autonomy. Courts recognized abortion rights in cases of rape and acknowledged reproductive choice as a component of personal liberty.
Changing Youth Concerns and Aspirations
Why in News?
In the ever-evolving landscape of youth concerns and aspirations, a recent survey conducted by Lokniti-CSDS across 18 states in India sheds light on the shifting priorities of the young population.
- The survey highlights the rising prominence of unemployment and price rise as pressing issues, the intersection of these concerns with economic classes and gender, and the evolving preferences in job aspirations.
What are the Major Highlights of the Survey?
- Unemployment, Price Rise and Gender Disparity:
- A 7% point increase in the share of respondents identifying price rise as a primary concern.
- 40% of highly educated respondents (graduate and above) pointing to unemployment as their most pressing concern.
- 27% of non-literate individuals expressed concern about unemployment, attributed to their flexibility in undertaking various job opportunities.
- Poverty and price rise emerged as more prominent issues for young women, regardless of their economic background.
- Occupational Diversity: Insights into Youth Employment:
- Almost half (49%) of the respondents were engaged in some form of work.
- 40% held full-time jobs, while 9% worked part-time.
- 23% of employed youth were self-employed, showcasing a significant entrepreneurial inclination.
- Professions such as doctors and engineers constituted 16% of the workforce.
- Agriculture and skilled labor comprised 15% and 27% respectively.
- Job Aspirations and Preferences:
- 16% of respondents expressed a preference for jobs in the health sector.
- The education sector was the second most preferred, chosen by 14% of youth.
- Science and technology-related jobs, along with starting their own businesses, garnered 10% support each.
- Government jobs continued to hold allure, with 60% of respondents opting for them when given a choice between a government job, a private job, or starting their own business.
- The preference for self-employment has grown steadily from 16% in 2007 to 27% in 2023, indicating an increasing entrepreneurial inclination among the youth.
What are the Opportunities and Challenges Related to Youth Population in India?
- Status of Youth Population: India has more than 50% of its population below the age of 25 and more than 65% below the age of 35.
- India is home to a fifth of the world’s youth demographic and this population advantage could play a critical role in achieving the nation’s ambitious target to become a USD 5 trillion economy.
- Opportunities:
- Human Capital Investment: India's youth population is a potential demographic dividend, which means if harnessed correctly, it can contribute significantly to economic growth.
- A youthful population provides an opportunity to focus on education and skill development, creating a highly skilled workforce that can meet the demands of various industries.
- Innovation and Entrepreneurship: The youth are often more open to innovation, new technologies, and entrepreneurship.
- They can drive the development of new industries and start-ups, fostering economic diversification.
- Also, with a significant portion of India's population engaged in agriculture, youth involvement in modernizing and optimizing farming practices through technology and sustainable methods can lead to increased agricultural productivity.
- Digital Connectivity: India's youth are tech-savvy and can play a crucial role in adopting and promoting digital technologies, contributing to the growth of the digital economy.
- Social Change and Activism: Young people are often at the forefront of social and political change.
- They can drive positive social movements, advocate for change, and raise awareness about critical issues.
- Human Capital Investment: India's youth population is a potential demographic dividend, which means if harnessed correctly, it can contribute significantly to economic growth.
- Challenges:
- Underemployment and Skill Mismatch: While unemployment is often discussed, underemployment and skill mismatch are equally pressing issues. Many young Indians find jobs that are below their skill levels or do not align with their education.
- This not only leads to dissatisfaction but also hampers productivity and economic growth.
- Mental Health and Stigma: Mental health problems among the youth are on the rise, yet there is a significant stigma associated with seeking help.
- This stigma is deeply ingrained in Indian society and can discourage young people from accessing proper care.
- Digital Divide within Youth: While India has a large and growing youth population, access to digital technology is still uneven.
- This digital divide creates disparities in education, employment opportunities, and access to information.
- Gender Inequality and Traditional Norms: Despite progress, gender inequality remains a significant concern.
- Traditional norms and patriarchal attitudes persist, affecting young women's education, employment, and agency.
- Political Apathy and Youth Representation: Despite comprising a substantial portion of the population, the youth in India often feel disconnected from the political process.
- This leads to inadequate representation of their concerns and aspirations.
- Underemployment and Skill Mismatch: While unemployment is often discussed, underemployment and skill mismatch are equally pressing issues. Many young Indians find jobs that are below their skill levels or do not align with their education.
Way Forward
- Integrated Skill Ecosystem: There is a need to develop a comprehensive skill ecosystem that combines formal education with experiential learning, apprenticeships, and online platforms.
- This can bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical skills, enhancing employability.
- Gamified Civic Engagement Platforms: Develop gamified mobile applications that engage youth in civic activities and political processes.
- By turning civic participation into an interactive and rewarding experience, these platforms can encourage more informed voting, increase political awareness, and foster a sense of ownership in governance.
- Entrepreneurship in Traditional Crafts: Foster entrepreneurship among young artisans by combining traditional crafts with modern design and marketing techniques.
- This could involve creating platforms for selling handcrafted products online, preserving cultural heritage while generating income for youth in rural areas.
- Youth Diplomacy and Cultural Exchanges: Facilitate cultural exchanges between young people from India and other countries to foster global understanding, diplomacy, and cross-border friendships.
- The Y20 Summit can facilitate this.
Eastern Equine Encephalitis
Context
A rare mosquito-borne illness eastern equine encephalitis reported in Alabama and New York.
Eastern equine encephalitis (EEE)
- It is a viral disease.
- Eastern equine encephalitis (EEE) virus is spread to people by the bite of an infected mosquito.
- Only a few cases are reported in the United States each year.
- Most cases occur in eastern or Gulf Coast states.
Cause of concern for EEE
- Although rare, EEE is very serious.
- Approximately 30% of people with EEE die and many survivors have ongoing neurologic problems.
- There are no vaccines to prevent or medicines to treat EEE.
- We can only reduce the risk of infection with the EEE virus by using insect repellent, wearing long-sleeved shirts and long pants, and taking steps to control mosquitoes indoors and outdoors.
Symptoms
- Most people infected with the eastern equine encephalitis (EEE) virus do not develop symptoms.
- EEE can result in febrile illness (fever) or neurologic disease, including meningitis (infection of the membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord) or encephalitis (infection of the brain).
- Febrile illness is characterized by fever, chills, body aches, and joint pain. There is no central nervous system involvement.
- Signs and symptoms of neurologic disease include all the above symptoms. However neurologic disease and encephalitis may occur after several days of systemic illness.
Treatment
- There are no medications to prevent or treat EEE virus infections.
- Antibiotics are not effective against viruses, such as the EEE virus.
- Rest, fluids, and over-the-counter pain medications may relieve some symptoms.
- For severe diseases, patients often need to be hospitalized to receive supportive treatment.
Mosquito-Borne Diseases
- Chikungunya
- Chikungunya virus is primarily found in Africa and Asia.
- It was found in 2013 for the first time in the Western Hemisphere.
- It is transmitted by the bite of the Aedes aegypti mosquito and Aedes albopictus mosquito.
- Chikungunya is not transmitted from one person to another. The virus needs a vector—a means of transportation: mosquitoes.
- Dengue
- Dengue fever is primarily a tropical disease.
- The virus is transmitted to humans through the bites of infected female mosquitoes, primarily the Aedes aegypti mosquito.
- Malaria
- Malaria is a mosquito-borne disease caused by a parasite.
- It is found in many countries, including sub-Saharan Africa, South Asia, as well as Central and South America.
- The vector is the anopheline mosquito and the disease-causing organism is the malaria parasite.
- Yellow Fever
- Yellow fever virus is a rare tropical illness.
- Yellow fever is caused by an arbovirus (a virus transmitted by vectors such as Aedes aegypti mosquitoes, ticks or other arthropods).
- Zika Virus
- Most people who become infected with the Zika virus have mild symptoms or no illness at all.
- The virus has been linked to serious health conditions, including Zika congenital syndrome in babies.
- Transmission by aegypti and Ae. albopictus.
|
38 videos|5269 docs|1114 tests
|





















