Mitosis and Meiosis | Botany Optional for UPSC PDF Download
The cell cycle
Eukaryotic cells that are actively dividing go through a series of stages collectively referred to as the cell cycle. This cycle consists of two gap phases, denoted as G1 and G2, an S phase where genetic material replication occurs, and an M phase which involves mitosis to segregate genetic material and ultimately leads to cell division.
- G1 Phase: During this phase, various metabolic changes occur to prepare the cell for division. At a specific juncture called the restriction point, the cell commits to division and proceeds into the S phase.
- S Phase: The S phase is characterized by DNA synthesis, resulting in the replication of the genetic material. At the end of this phase, each chromosome comprises two identical sister chromatids.
- G2 Phase: Metabolic changes in the G2 phase assemble the cytoplasmic components required for mitosis and cytokinesis.
- M Phase: This phase involves nuclear division, known as mitosis, followed by cell division, called cytokinesis.
The interval between mitotic divisions, encompassing G1, S, and G2, is collectively referred to as interphase.
Mitosis
- Mitosis is a type of cell division in eukaryotes that results in the production of two daughter cells, each possessing the same genetic material as the parent cell. It ensures that replicated chromosomes from the S phase are distributed in a way that guarantees each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes. In actively dividing animal cells, this entire process typically takes approximately one hour.
- During mitosis, replicated chromosomes are connected to a structure called the "mitotic apparatus," which aligns and then separates the sister chromatids to achieve an equitable distribution of genetic material. This division of genetic material within the cell nucleus is known as karyokinesis and is followed by the division of the cell cytoplasm, termed cytokinesis, resulting in the formation of two daughter cells.
- In certain single-celled organisms, mitosis serves as the foundation for asexual reproduction. In diploid multicellular organisms, sexual reproduction involves the fusion of two haploid gametes to generate a diploid zygote. Mitotic divisions in the zygote and its subsequent daughter cells are responsible for the subsequent growth and development of the organism. In the adult organism, mitosis plays a role in tasks such as cell replacement, wound healing, and tumor formation.
- Mitosis, though a continuous process, is conventionally categorized into five distinct stages: prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.

Mitosis is a process of eukaryotic cell division that leads to the creation of two daughter cells, each inheriting the same genetic material as the parent cell. It involves several stages:
- Prophase: During this stage, which occupies more than half of mitosis, the nuclear membrane disintegrates into small vesicles, and the nucleolus breaks down. The centrosome, responsible for organizing microtubules that form the mitotic spindle, duplicates itself, producing two daughter centrosomes that move to opposite ends of the cell. Chromosomes condense into compact structures, each consisting of two identical sister chromatids linked by a centromere.
- Prometaphase: Chromosomes, led by their centromeres, migrate to the cell's equatorial plane, forming the metaphase plate. Spindle fibers bind to structures associated with the centromere called kinetochores, with individual spindle fibers attaching to kinetochores on each side of the centromere.
- Metaphase: Chromosomes align themselves along the metaphase plate of the spindle apparatus.
- Anaphase: The centromeres divide, causing sister chromatids of each chromosome to separate and move toward opposite ends of the cell, guided by spindle fibers attached to kinetochores. These separated sister chromatids become individual daughter chromosomes, ensuring that each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes.
- Telophase: This marks the final stage of mitosis, where many processes reverse those observed during prophase. The nuclear membrane reforms around the chromosomes, which uncoil and become diffuse. Spindle fibers disappear.
- Cytokinesis: The final step involves cellular division, forming two new cells. In plant cells, a cell plate forms along the metaphase plate, while in animal cells, there is cytoplasmic constriction. The cell then enters interphase, the interval between mitotic divisions.
Meiosis, on the other hand, is a type of cell division that produces haploid sex cells or gametes from diploid cells. It consists of one DNA replication followed by two successive nuclear and cellular divisions, known as Meiosis I and Meiosis II.
The process reduces the cell from diploid to haploid and generates genetic diversity through various mechanisms:
- Exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during Prophase I.
- Random alignment of maternal and paternal chromosomes in Metaphase I.
- Random alignment of sister chromatids at Meiosis II.

Meiosis has several stages:
- Prophase I: Chromosomes pair and exchange genetic material, with distinct phases like leptotene, zygotene, pachytene, diplotene, and diakinesis.
- Prometaphase I: Spindle apparatus forms, and chromosomes attach to spindle fibers via kinetochores.
- Metaphase I: Homologous chromosome pairs align along the metaphase plate.
- Anaphase I: Homologous chromosomes separate and move to opposite poles.
- Telophase I: Chromosomes diffuse, and nuclear membranes reform.
- Cytokinesis I: Cellular division resulting in two haploid cells, followed by Meiosis II, which is analogous to mitosis but involves half the number of chromosomes.
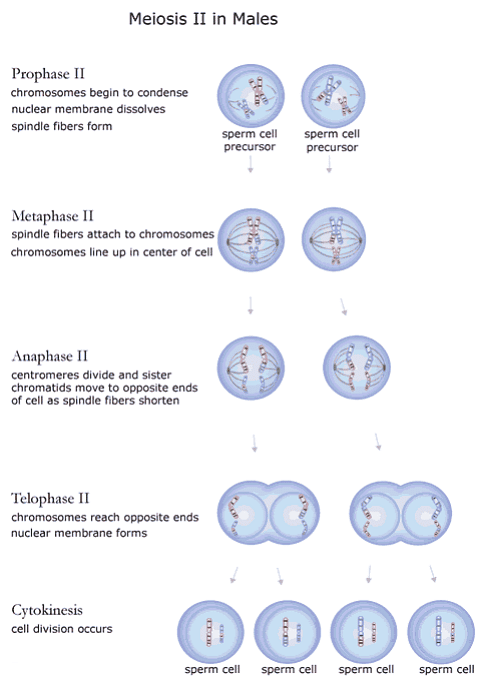
In females, meiosis plays a crucial role in producing eggs (ova) and contributes to genetic diversity.

|
179 videos|140 docs
|
FAQs on Mitosis and Meiosis - Botany Optional for UPSC
| 1. What is the cell cycle? |  |
| 2. What is mitosis? |  |
| 3. What is meiosis? |  |
| 4. What happens during interphase? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of mitosis and meiosis? |  |

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
















