Digital Signature Certificate | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Issuing Authority |

|
| Digital Signatures |

|
| How Digital Signatures Work |

|
| Key Uses of Digital Signatures |

|
| Conclusion |

|
Introduction
Digital Signature Certificates (DSC) are electronic equivalents of physical certificates like passports or driver's licenses. They serve as proof of identity and are used to validate digital documents, messages, or transactions.
Issuing Authority
DSCs are issued by licensed Certifying Authorities (CAs) authorized under the Indian IT Act 2000, granting them the right to issue digital signature certificates.
Digital Signatures
A digital signature is a mathematical technique used to verify the authenticity and integrity of electronic content. It's akin to a handwritten signature, but offers greater security.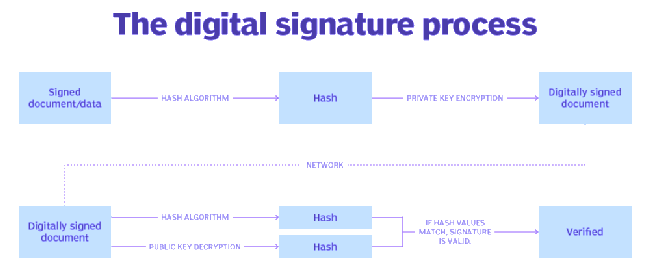
How Digital Signatures Work
Digital signatures follow a Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) protocol, involving the use of public and private keys. The private key, securely held by the signer, is used to create an encrypted signature (hash) of the document. Any alteration to the document after signing invalidates the digital signature.
Key Uses of Digital Signatures
- Streamlining Industries: Various industries leverage digital signatures to enhance processes and document integrity.
- Government Applications: Governments worldwide use digital signatures for tax processing, business-to-government transactions, legal ratification, and contract management.
- Healthcare Sector: Digital signatures improve efficiency, data security, e-prescribing, and hospital operations within the healthcare industry.
- Manufacturing Efficiency: Manufacturing companies employ digital signatures in product design, quality assurance, marketing, and sales processes to expedite operations.
- Financial Services: The U.S. financial sector relies on digital signatures for contracts, paperless banking, loans, insurance documentation, and mortgages.
- Cryptocurrency Authentication: Digital signatures play a crucial role in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin by authenticating blockchain transactions and proving ownership.
Conclusion
Digital Signature Certificates are essential tools in the digital age, offering secure validation of electronic content and enabling streamlined processes across various sectors. Digital signatures are key to ensuring document authenticity and data integrity, making them invaluable in today's digital world.
|
90 videos|491 docs|209 tests
|















