Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Important Dates, History, Class 10
Important Dates, History, Class 10 PDF Download
Chapter 1
- 1707 - The Act of Union between England and Scotland
- 1789 - The French Revolution
- 1807 - Giuseppe Mazzini was born
- 1815 - Napoleon was defeated
- 1815 - The Vienna Convention; European powers (Britain, Russia, Prussia, Austria) met to settle Europe
- 1821 - The struggle of the Greeks for independence began
- 1824 - English poet Lord Byron died
- 1830 - The first upheaval took place in France (July Revolution)
- 1831 & 1848 - Failure of revolutionary uprisings
- 1832 - Treaty of Constantinople
- 1833 - A merchant traveling from Hamburg to Nuremberg had to pass through 11 customs barriers
- 1834 - A customs union of Zollverein was formed
- 1848 - Frederic Sorrieu prepared paintings visualizing a world of democratic republics
- 1848 - Paris was in great turmoil
- After 1848 - Autocratic monarchies in Central and Eastern Europe began reforms
- 1859 - Sardinia and Piedmont defeated the Austrian forces
- 1861 - Victor Emmanuel II was proclaimed King of Unified Italy
- 1867 - Habsburg rulers granted more autonomy to Hungary
- 1871 - The Prussian King William I was proclaimed German Emperor
Chapter 2
- 1909 - Gandhi wrote Hind Swaraj
- 1915 - Gandhi returned to India
- 1917 - Gandhi went to Champaran, Bihar
- 1917 - Kheda Satyagraha in Gujarat
- 1918 - Ahmedabad Mill Strike
- 1918-1919 & 1920-1921 - Crop failures led to famine
- 1919 - Rowlatt Act
- 13 April 1919 - Jallianwala Bagh massacre
- 1919 - Khilafat Committee was formed in Bombay
- Summer 1920 - Gandhiji and Shaukat Ali toured India
- Nagpur Session of 1920 - Non-Cooperation Programme adopted
- January 1921 - Non-Cooperation Khilafat Movement began
- 6 January 1921 - Police fired at peasants in Rae Bareli
- 1921 Census - 12-13 million people died due to famine and epidemics
- 1921 - Houses of talukdars and merchants attacked
- 1924 - Raju was captured and executed
- February 1922 - Gandhi withdrew the Non-Cooperation Movement
- 1927 - Indian Chamber of Commerce and Industry established
- 1928 - Simon Commission arrived in India
- October 1929 - Lord Irwin offered Dominion Status
- December 1929 - Purna Swaraj was demanded
- 26 January 1930 - Independence Day celebrated for the first time
- 6 April 1930 - Salt Satyagraha started
- April 1930 - Protests in Peshawar
- 1930 - Sir Muhammad Iqbal retired as president of Muslim League
- 5 March 1931 - Gandhi-Irwin Pact
- December 1931 - Political leaders released from jail
- By 1934 - Civil Disobedience Movement lost momentum
- Poona Pact (September 1932)
- 1930 & 1932 - Strikes by railway and dockworkers
- 14 July 1942 - Quit India Resolution adopted
Chapter 3
- 3000 BC - Coastal trade linked Indus Valley Civilization with West Asia
- By 1890 - A global agricultural economy took shape
- Till the 1870s - Animals were shipped live from America to Europe
- 1885 - European powers met in Berlin to divide Africa
- Late 1880s - Rinderpest arrived in Africa
- 1920s - The housing and consumer boom in the US
- By 1929 - The world entered the Great Depression
- 1929-Mid 1930s - The Great Depression period
- By 1935 - Economic recovery in industrial nations
- 1928-1934 - India's exports and imports nearly halved
Chapter 4
- 1760 - Britain imported 2.5 million pounds of raw cotton
- By 1787 - Cotton imports increased to 22 million pounds
- 1781 - James Watt improved and patented the steam engine
- By the 1750s - Indian merchant networks declined
- 1760s - East India Company power increased, but Indian textile exports remained strong
- Up to 1840 - Cotton led the first phase of industrialization
- By 1850s - Reports of decline in Indian weaving industry
- 1854 - First cotton mill in Bombay
- By 1874 - First spinning & weaving mill in Madras began production
- Between 1900-1912 - Cotton production in India doubled
- Between 1900-1940 - Cloth production expanded, especially handloom
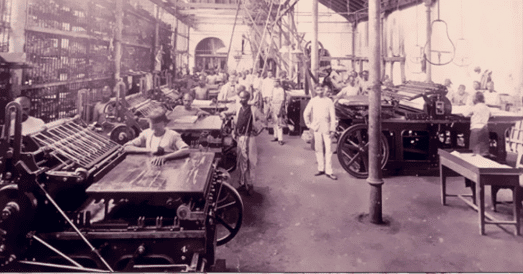 First Cotton Mill in Bombay
First Cotton Mill in Bombay
Chapter 5
- From 594 AD - Books in China were printed using woodblocks
- 768-778 AD - Hand printing technology introduced in Japan
- 868 AD - First and oldest Japanese printed book
- 1295 - Marco Polo returned to Italy
- By 1448 - Gutenberg perfected the printing press
- 1450-1550 - Printing press spread in Europe
- 1517 - Martin Luther wrote 95 Theses criticizing the Church
- 1579 - First Tamil book was written in Cochin
- 1710 - Dutch Protestant Missionaries printed 32 Tamil texts
- 1713 - First Malayalam book printed
- 1810 - Ramcharitmanas of Tulsidas printed in Calcutta
- 1821 - Sambad Kaumudi published by Raja Ram Mohan Roy
- 1822 - Jam-e-Jahan Numa and Shamsul Akhbar started
- 1867 - Deoband Seminary founded
- 1871 - Gulamgiri published
- 1878 - Vernacular Press Act
- 1900 - Dawn of the Century was written
- 1907 - Punjab revolutionaries deported
- 1930s - The Great Depression
FAQs on Important Dates, History, Class 10
| 1. What are the key historical events that students need to remember for Class 10 exams? |  |
Ans. Students should focus on significant events such as the French Revolution, Industrial Revolution, World Wars, Indian Independence Movement, and the formation of the United Nations. Understanding the causes and effects of these events is crucial for the exam.
| 2. How can I effectively memorize important dates in history for my Class 10 exams? |  |
Ans. To memorize important dates, students can create timelines, use flashcards, or associate dates with significant events or stories. Additionally, summarizing events in their own words can help reinforce memory retention.
| 3. Are there any recommended study materials for preparing for the history section of the Class 10 exam? |  |
Ans. Yes, students should refer to their NCERT textbooks, as they cover the syllabus comprehensively. Supplementary resources like reference books, online lectures, and study guides can also be beneficial for deeper understanding.
| 4. What strategies can I use to answer long-answer questions in the history exam? |  |
Ans. For long-answer questions, students should structure their answers with an introduction, main body, and conclusion. It's important to include relevant dates, events, and significant figures, while also providing analysis and context to demonstrate understanding.
| 5. How important is the understanding of historical context in answering questions in the Class 10 history exam? |  |
Ans. Understanding historical context is crucial as it helps students connect events and their impacts. It allows for more insightful answers in exams, as students can explain the significance of events and how they relate to broader historical themes.
Related Searches
















