Short & Long Question Answers with Solution: Locomotion and Movement - NEET PDF Download
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Where do muscle contractions derive their energy from?
Ans: Myosin relies on ATP for its function. Within every myosin molecule, there exists an enzyme called myosin ATPase, situated at its head. When myosin ATPase is accompanied by calcium ions (Ca2+), magnesium ions (Mg2+), inorganic phosphate, and ADP, it facilitates the breakdown of ATP, releasing energy from the myosin head. This energy enables myosin to form cross-bridges and bind to actin. These activated cross-bridges then move, leading to the sliding of thin myofilaments against thick myofilaments, ultimately causing muscle contraction.
Q2: What is Gout?
Ans: Gout is a condition characterized by joint inflammation resulting from the accumulation of uric acid crystals within synovial joints, leading to discomfort and impaired mobility.
Q3: Old people usually suffer from inflamed and stiff joints, name the condition. State the reasons for the symptoms.
Ans: This ailment is called arthritis, which is also known as joint pain or joint disease. The likelihood of developing arthritis rises as a person grows older. Arthritis occurs when the protective cartilage covering the bones within a joint deteriorates.
Q4: What is the significance of locomotion in animals?
Ans: In the animal kingdom, locomotion serves a vital function, enabling creatures to transition from one location to another. Animals engage in various forms of movement for a multitude of purposes necessary for their survival. Consequently, they utilize methods such as walking, running, jumping, flying, swimming, and evading predators.
Q5: Define the following terms with respect to the rib cage:
(a) Bicephalic ribs
(c) True ribs
(c) Floating ribs
Ans: (a) Every rib possesses two connecting surfaces on its rear end, and they are known as bicephalic ribs.
(b) The initial seven pairs of ribs are ventrally connected to the sternum through hyaline cartilage and dorsally linked to the thoracic vertebrae.
(c) These represent the final two pairs of ribs, and they lack ventral attachment to the sternum, which accounts for their name.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: What are the different types of movements?
Ans: Motion is the act of altering one's position or location, and it varies among different organisms.
There are three primary types of movements categorized based on the method of locomotion:
- Amoeboid Movement: This form of motion is the most prevalent mode of locomotion among all eukaryotic cells. It is observed primarily in phagocytes within cells and is most commonly associated with amoebas.
- Ciliary and Flagellar Movement: This type of movement occurs within the internal tubular organs lined with ciliary epithelium. Some of our internal tubular organs display ciliary movement.
- Muscular Movement: This is a more intricate type of motion that involves muscle fibers with the capacity to contract and relax. It is observed in all higher vertebrates.
Q2: State the differences between the pectoral and pelvic girdle.
Ans: Both structures are known to provide support to the lower and upper parts of the body.
Following are the differences: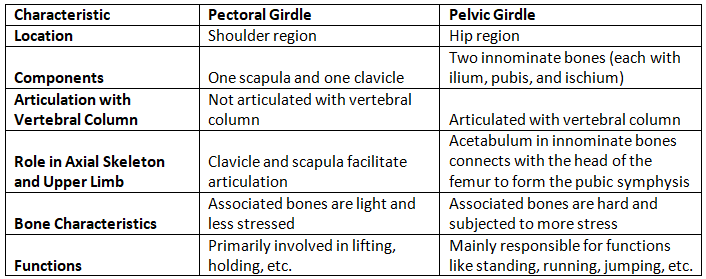
Q3: Does calcium ion concentration in blood cause tetany in some cases? Compare fluctuation in blood calcium with tetany.
Ans: Calcium is a crucial element in controlling muscle contraction. The parathyroid hormone (PTH), produced by the parathyroid gland, elevates the blood calcium levels. In cases of hypoparathyroidism, where PTH is deficient, there is a decline in blood calcium levels. This leads to heightened excitability of muscles and nerves, resulting in seizures and muscle cramps. It can also cause prolonged contractions in facial, hand, foot, and laryngeal muscles. This condition is known as parathyroid tetany.
Q4: Describe the significance of Ca2+ ions in the contraction of muscles.
Ans: Calcium plays a pivotal role in the muscle contraction process. When muscles contract, an action potential travels from the motor endplate, passing through the sarcolemma and then into the T-tubules and sarcoplasmic reticulum. This action triggers the release of calcium ions (Ca2+) into the sarcoplasm. The interaction between calcium ions and troponin leads to a change in the shape and position of troponin, subsequently altering the position and configuration of tropomyosin, which is bound to troponin. This alteration exposes the active sites on the F-actin molecule, facilitating the binding of myosin cross-bridges to these active sites.
Q5: How does the slipped disc affect the lower back and overall health?
Ans: The intervertebral discs, located between the vertebrae, serve as protective cushions for the bones. They absorb the shocks generated by everyday activities like lifting, walking, and twisting. Each vertebral disc consists of two parts: a soft inner portion with a gel-like consistency and a tough outer ring. When there is weakness or injury, the inner part may protrude through the outer ring, resulting in a condition known as a slipped disc.
This can lead to increased pressure on the muscles and nerves in the vicinity, affecting health in the following ways:
- Numbness and pain on one side of the body.
- Nighttime exacerbation of pain.
- Pain that can radiate down the legs and arms.
- Pain occurring after prolonged walking or sitting.
- Unexplained muscle weakness.
- Sensations like burning, aching, and tingling in the affected area.
If left untreated, a slipped disc can cause severe nerve damage, which may be permanent. In some cases, it can disrupt nerve impulses to the cauda equina nerves in the lower back and legs, leading to loss of bladder control.













