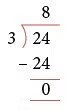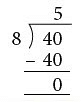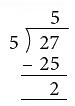Multiplication and Division | Mathematics for Class 2 (Joyful-Mathematics) PDF Download
Multiplication as Repeated Addition
Adding the same number again and again is called repeated addition.
Aryan has 5 tricycles. Each tricycle has 3 wheels. What is the total number of wheels in all the tricycles?

There are 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 = 15 wheels in all.
3 is repeatedly added 5 times.
We write it as 5 × 3 = 15.
We say, 5 times 3 is 15 or 5 threes are 15 or 5 into 3 is 15.
Repeated addition of the same number is called multiplication.
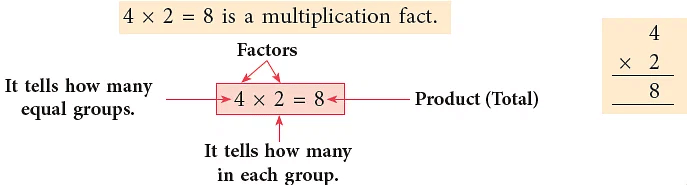
4 × 2 = 8 is a multiplication fact.
‘×’ is the sign of multiplication.
So, instead of adding the same number again and again, we can multiply to find out the answer.
Study the following.
Here are 4 baskets with 2 mangoes in each.
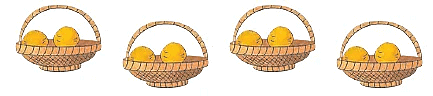
How many mangoes are there in all?
By adding repeatedly, we find that there are 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 = 8 mangoes in all.
Using multiplication,
we write 4 × 2 = 8 and read as 4 times 2 are 8 or 4 multiplied by 2 is 8.
Multiplication on the Number Line
We already know that multiplication is repeated addition. We can represent multiplication on the number line by skip counting.
Let us find 3 × 5.
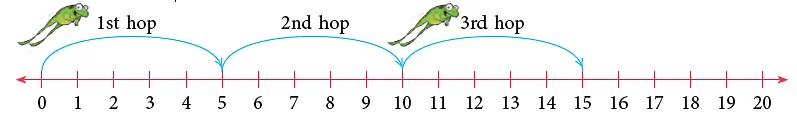
3 × 5 means take 3 skips of 5s starting from 0, as shown above.
We have reached 15 after 3 skips of 5s. So, 3 × 5 = 15.
Properties of Multiplication
Order Property of Multiplication
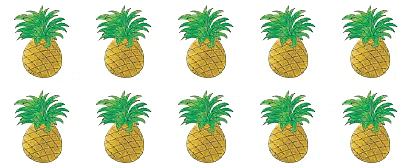
There are 2 rows of 5 pineapples each.
The multiplication fact becomes 2 × 5 = 10.
We can also think that there are 5 columns of 2 pineapples each.
Now, the multiplication fact becomes 5 × 2 = 10.
Since product is the same in both the cases,
we have 2 × 5 = 5 × 2 = 10.
We may multiply the numbers in any order, the product would be the same.
This basic property of multiplication is called the order property of multiplication.
Multiplicative Property of 1
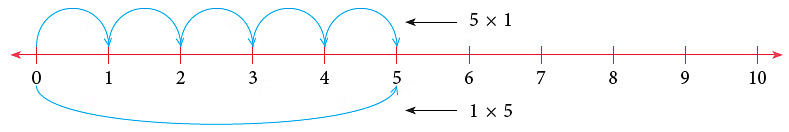
5 groups of 1 = 5 × 1 = 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 5
1 group of 5 = 1 × 5 = 5
So, 5 × 1 = 1 × 5 = 5.
We can show the above results using a number line as shown.
The above discussion shows that
Any number multiplied by 1 equals that number. This is called the multiplicative property of 1.
Multiplicative Property of 0

There are 3 empty baskets, which means 3 groups of nothing.
So, 3 × 0 = 0.
Also, by order property 3 × 0 = 0 × 3 = 0.
Thus, we have
Any number multiplied by 0 equals 0. This is called the multiplicative property of 0.
Multiplication Tables
You have already learnt and memorised tables of 1 to 5 in Class 1. Let us revise the same.
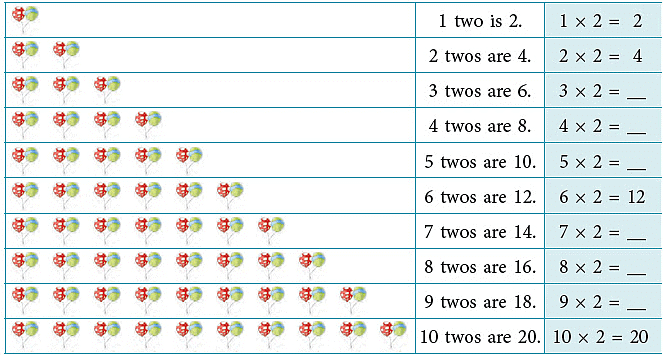
Multiplication Table of 2
Count and build the table of 2.
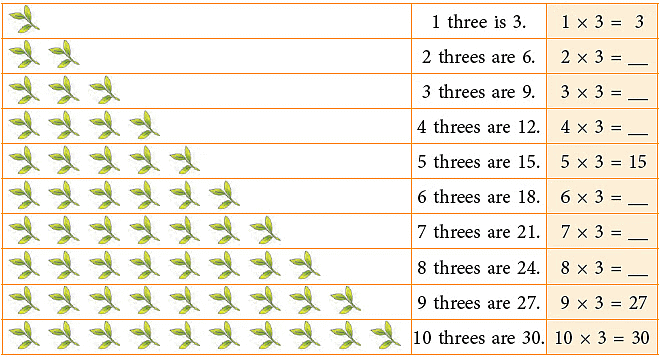
Multiplication Table of 3
Count and build the table of 3.
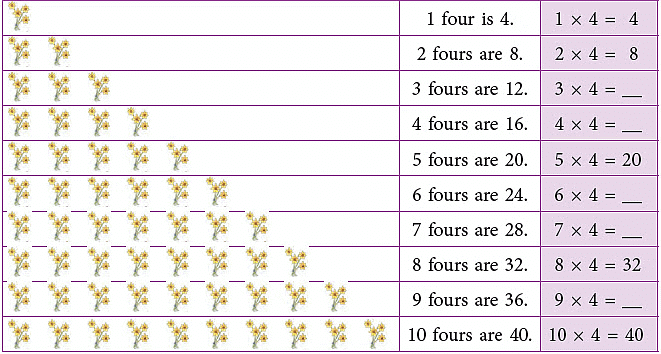
Multiplication Table of 4
Count and build the table of 4.
Multiplication Table of 5
Count and build the table of 5.

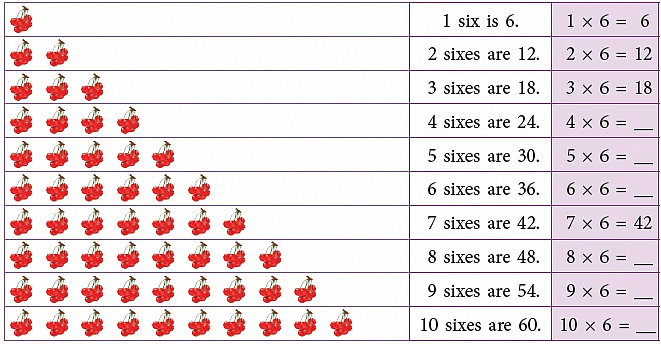
Multiplication Table of 6
Count and build the table of 6.
Multiplication Table of 7
Count and build the table of 7.
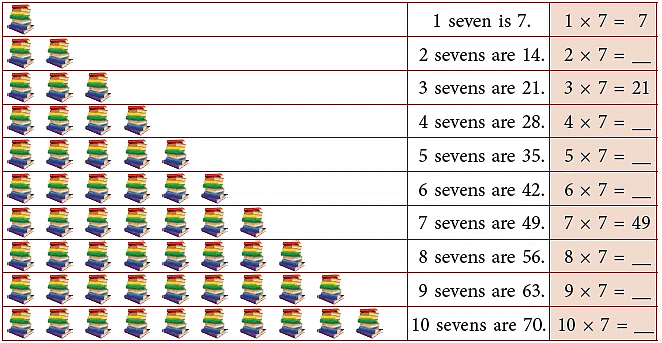
Multiplication Table of 8
Count and build the table of 8.
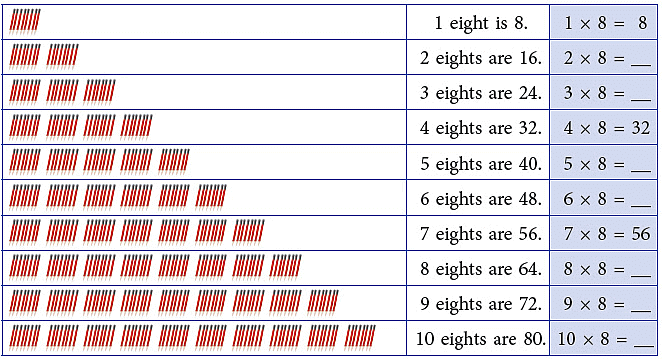
Multiplication Table of 9
Count and build the table of 9.
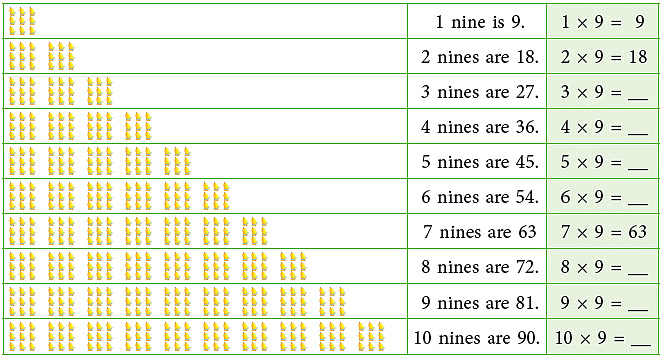
Multiplication Table of 10
Count and build the table of 10.
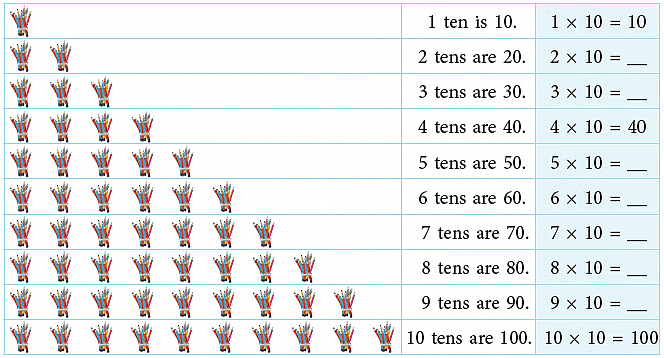
Problems Based on Real Life Situations
Example 1: There are 6 bananas in a bunch. There are 9 bunches. How many bananas are there in all?
Bananas in 1 bunch = 6
Bananas in 9 bunches = 9 × 6 = 54
Example 2: Reena has 5 pairs of gloves, 3 pairs of socks and 8 pairs of bangles.
How many items are there in total?
Number of gloves = 5 pairs = 5 × 2 = 10
Number of socks = 3 pairs = 3 × 2 = 6
Number of bangles = 8 pairs = 8 × 2 = 16
Total number of items = 10 + 6 + 16 = 32
What is Division
Division means equal sharing or equal grouping.
Equal Sharing
1. Mamta wants to share 4 chocolates between 2 of her friends Sonu and Bunty. How many chocolates will each of them get?
First, she gives one chocolate each to Sonu and Bunty.
Now, both have 1 chocolate each.
Mamta now has 2 chocolates left. Again, she gives 1 chocolate each to Sonu and Bunty.
Now, Mamta has 0 chocolates and her friends have 2 chocolates each.
So, if we divide (share equally) 4 chocolates between 2, each one of them gets 2.
We say that 4 divided by 2 is 2 and write it as 4 ÷ 2 = 2.
2. Mohit has 10 packets of chips. He wants to share them equally with his cousin. How many packets will each one of them get?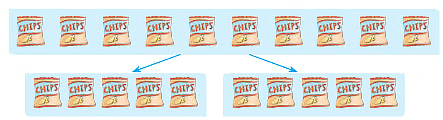 Clearly, each one of them will now have 5 packets of chips.
Clearly, each one of them will now have 5 packets of chips.
We say that 10 divided by 2 is 5 and write 10 ÷ 2 = 5.
Equal Grouping
Let us divide 12 balloons into three equal groups. How many balloons will each group contain?
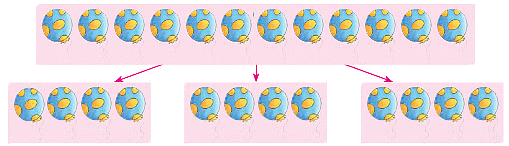
Clearly, each group will contain 4 balloons.
We write 12 ÷ 3 = 4 and read as 12 divided by 3 is equal to 4.
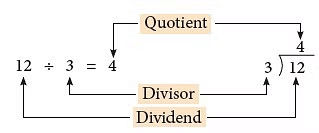
12 ÷ 3 = 4 is a division fact.
In the division fact, 12 ÷ 3 = 4,
- 12 is called the dividend.
- 3 is called the divisor.
- 4 is called the quotient.
Note: ‘÷’ is the symbol of division.
Thus, we can say that division means dividing or separating into equal groups.
Division as Repeated Subtraction
We know that multiplication is repeated addition. Similarly, division is repeated subtraction.
Sidhu was ill. The doctor gave him 12 tablets. For how many days did the medicine last if he had to take 2 tablets daily?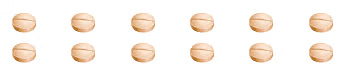
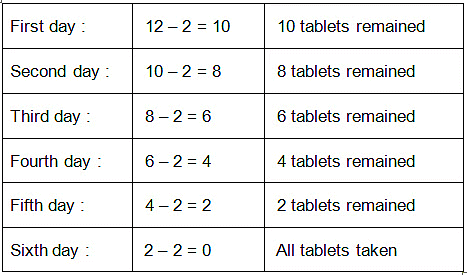
Last 2 tablets were taken on the sixth day. The medicine lasted 6 days. Here, 2 has been subtracted 6 times.
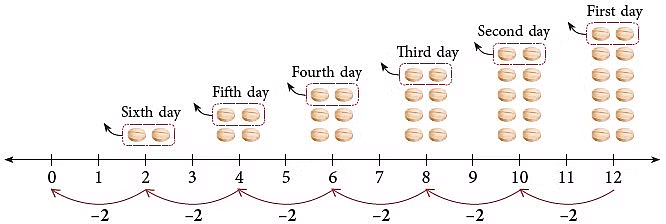
The above repeated subtraction sentence
12 – 2 – 2 – 2 – 2 – 2 – 2 = 0
can be written in the division form as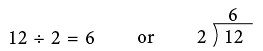
Division as Repeated Subtraction on the Number Line
How many times can you subtract 5 from 25?
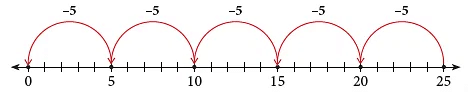
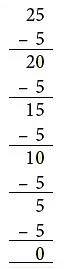
Start at 25. Jump backwards to the left 5 steps at a time in one jump till you reach 0.
The number of jumps is 5.
25 ÷ 5 = 5.
So, you can subtract 5 five times from 25.
Relation between Multiplication and Division
The picture shows 12 balls arranged in groups of 4.
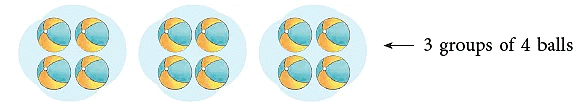
It shows a multiplication fact: 3 × 4 = 12 and a division fact: 12 ÷ 4 = 3.
12 balls can also be arranged in groups of 3 as shown.
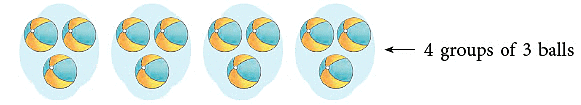
It shows a multiplication fact: 4 × 3 = 12 and a division fact: 12 ÷ 3 = 4.
Thus, we observe that the
- multiplication fact 3 × 4 = 12 gives the division fact 12 ÷ 4 = 3.
- multiplication fact 4 × 3 = 12 gives the division fact 12 ÷ 3 = 4.
By the order property of multiplication we know that, 3 × 4 = 4 × 3 = 12.
So, the multiplication fact, 3 × 4 = 12 or 4 × 3 = 12, gives two related division facts, 12 ÷ 4 = 3 and 12 ÷ 3 = 4.
A few examples are given below.
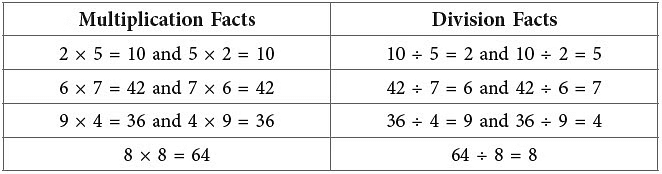
From the above examples, we see that multiplication and division are inverse operations.
For every multiplication fact, with two different factors, there can be two division facts and vice-versa. However, a multiplication fact of same number gives only one division fact.
Example: 5 × 5 = 25 gives 25 ÷ 5 = 5.
Division using Multiplication Tables
Let us find 18 ÷ 6.
Recite the multiplication table of 6 till you reach 18.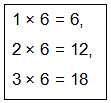 Since 3 times 6 is 18, so, 18 ÷ 6 = 3.
Since 3 times 6 is 18, so, 18 ÷ 6 = 3.
Similarly, to find 32 ÷ 8, recite the table of 8 till you reach 32.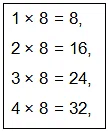 Since 4 times 8 is 32, so, 32 ÷ 8 = 4.
Since 4 times 8 is 32, so, 32 ÷ 8 = 4.
Terms Related to Division
In a division sum,
- the number to be divided is called the dividend.
- the number by which we divide is called the divisor.
- the answer we get after division is called the quotient.
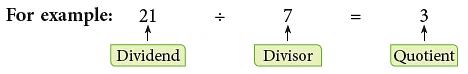
Properties of Division
1. Division of a number by itself
Three bananas are distributed equally among 3 girls. How many bananas does each girl get?
Each girl gets 1 banana. So, 3 ÷ 3 = 1.
Any number divided by itself gives 1 as the answer.
2. Division of a number by 1
There are 5 laddoos in a plate. When all the 5 laddoos are given to 1 child, there are no laddoos left.
This gives 5 ÷ 1 = 5.
3. Division of 0 by any number
Zero divided by any number except 0 is zero.
Examples: 0 ÷ 7 = 0, 0 ÷ 8 = 0.
If 0 objects are distributed among any number of children, each child gets nothing.
Long Division Method
Example 1: Divide 24 by 3.
Step 1. Arrange the numbers as
that is,
Step 2. Recite the table of 3 till you reach 24.
1 × 3 = 3, 2 × 3 = 6, 3 × 3 = 9, 4 × 3 = 12,
5 × 3 = 15, 6 × 3 = 18, 7 × 3 = 21, 8 × 3 = 24
Step 3. Stop at 24 and write 8 as the quotient.
Step 4. Write 24 below 24 and subtract.
Thus, 24 ÷ 3 = 8.
Division with Remainder
Look at the following examples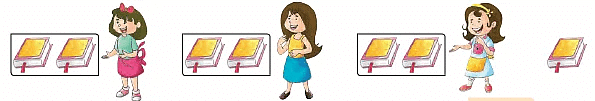
There are 7 notebooks and 3 girls. Each girl gets 2 notebooks.
when divided equally and 1 notebook remains.
7 = 3 times 2 and 1
Now, suppose there are 13 apples and 6 boys. How many apples does each boy get when divided equally? How many apples remain?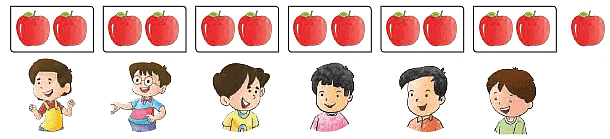
13 = 6 times 2 and 1
Each boy gets 2 apples and 1 apple remains.
When 13 is divided by 6, the quotient is 2 and the remainder is 1.
We write the result as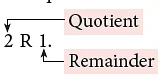
Problems Based on Real Life Situations
Example: 40 pencils are to be packed equally in 8 boxes. How many pencils
will be there in each box?
Total number of pencils = 40
Number of boxes = 8
Each box has (40 ÷ 8) pencils = 5 pencils.
Example: Annie wants to put 27 flowers equally in 5 vases. She keeps the remaining flowers with herself. How many flowers did she keep with herself?
Total number of flowers = 27
Number of vases = 5
Each vase has (27 ÷ 5) flowers = 5 flowers and 2 remain
Each vase has 5 flowers and 2 flowers remain with Annie.
|
28 videos|262 docs|22 tests
|