Important Questions: Era of One-Party Dominance | Political Science Class 12 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Explain the major difference of ideology between that of the Congress and the Jana Sangh.
Ans: Following are the major difference in ideology between that of the Congress and the Jana Sangh:
- Jana Sangh was opposed to the granting of concessions to religious and cultural minorities, but Congress supported this policy.
- Jana Sangh was against Article 370, but The Congress Party favored it.
Q2: When and why was the Communist Party of India (CPI) divided into two factions?
Ans: The Communist Party of India split in 1964 due to the ideological rift between the Soviet Union and China. The pro-Soviet faction remained as the CPI, while the opponents formed the CPI (M).
Q3: In which year first general election was held in India?
Ans: The first general election was held in 1952.
Q4: During the first three general elections, the Congress won more seats than any other party. Which party stood at the second number during these:
Ans: The Communist Party of India stood at the second number during these elections.
Q5: What inspired the formation of the Communist group in 1920e in different parts of India?
Ans: In the early 1920s, Communist groups emerged in different parts of India by being inspired by the Bolshevik Revolution in Russia.
Q6: Which political party of India had leaders like A.K. Gopalan, E.M.S. Namboodiripad and SA. Dance?
Ans: Communist Party of India had the leaders like A.K. Gopalan, E.M.S. Namboodiripad and S.A. Dange.
Q7: Name the founder President of the Congress Socialist Party. What name was given to this party after 1948?
Ans: Acharya Narendra Deva was the founder President of the Congress Socialist Party. After 1948, this party was known as the Socialist Party.
Q8: What do you mean by defection?
Ans: Defection means an elected representative leaves the party on whose symbol he was elected and joins another party.
Q9: Which political party laid emphasis on the idea of one party, one culture and one nation?
Ans: Bharatiya Jana Sangh.
Q10: Which political party of India had leaders like A.K. Gopalan, E.M.S. Namboodiripad, and S.A. Dange?
Ans: Communist Party of India.
Q11: Who was the founder of Bharatiya Jana Sangh?
Ans: Shyama Prasad Mukherjee in 1951.
Q12: In which year was the Election Commission of India set up and who was the first chief Election Commissioner of India?
Ans: 25 January 1950, Sukumar Sen.
Q13: Name the founder president of the Congress Socialist Party. What name was given to this party after 1948?
Ans: The founder president of the Congress Socialist Party was Acharya Narendra Dev and after 1955 it came to be known as Socialist Party.
Q14: Differentiate between one party dominance and one party system.
Ans: One party dominance refer to representation on behalf of popular consensus alongwith free and fair elections i.e. Congress in India whereas one party system refers representation based on malpractice, fraud etc. to ensure winning of a particular party.
Q15: When and why was the electronic voting machine used in India for the first time?
Ans: The electronic voting machine was used in India in 1990 for first time for more accuracy and fair dealing while counting as well as it helps to check Booth capturing and other malpractices.
Q16: How did socialist party origin?
Ans: The founder president of the Congress socialist party was Acharya Narendra Dev and after 1955 it came to be known as Socialist Party.
Q17: Define faction.
Ans: Faction are the groups formed inside the party i.e. coalitions made in Congress created various factions which were based on either ideological considerations or personal ambitions.
Q18: When and by whom PRI was founded?
Ans: The ‘Institutional Revolutionary Party’ (PRI) was founded in 1929 by Plutareo Elias Calles in Mexico which represented the legacy of Mexican Revolution.
Q19: How did the dominance of Congress Party in the first three general elections help in establishing a democratic set-up in India?
Ans: The first general election was the first big test of democracy in a poor and illiterate country. Till then democracy had existed only in the prosperous countries. By that time many countries in Europe had not given voting rights to all women. In this context India’s experiment with universal adult franchise appeared very bold and risky. India’s general election of 1952 became a landmark in the history of democracy all over the world. It was no longer possible to argue that domocratic elections could not be held on conditions of poverty or lack of education. It proved that democracy could be practised anywhere in the world. The next two general elections strengthened democratic set-up in India.
Q20: Highlight any two features of ideology of Bharatiya Jana Sangh.
Ans:
- Bharatiya Jana Sangh laid emphasis on ideology of one country, one culture and one nation.
- Bharatiya Jana Sangh called for reunity of India and Pakistan in Akhand Bharat.
Q21: Explain the major difference of ideology between that of Congress and the Bharatiya Jana Sangh.
Ans: The major difference of ideology between Congress and the Bharatiya Jana Sangh was that Bharatiya Jana Sangh emphasised on one party country. One culture, one nation i.e. a Hindu nation or Hindutva whereas Congress formed ideological and social coalitions accommodating social diversities.
Q22: State any two ideologies of the Swatantra Party.
Ans: Swatantra Party was founded by Senior Congress leader C. Rajgopalachari in August 1959:
- The party believed that prosperity could come only through individual freedom.
- This party was against land ceilings in agriculture and opposed to cooperative farming.
Q23: How has the method of voting changed from the first General Election of 1952 to the General Election of 2004?
Ans:
- In the first General Election a box was placed inside each polling booth for each candidate with the election symbol of the candidate. Each voter was given a blank ballot paper to drop into the box, they wanted to vote for.
- After first two elections, this method was changed. Now ballot paper carried the names and symbols of candidates and the voter stamped against the name of candidate to vote for.
- In 2004, Electronic Voting Machine were introduced to press the button according to choice of the voter containing the name of candidate and symbol of political party.
Q24: When was Communist Party emerged?
Ans: The Communist Party emerged in 1920 in different parts of India. It took the inspiration from Bolshevik revolution in Russia. The important leaders of CPI were A.K. Gopalan, S.A. Dange, E.M.S. Namboodiripad, P.C. Joshi, Ajay Ghosh etc.
Q25: “India’s experiment with universal adult franchise appeared very bold and risky”. Justify the statement.
Ans: Because:
- Country’s vast size and electorates made these elections unusual.
- The year 1952, it was a big test for poor and illiterate country.
- Till then, democracy had been existed only in the prosperous countries mainly in Europe and North America where everyone was almost literate.
Q26: Mention the aims and goals of Socialist Party of India. Why the party could not prove itself as an effective alternative to the Congress?
Ans: Aims and goals of socialist party of India:
- The Socialist Party believed in the ideology of democratic socialism to be distinguished from Congress and Communists both.
- It criticised Congress for ignoring the workers and peasants.
It became difficult for socialist party to prove itself as an effective alternative to Congress because Congress Party declared its goal to be the socialist pattern of society in 1955.
Q27: What were the reasons for dominance of one party system in India?
Ans: The dominance of Congress in India was due to following reasons:
- Congress was identified with the freedom struggle for building national unity and solidarity.
- Congress was associated with Mahatma Gandhi’s name.
- It had a broad based manifesto to include the various section of society.
- Congress bore a popular appeal of charismatic leader like Mahatma Gandhi, J.L. Nehru, Sardar Patel, Indira Gandhi etc.
- Congress focused on building role of the party.
Q28: How did India’s first general elections of 1952 become a landmark in the history of democracy all over the world?
Ans: Because:
- These elections were competitive among various parties.
- The participation of people was encouraging also.
- The results were declared in a very fair manner, even to be accepted by the losers in a fair manner.
- This experiment of India, proved the critics wrong also.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q29: What distinguished the dominance of the congress party of India from the one-party dominance in other countries? Explain.
Ans: In India, the Indian National Congress dominates Indian Politics up to 1967. Besides India, there were certain other countries where one party dominated. There are some countries like China, Cuba, North Korea, etc., where only one party is allowed under the constitution. A few years ago in Mexico one-party dominated like South Korea and Taiwan. In India multi-party system exists. Many political parties contested elections and elections are held free and fair. Congress party has managed to win election after elections. Congress’s dominance was on the support of the masses. However, in Mexico, there was no democratic system in a reality.
Q30: Highlight the circumstances that compelled the socialists to form a separate socialist party in 1948. Mention any two grounds on which they criticized the Congress Party.
Ans: The Congress Socialist Party (CSP) was formed within the Congress in 1934. This was formed by a group of young leaders, who wanted to bring more radical find social changes to Congress. In 1948, Congress amended its constitution and ended the dual partnership. This compelled the socialists to form a separate socialist party in 1948. They believed in democratic-socialism which distinguished them both from the congress as well as from the communist. The Congress Socialist Party criticized the Congress for the following reasons
- Congress favored the landlords and capitalists.
- Congress ignores the rights of workers and peasants.
Q31: Describe any four features of the ideology followed by the Swatantra Party founded in 1959.
Ans: Rajagopalachari founded the Swatantra Party in 1959.
- The Swatantra Party firmly believed that the government should not interfere in economic matters.
- The party was against centralized planning, nationalization, and the public sector.
- It was also against land ceilings in agriculture and opposed co-operative farming.
- It was also opposed to the progressive tax regime.
Q32: Examine the dramatic changes that took place in the party system in India from 1969 to 1977. Ans:
- The Oldest Party: Congress party was divided in 1969.
- In Congress: Indira Gandhi became very popular, but her organization was weak.
- From 1969 to 1977 opposition parties organized themselves.
- In 1977 opposition party known as Janta Party formed the government for the first time in India.
Q33: Explain any four reasons for the dominance of the Congress Party in the first three general elections in India.
Ans: Indian National Congress dominated in the first three general elections. Following factors were mainly responsible for the dominance of the Congress party:
- Indian National Congress is the oldest party in Asia. Congress party was established in 1885.
- Congress party played a very important role in the freedom struggle. In fact, the history of the National movement in the history of the Congress party. Many leaders and thousands of workers of the Congress party remained in jail for years.
- Congress party was led by Pt. Jawaharlal Nehru, Dr. Rajendra Prasad, Acharya J.B., Kripalani, Dr. Pattabhi Sitaramayya, etc.
- Congress party was the only party having proper organization at the root level. Its nation-wide organization enabled the Government to keep in close touch with the people and to function as an effective democracy.
Q34: Describe the organisation of Congress Party as a social and ideological coalitions.
Or
“For a long time Congress Party had been a social and ideological coalition”. Justify the statement.
Ans:
- It accommodated the revolutionary conservative, extremist and moderates with all other shades of the centre.
- Congress became a platform for numerous groups, interests and even political parties to take part in national movement.
- In pre-independence days, many organisations and parties were allowed to co-exist within the Congress.
- Some of these like ‘Congress Socialist Party’ later separated from the Congress and became an opposition party.
Q35: How was one party dominance of India different from the other examples of one party dominance in the world?
Or
Examine the comparative analysis of nature of Congress dominance.
Ans: India is not the only country to have dominance of one party but we have some other examples also for the same. But the dominance of one party in India does not compromise democratic spirit of constitution whereas other nations have compromised it:
- In countries like China, Cuba and Syria are permitted to be ruled by one party only by the constitutional provisions.
- Myanmar, Belarus, Egypt also experience one party system due to legal and military measurer.
- In India, Congress dominates on behalf of free and fair elections based on democracy where the losing of other party is also fair.
Q36: “In India, hero-worship, plays a part in its politics unequalled in magnitude by the part it plays in the politics of any other country But in politics, hero-worship is a sure road to degradation and eventual dictatorship”.Babasaheb Dr. B.R. Ambedkar Analyse the statement.
Ans: The above mentioned statement speaks of accommodating diversities by the leader of India which was a challenging path to democracy. Our leaders wanted to represent politics as a way of solution of problems in place of making politics a problem.
Q37: Examine the dominance of Congress in the first three General Elections.
Ans:
- In the first election Congress won 364/489 seats as per expectations.
- The Communist Party next to Congress won only 16 seats.
- Congress scored higher in state elections also except Travancore- Cochin (Kerala), Madras and Orissa.
- Hence, country ruled at national and state level both by declaring Pt. J.L. Nehru as the first Prime Minister of India.
- In second and third elections also, Congress maintained the same position in Loksabha by winning of three fourth seats in the years 1957 and 1962 respectively.
Q38: Read the passage given below carefully and answer the questions:
This coalition-like character of the Congress gave it an unusual strength. Firstly, a coalition accommodates all those who join it. Therefore, it has to avoid any extreme position and strike a balance on almost all issues. Compromise and inclusiveness are the hallmarks of a coalition. This strategy put the opposition in a difficulty. Anything that the opposition wanted to say, would also find a place in the programme and ideology of the Congress. Secondly, in a party that has the nature of a coalition, there is a greater tolerance of internal differences and ambitions of various groups and leaders are accommodated. The Congress did both these things during the freedom struggle and continued doing this even after Independence. That is why, even if a group was not happy with the position of the party or with its share of power, it would remain inside the party and fight the other groups rather than leaving the party and becoming an ‘opposition’.
1. What do you mean by a faction?
2. How did coalition-like character affect the nature of Congress Party?
3. How did Congress avoided to increase number of ‘opposition’?
Ans:
1. Factions are the groups formed inside the party based on either ideological considerations or on personal ambitions and rivalries.
2. Coalition-like character of Congress accommodated all social diversities and maintained a balance on almost all issues. Even a proper space for the programmes and ideology of opposite parties was also given. In such a way Congress showed greater tolerance towards internal differences.
3. Alongwith its coalition-like character, Congress did not let the groups to leave the party to become an opposition.
Q39: Read the passage given below carefully and answer the questions:
The socialists believed in the ideology of democratic socialism which distinguished them both from the Congress as well as from the Communists. They criticised the Congress for favouring capitalists and landlords and for ignoring the workers and the peasants. But the socialists faced a dilemma when in 1955 the Congress declared its goal to be the socialist pattern of society. Thus it became difficult for the socialists to present themselves as an effective alternative to the Congress. Some of them, led by Rammanohar Lohia, increased their distance from and criticism of the Congress party. Some others like Asoka Mehta advocated a limited cooperation with the Congress.
1. Mention the ideology of Socialists.
2. Name some leaders of the Socialist Party.
3. Why did it become difficult for socialists to present themselves as an effective alternative to the Congress?
Ans:
1. Socialists believed in the ideology of democratic socialism to be distinguished from Congress as well as from Communists.
2. Ram Manohar Lohia, Ashok Mehta and Acharya Narendra Dev, Jayaprakash Narayan etc.
3. Because in 1955, Congress declared its goal to be the socialist pattern of society.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q40: Highlight the political ideology of the Communist Party of India.
Ans: The following are the Political Programmes of the Communist Party of India-
- The C.P.I. attaches the utmost priority to safeguarding the integrity, security, and sovereignty of India.
- The C.P.I. favors the preservation and strengthening of the secular democratic set up of the country in the struggle against all types of divisive forces.
- The manifesto calls for 10 percent job reservation for the economically weaker sections of forwarding castes in addition to the implementation of the Mandal Commission report. The party is for the implementation of a 30 percent job reservation for women.
- The party is for the speedy implementation of comprehensive measures for social justice.
- The party has demanded a restructuring of Centre-State relations in the true spirit of federalism. The state should be given more powers as recommended by the Sarkaria Commission.
- The Party called for the abrogation of Article 356 of the Constitution and for enlarging the democratic and civil rights of the people.
- The fate of the state government is to be decided on the floor of the house.
- The Party has demanded real decentralization to be carried out by conferring more power and financial resources to elected bodies at district, block, and Panchayat levels.
- The party favors effective steps for the elimination of corruption. Lok Pal Bill which includes within its scope, legislators, and also the Prime Minister should be adopted. Transfers and postings which are a fertile source of corruption should be done by a committee of senior officials.
- All legislators, MPs, MLAs, ministers, and high officials must disclose their assets and place them before parliament and assemblies.
- It has demanded the repeal of all undemocratic statutes including ESMA and NSA and enlarging the democratic and civil rights of the people.
- The Party is committed to strengthening the parliamentary democratic system.
Q41: Describe the changing methods of voting in India from 1952 to today.
Ans: India is the largest democratic country in the world. Therefore regular election is going on by the election commission of India. For the passage of time, there is a change in the voting method of election. In the general elections of 2019 Electronic Voting Machine (EVM) was used to record voters’ preference whereas in the first general election, in each polling booth, a box for each candidate with the election symbol of that candidate was placed. Each voter was given a blank ballot paper which they had to drop into a box of the candidate they want to vote for.
But it was a very time consuming and expensive method. Booth capturing was another drawback of the ballot paper system, therefore, the government of India and election commission of India decided to go with EVM as a pilot project in the general election held in 2004, in 2019 Loksabha election the entire election held with EVM and V.V.PAT (Voter Verifiable Paper Audit Trail).
Q42: How did the dominance of The Congress party affect the democratic nature of Indian politics? Explain.
Ans: In India, the multi-party system exists. Several political parties participate in elections. But Indian National Congress dominated at the centre as well as the states till 1967. The prevalence of ‘one-party dominant system’ has adversely affected the democratic nature of Indian politics. In fact, the dominance of a single party is opposed to democracy as other political parties cannot flourish. Due to a lack of organized opposition, the Congress party never fulfilled the promises made to the people. Congress remained in power for a long period and hence no other party got a chance to rule.
Its administration has become virtually inefficient leading to widespread corruption. Pt. Jawaharlal Nehru himself accepted the fact that “The Congress has developed into a monolithic organization making it virtually impossible for the growth of a sound party system in the country”. According to R.A. Gopalaswami “The party system which has emerged in our country is not only incompatible with the particular democratic institutions we have adopted but constitutes a clear danger to the survival of democracy of India.”
Q43: Highlight any three major reasons for the dominance of the Congress Party in the first three general elections after Independence.
Ans: After Independence, the Congress Party dominated the political scene at the center as well as in states before 1967. The Congress secured 364, 371, 361, and 283 seats in the elections of 1952, 1957, 1962, and 1967 respectively. The dominance of Congress was due to many reasons:
- The Congress Party was established in 1885 and it played a very important role in the national movement. In fact, the history of the national movement is almost the history of the Congress Party. Congress Party wholeheartedly fought for India’s independence and did not worry about sacrifices.
- Congress provided able leadership to the Indian masses from 1885 to 1947. The Congress Party was led by such great personalities as Mahatma Gandhi, Pt. Jawaharlal Nehru, Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel, Mrs. Indira Gandhi.
- The Congress Party was a well-organized party and no other political party had such a well-knit organization.
- After Independence, The Congress Party not only tried to solve the problems of the masses but also faced the challenges before the nation.
Moreover, the Congress Party represents a mixture of almost all shades of opinion. It is, in fact, a ‘Grand Coalition’. It was rather a privileged party to harbor all sorts of political ideologies under the garb of freedom struggle.
Q44: Describe the various steps taken to hold the first general elections in India. How far these elections were successful?
Ans: The first general elections had to be postponed twice and finally held from October 1951 to February 1952:
- These elections were referred to as 1952 elections because most parts of country voted in January 1952.
- It took six months for campaigning, polling and counting to be completed.
- Elections were competitive because there were on an average more than four candidates for each seat.
- The level of participation was en-couraging to vote out in the election.
- The results were declared and accepted as fair even by losers to prove critics wrong.
These elections were successful:
- The losing of the parties was also accepted as fair.
- These elections became a landmark in the history of democracy.
- It was no longer possible to argue that democratic elections could not be held in conditions of poverty or lack of education. Instead, it can be practised anywhere in the world.
Q45: Why was Congress considered as a social and ideological coalition in independence days? Explain.
Ans: The Congress Party became a social and ideological coalition for it merged different social groups alongwith their identity holding different beliefs:
- It accommodated the revolutionary, conservative, pacifist, radical, extremist and moderates and the right and the left with all other shades of the centre.
- Congress became a platform for numerous groups, interacts and even political parties to take part in the national movement.
Ideological currents present within the Congress:
- In pre-independence days, many organisations and parties with their own constitutions and organisational structures were allowed to exist within the Congress.
- Some of these like ‘Congress Socialist Party”, later separated from the Congress and became an opposition party.
Q46: How was the one party dominance in India different from the one party system in Mexico? In your opinion which of the two political systems is better and why?
Ans: There was a difference between one party domination in India and Mexico. In Mexico, this was a one party system only not dominance because:
- In India, the Congress Party dominated on behalf of popular consensus but Institutional Revolu-tionary Party (PRI) (in Spanish) ruled on behalf of perfect dictatorship.
- In India, free and fair elections took place, where the losing of election was also fair but in Mexico, elections were based on malpractices, dominated by PRI.
In our opinion one party dominance¬like India is better because this sort of dominance:
- Accommodates social diversities.
- Encourage large number of parti-cipation.
- Ensures democratic spirit as well as maintains the same.
- Bear respect even for opposition.
Q47: How did opposition parties emerge in India? What was their importance?
Ans: Some of the diverse opposition parties had come into existence before the first general elections in 1952 as non-Congress parties which succeeded to gain only a taken of representation in Lok Sabha and State Assemblies. These parties maintained a democratic character of the system:
- These offered a criticism based on principles to keep ruling party under check.
- These parties groomed the leaders also to play a crucial role in shaping the country.
- In the early years, these was a lot of respect between leaders of Congress and opposition parties i.e. interim government included even opposition leaders like Dr. Ambedkar, Jayaprakash Narayan, Shyama Prasad Mukherjee into the cabinet.
Q48: Study the picture given below and answer the questions that follow:1. What does the cartoon represent?
2. What does the term ‘Tug of war’ refer to?
3. Who has been shown on the branches of tree?
Ans:
1. Cartoon represents dominance of Congress which is being tug by opposition parties to throw Congress out of power.
2. ‘Tug of war’ refer to pulling out the Congress by criticism and mentioning its weaknesses in an honest and justified manner.
3. Pt. Jawahar Lai Nehru alongwith his colleagues in the cabinet.
Q49: In the outline political map of India given below, five States have been marked as A, B, C, D and E. With the help of the information given below, identify them and write their correct names in your answer book along with the serial number of the information used and the related alphabet in the map.(i) The State to which C. Rajagopalachari, the first Indian Governor-General of India, belonged.
(ii) The State where the first non-Congress Government was formed by E.M.S. Namboodiripad.
(iii) The State to which Rafi Ahmed Kidwai, the Union Minister for Food and Agriculture (1952-54) belonged.
(iv) The State which faced the most acute food crisis in 1965-1967.
(v) The State which led the country to White Revolution through Dairy Cooperative Movement.
Ans:
A — (iv) Bihar B — (iii) Uttar Pradesh C — (v) Gujarat D — (i) Tamil Nadu C — (a) Kerala
Q50: On a political outline map of India locate and label the following and symbolise them as indicated: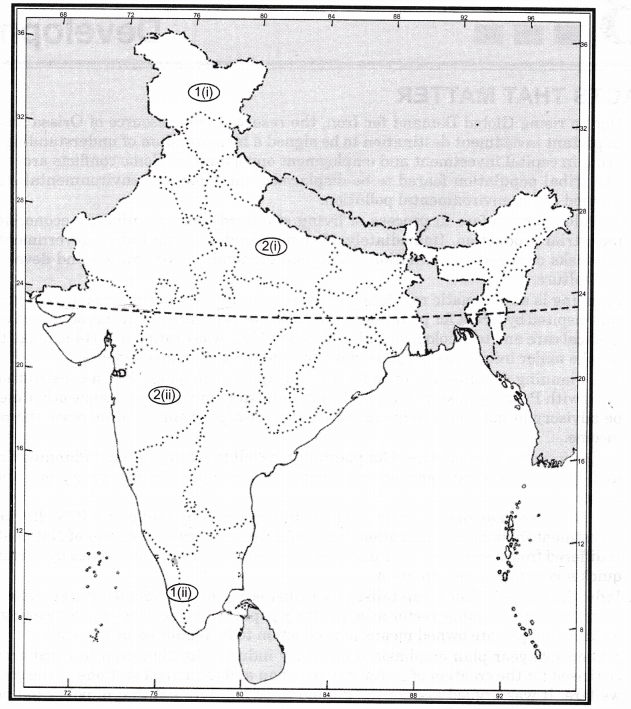 1. Two states where Congress was not in power at some point during 1952-67.
1. Two states where Congress was not in power at some point during 1952-67.
2. Two states where the Congress remained in power through this period.
Ans:
1. (i) Jammu & Kashmir (ii) Kerala
2. (i) Uttar Pradesh (ii) Maharashtra
|
34 videos|308 docs|51 tests
|
















