Important Questions: National Income Accounting | Economics Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Define intermediate goods.
Ans: Intermediate goods are those goods, which are not meant for final consumption. These are raw materials used in the production of other goods, and services.
Q2: What is saving?
Ans: Saving is defined as that part of National Income, which is not spent on final consumption expenditure.
Q3: Define corporation tax.
Ans: Corporation tax is a tax on the income of the corporations.
Q4: How rate of saving is calculated?
Ans: Rate of saving is calculated as: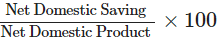
Q5: Define flow concept.
Ans: Flow is an economic variable that is measured over a specific period of time. It is a dynamic concept.
Q6: Define an open economy.
Ans: An open economy is the one, which undertakes economic transactions with the rest of the world.
Q7: What do you mean by money flow?
Ans: Money flow refers to the flow of money value across different sectors in an economy.
Q8: Define a closed economy.
Ans: A closed economy is the one, which does not undertake economic transactions with the rest of the world.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q9: What is the difference between final and intermediate good?
Ans: Final goods are those goods which are ready for consumption or capital formation by final users. Intermediate goods, on the other hand, are those goods which not meant for final consumption. These are raw materials used in the production of other goods and services. For example: A chair is a final good, but wood, cane, foam, cloth, etc. used to produce chair are all intermediary goods.
Q10: Distinguish between consumer goods and capital goods. Which of these are final goods?
Ans: Consumer goods are those goods which directly satisfy the wants of the consumer. These are used as final consumption goods. Consumer goods may be durable items, semi-durable items, non-durable and services. Capital goods, on the other hand, are those goods which are producer’s fixed assets, and are used in the production of other goods and services. Both, consumer goods and capital goods are final goods as these are meant for final use by the user.
Q11: What is real flow and money flow?
Ans: Real flow refers to the flow of goods and services across different sectors in an economy. Households provide factors of production such as land, labour, capital and entrepreneur to the firms. The firms, in turn, provide the goods and services so produced to the households. Money flow refers to the flow of money value across different sectors in an economy. Factor incomes such as rent, wages, interest and profit flow from production sector to household sector and the payment for consumption of final goods and services or consumption expenditure flow from household sector to production sector.
Q12: Distinguish between goods and services.
Ans: Goods are physical products, capable of being delivered to a purchaser. It involves the transfer of ownership from seller to buyer. For example: television, computers, car, etc. Services are all those economic activities essentially intangible that provide satisfaction of wants and are not necessarily linked to the sale of a product. For example: transportation, banking, insurance, etc.
Q13: Which among the following are final goods and which are intermediate goods? Give reasons.
(a) Milk purchased by a tea stall
Ans: Milk purchased by a tea stall is an intermediate good that will be used to produce the final good, that is, tea.
(b) Bus purchased by a school.
Ans: Bus purchased by a school is a final product because it is used by the students and staff for final consumption. It is a kind of investment by the school as the school will use the bus for several years.
(c) Juice purchased by a student from the school canteen
Ans: Juice purchased by a student from the school canteen is a final product because it is ready for the final consumption.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q14: Describe the precautions that should be taken while measuring national income using the expenditure method.
Ans: The following precautions should be taken while measuring the national income using expenditure method:
- While calculating the total expenditure, only the final-expenditure must be included and not the intermediate expenditure. If both of these are included, the problem of double counting arises.
- Expenditure on second hand goods should not be included in final expenditure since the production of old goods took place in previous years and not in the current year.
- The expenditure on old or new shares should not be included in final expenditure because it is only a transfer of wealth, which has not affected production at all.
- Only gross investment should be included in total expenditure. Gross investment also includes expenditure on depreciation.
- Factor income (property income, labour income, interest, rent, wages) received by domestic residents from foreign countries should be included in exports, Similarly, factor income paid by domestic territory to foreign residents should be included in imports.
Q15: “Higher Gross Domestic Product (GDP) means greater per capita availability of goods in the economy.” Do you agree with the given statement? Give valid reason in support of your answer.
Ans: The given statement is not true. Higher Gross Domestic Product (GDP) does not necessarily mean greater per capita availability of goods in the economy. The level of economic welfare may not rise if with an increase in the level of Gross Domestic Product (GDP), the distribution of GDP becomes more unequal. Since only a few people benefit from the increase in the level of income, rich are becoming richer and poor are becoming poorer. If GDP growth increases the gap between rich and poor, then it cannot be treated as an index of welfare for a country. Moreover, if the population growth rate is more than the rate of growth of GDP, the per capita availability of goods and services will actually decline.
Q16: Distinguish between domestic product and national product giving suitable examples in support of your answer.
Ans: Domestic product is defined as the market value of all the final goods and services produced by the factors of production located in the country during a period of one year.
On the other hand, national product is the market value of all the final goods and services produced by the factors of production located in the country during a period of one year plus Net Factor income from Abroad (NFIA). NFIA is the difference between the incomes of residents for factor services to the rest of the world and payments to the factor services of non-residents in the domestic territory during a period of one year,
National Product = Domestic Product + NFIA
Example: If the domestic product is ₹ 5,000 and Net Factor Income from Abroad is ₹ 100, then theNational product will be:
National Product = ₹ 5000 +₹ 100 = ₹ 5100.
Q17: Explain the expenditure method of estimating National Income.
Ans: The expenditure method of estimating National Income calculates the sum total of the expenditure by all the final users of goods and sendees plus the addition to the stock with the producers and distributors. According to this method, expenditures on consumption and investment goods and government expenditures are aggregated as follows:
- Consumption Expenditure (C): Consumption expenditure includes expenditure on all goods and services produced and sold to the final consumer during the year.
- Investment Expenditure (I): Investment is the use of today’s resources to expand tomorrow’s production or consumption. Investment expenditure is expenditure incurred on by business firms on:
- New plants;
- Adding to the stock of inventories; and
- Newly constructed houses
- Government Expenditure (G): Government expenditure includes all government expenditure on currently produced goods and services but excludes transfer payments while computing national income.
- Net Exports (X – M): Net exports are defined as total exports minus total imports. Under the expenditure method, National Income is calculated by summing up the final consumption expenditure, expenditure by business on plants, government spending, and net exports.
National Income = C + I + G + (X-M)
|
64 videos|275 docs|52 tests
|
FAQs on Important Questions: National Income Accounting - Economics Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What is national income accounting? |  |
| 2. What are the components of national income? |  |
| 3. Why is national income accounting important? |  |
| 4. How is national income calculated? |  |
| 5. What are the limitations of national income accounting? |  |






















