Diagram Based Questions: Chemical Reactions and Equations | Science Class 10 PDF Download
Q1: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below:

(i) What is the purpose of burning a magnesium ribbon in air in this experiment?
(ii) Describe the appearance of the magnesium ribbon before it is burnt.
(iii) What happens to the magnesium ribbon when it is burnt in air?
(iv) How is magnesium oxide collected in this experiment?
(v) Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction that takes place when magnesium burns in air.
Ans: (i) The purpose of burning a magnesium ribbon in air is to observe the reaction of magnesium with oxygen and to collect the product, which is magnesium oxide.
(ii) Before burning, the magnesium ribbon appears as a shiny, silver-colored metal strip.
(iii) When the magnesium ribbon is burnt in air, it reacts with oxygen to form magnesium oxide. During this reaction, the magnesium ribbon glows brightly and produces a white powder (magnesium oxide).
(iv) Magnesium oxide is collected in a watch-glass. It is the white powder that forms on the surface of the watch-glass as a result of the reaction between magnesium and oxygen.
(v) The balanced chemical equation for the reaction is:
2Mg(s) + O2(g) -> 2MgO(s)
Q2: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below:
(i) What is the chemical reaction that occurs when dilute sulfuric acid reacts with zinc?
(ii) How can we test the presence of hydrogen gas during this experiment?
(iii) What is the role of zinc in this reaction?
(iv) Why do we use dilute sulfuric acid in this experiment instead of concentrated sulfuric acid?
(v) What is the significance of the "↑" symbol in the chemical equation for this reaction?
Ans: (i) The chemical reaction between dilute sulfuric acid and zinc is represented as:
Zn + H2SO4 -> ZnSO4 + H2↑
In this reaction, zinc displaces hydrogen from sulfuric acid, forming zinc sulfate and hydrogen gas.
(ii) To test the presence of hydrogen gas, you can bring a burning splint near the mouth of the test tube where the reaction is happening. If you hear a "pop" sound and see a flame, it indicates the presence of hydrogen gas.
(iii) Zinc acts as a reducing agent in this reaction. It donates electrons to hydrogen ions in sulfuric acid, leading to the production of hydrogen gas.
(iv) We use dilute sulfuric acid because it is safer and less reactive than concentrated sulfuric acid. Concentrated sulfuric acid is highly corrosive and can produce a vigorous reaction with zinc, making it
(v) The "↑" symbol indicates that hydrogen gas is produced as a gas and is released into the air during the reaction. It helps us understand that hydrogen gas is one of the products of the reaction and is liberated in the form of bubbles.
Q3: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below:
(i) What are the reactants in the experiment for the formation of slaked lime?
(ii) Describe the appearance of calcium oxide (CaO) before the reaction with water.
(iii) What is the chemical formula of the product formed in this experiment, and what is its common name?
(iv) Explain how the appearance of the mixture changes during the reaction between calcium oxide and water.
(v) Why is the formation of slaked lime considered a combination reaction?
Ans: (i) The reactants in this experiment are calcium oxide (CaO) and water (H2O).
(ii) Calcium oxide appears as a white, powdery substance before the reaction with water.
(iii) The chemical formula of the product formed is calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2), and its common name is slaked lime.
(iv) During the reaction, the mixture changes from a white, powdery substance (calcium oxide) to a thick, white, and pasty substance (slaked lime or calcium hydroxide).
(v) The formation of slaked lime is considered a combination reaction because it involves the combination of two substances, calcium oxide and water, to form a single product, calcium hydroxide, without the release of any additional substances.
Q4: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below: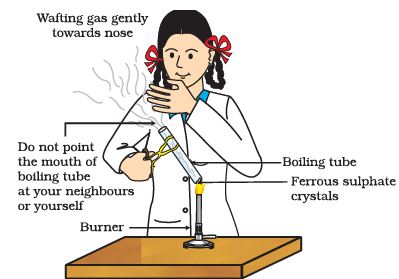
(i) What is the purpose of heating the boiling tube containing crystals of ferrous sulfate in this experiment?
(ii) What is the appearance of ferrous sulfate crystals before heating, and how does it change after heating?
(iii) Why is it important to observe the odor during this experiment?
(iv) Describe the odor you would expect when heating ferrous sulfate crystals, and explain the chemical reaction responsible for it.
(v) How would you test the presence of sulfur dioxide gas in this experiment?
Ans: (i) To observe the effect of heating on the crystals of ferrous sulfate.
(ii) Before heating, the ferrous sulfate crystals are usually green in color. After heating, they turn white and lose their water of crystallization.
(iii) Odor observation helps identify the presence of sulfur dioxide gas, which is released when ferrous sulfate is heated.
(iv) The odor would be of burning sulfur or a pungent, rotten egg smell. This is due to the decomposition of ferrous sulfate, which releases sulfur dioxide gas (SO2) when heated.
(v) You can pass the gas produced during heating through a glass tube into a solution of sodium hydroxide (NaOH). If sulfur dioxide gas is present, it will react with NaOH to form sodium sulfite (Na2SO3), which can be detected by the formation of a white precipitate.
Q5: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below:
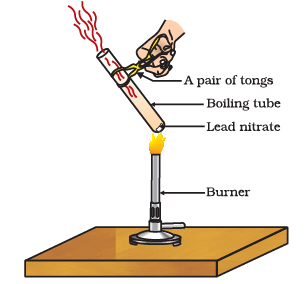
(i) What is the initial substance in the experiment shown in Figure?
(ii) What is the evidence that a chemical reaction has occurred during heating?
(iii) Write the chemical equation for the thermal decomposition of lead nitrate.
(iv) What is the role of heat in this experiment?
(v) Why is it important to use tongs while heating the boiling tube?
Ans: (i) The initial substance in the experiment is lead nitrate (Pb(NO3)2).
(ii) The evidence of a chemical reaction is the emission of brown fumes, which are identified as nitrogen dioxide (NO2). This indicates that a chemical change has taken place.
(iii) The chemical equation for the thermal decomposition of lead nitrate is:
2Pb(NO3)2(s) → 2PbO(s) + 4NO2(g) + O2(g). This equation represents the conversion of lead nitrate into lead oxide, nitrogen dioxide, and oxygen.
(iv) Heat is used as an energy source to break the chemical bonds in lead nitrate (Pb(NO3)2). This process, known as thermal decomposition, results in the formation of lead oxide (PbO), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and oxygen (O2).
(v) Tongs are used to hold the boiling tube because the experiment involves high temperatures, and it can become very hot. Using tongs ensures the safety of the experimenter by preventing direct contact with the hot glass, which could cause burns or injuries.
Q6: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below:
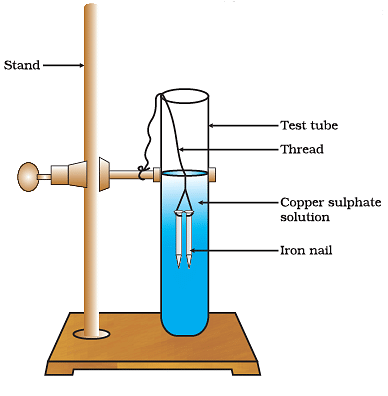
(i) Describe the setup of the experiment where iron nails are dipped in copper sulfate solution.
(ii) What is the initial color of the copper sulfate solution, and what happens to it as the experiment proceeds?
(iii) Explain the chemical reaction that occurs when iron nails are dipped in copper sulfate solution.
(iv) What is the solid substance that forms on the surface of the iron nails during the experiment?
(v) How can you confirm the presence of copper in the final solution after the experiment?
Ans: (i) In the experiment, take a beaker and fill it with copper sulfate solution. Place some iron nails in the solution and observe the changes over time. Ensure that the nails are fully immersed in the solution.
(ii) Initially, the copper sulfate solution is blue in color. As the experiment proceeds, the blue color of the solution starts to fade, and the solution turns greenish due to the formation of a new compound.
(iii) When iron nails are dipped in copper sulfate solution, a displacement reaction occurs. The iron in the nails reacts with copper sulfate to form iron sulfate and copper metal. The chemical equation for this reaction is:
Iron (Fe) + Copper Sulfate (CuSO4) → Iron Sulfate (FeSO4) + Copper (Cu)
(iv) A reddish-brown solid substance, which is copper, forms on the surface of the iron nails during the experiment. This is a visible result of the displacement reaction taking place.
(v) To confirm the presence of copper in the final solution, you can perform a simple test. Add a few drops of dilute hydrochloric acid (HCl) to the greenish solution. If copper is present, a brown gas (hydrogen gas) will be evolved, and you may also notice the solution turning blue again due to the formation of copper chloride. This confirms the presence of copper in the solution.
Q7: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below:

(i) What is the initial color of the copper wire before the oxidation experiment?
(ii) Describe the changes in the color of the copper wire after it undergoes oxidation.
(iii) Explain the role of heat in the oxidation of copper.
(iv) What type of chemical reaction is observed during the oxidation of copper?
(v) Why is the copper wire cleaned before the experiment?
Ans: (i) The initial color of the copper wire is reddish-brown.
(ii) After oxidation, the copper wire turns black due to the formation of copper oxide.
(iii) Heat is necessary for the oxidation of copper. It provides the energy required for copper atoms to react with oxygen in the air and form copper oxide.
(iv) The oxidation of copper is a chemical reaction called a redox reaction, where copper atoms lose electrons and combine with oxygen to form copper oxide.
(v) The copper wire is cleaned before the experiment to remove any impurities, such as grease or dirt, that might hinder the oxidation process and to ensure accurate observations during the experiment.
Q8: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below:

(i) Identify the chemical change when silver chloride is left exposed to sunlight.
(ii) Write balanced chemical reaction for product produced.
(iii) What type of chemical reaction is observed in this change ?
Ans: (i) Silver chloride is white in color. When exposed to sunlight, silver chloride absorbs sunlight and produces silver metal and chlorine gas. Hence the white color changes to greyish.
(ii) 2AgCl ----> 2Ag + Cl2
(iii) Type of the chemical reaction is photolytic decomposition reaction or photolysis.
|
85 videos|437 docs|75 tests
|
FAQs on Diagram Based Questions: Chemical Reactions and Equations - Science Class 10
| 1. What are the different types of chemical reactions? |  |
| 2. How do you balance a chemical equation? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the law of conservation of mass in chemical reactions? |  |
| 4. What are reactants and products in a chemical equation? |  |
| 5. How can diagrams help in understanding chemical reactions? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|


















