Worksheet: Displacing Indigenous Peoples | History Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Match the Columns |

|
| Assertion and Reason Based |

|
| Very Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: The American empires of Spain and Portugal did not expand after the ______ century.
Q2: Settlers in South Africa were primarily referred to as ______.
Q3: The natives in North America believed in a ______ economy.
Q4: The Europeans gave the natives blankets, iron vessels, guns, and ______ in exchange for local products.
Q5: The 'Gold Rush' in the USA began when traces of gold were found in ______.
Q6: The Indian Reorganisation Act of 1934 in the USA granted natives in reservations the right to ______.
Q7: The 'Declaration of Indian Rights' in 1954 allowed some native peoples to accept ______ citizenship.
Q8: In Australia, the 'White Australia' policy ended in ______.
Match the Columns
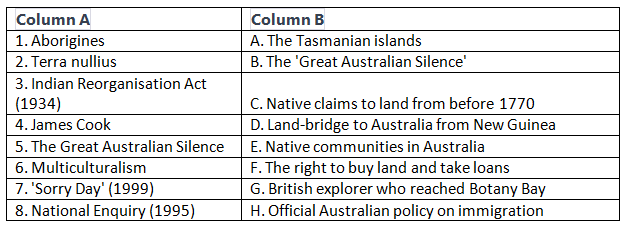
Q1: Match the items in Column A with those in Column B.
Assertion and Reason Based
Q1: Assertion: The American empires of Spain and Portugal did not expand after the seventeenth century.
Reason: Other European countries like France, Holland, and Britain began to extend trade activities and establish colonies in America, Africa, and Asia.
(a) The reason is true, and it explains the assertion.
(b) The reason is true, but it does not explain the assertion.
(c) The reason is false.
(d) The assertion is false.
Q2: Assertion: Native peoples in North America were friendly and welcoming to Europeans.
Reason: Europeans gave the natives blankets, iron vessels, guns, and alcohol in exchange for local products.
(a) The reason is true, and it explains the assertion.
(b) The reason is true, but it does not explain the assertion.
(c) The reason is false.
(d) The assertion is false.
Q3: Assertion: The Indian Reorganisation Act of 1934 allowed natives in reservations the right to buy land and take loans.
Reason: This act aimed to assimilate natives into mainstream American society.
(a) The reason is true, and it explains the assertion.
(b) The reason is true, but it does not explain the assertion.
(c) The reason is false.
(d) The assertion is false.
Q4: Assertion: The 'White Australia' policy in Australia ended in 1968.
Reason: Australia adopted a policy of multiculturalism, giving equal respect to native cultures and immigrant cultures.
(a) The reason is true, and it explains the assertion.
(b) The reason is true, but it does not explain the assertion.
(c) The reason is false.
(d) The assertion is false.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: What drove people to establish colonies in various parts of the world?
Q2: What was the impact of Europeans introducing alcohol to Native Americans?
Q3: What was the significance of the 'Gold Rush' in the USA?
Q4: Why were democratic rights denied to native peoples in British colonies in America?
Q5: Who played a key role in the abolition of slavery in the USA?
Q6: What is 'Terra nullius' in the Australian context?
Q7: When did the 'White Australia' policy come to an end?
Q8: What is the significance of 'Sorry Day' in Australia?
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Discuss the nature of control over colonies in South Asia by trading companies and their impact.
Q2: Compare and contrast the perspectives of American natives and Europeans regarding trade, nature, and the environment.
Q3: Explain the impact of the 'Gold Rush' on the growth of industries and the development of the USA.
Q4: Describe the changes in Australian immigration policies from the 'White Australia' policy to multiculturalism.
Q5: Analyze the factors that led to the improvement in the status of native peoples in the USA and Canada from the 1920s onwards.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: Discuss the historical context and consequences of the Indian Reorganisation Act of 1934 in the USA.
Q2: Evaluate the importance of the Australian High Court's recognition of native claims to land from before 1770 and its impact on indigenous rights in Australia.
You can access the solutions to this worksheet here.
|
27 videos|157 docs|27 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet: Displacing Indigenous Peoples - History Class 11 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What is the significance of displacing indigenous peoples in the context of humanities/arts? |  |
| 2. How does the displacement of indigenous peoples impact their cultural heritage? |  |
| 3. What are some common reasons for displacing indigenous peoples in the field of humanities/arts? |  |
| 4. How can the displacement of indigenous peoples be addressed in the field of humanities/arts? |  |
| 5. What are the potential consequences of ignoring the displacement of indigenous peoples in the field of humanities/arts? |  |















