Worksheet: The End of Bipolarity | Political Science Class 12 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Match the Column |

|
| Assertion and Reason Based |

|
| Very Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: The USSR came into being after the socialist revolution in _______.
Q2: The Soviet political system was centered around the _______ party.
Q3: The group of countries under Soviet control was known as the _______ bloc.
Q4: Mikhail Gorbachev became General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union in _______.
Q5: The Soviet Union collapsed in the year _______.
Q6: The economic system in the USSR was characterized by _______ planning and control.
Q7: The rise of _______ and desire for sovereignty led to the disintegration of the Soviet Union.
Q8: The model of transition from an authoritarian socialist system to a democratic capitalist system was known as _______ therapy.
Q9: India maintained good relations with post-communist countries due to its shared vision of a _______ world order.
Q10: The end of the Soviet bloc led to the emergence of new countries wanting to join organizations like _______ and _______.
Match the Column
Q1:
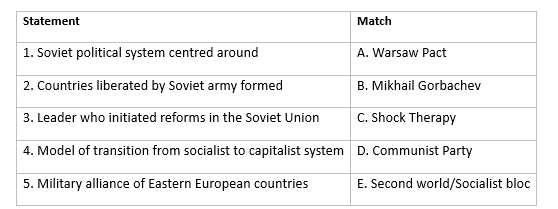
Assertion and Reason Based
Q1: Assertion: The Soviet political system was centered around the communist party.
Reason: The Soviet citizens had the freedom to form multiple political parties.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Q2: Assertion: Shock therapy brought ruin to the economies and disaster upon the people of the former Soviet bloc.
Reason: Shock therapy was a gradual and carefully planned economic reform process.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Q3: Assertion: The end of the Soviet bloc led to the emergence of new countries with independent aspirations.
Reason: These countries desired to maintain close ties with Russia only.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Q4: Assertion: India maintained good relations with post-communist countries due to shared interests and benefits.
Reason: Post-communist countries were primarily interested in military alliances with India.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: What inspired the socialist revolution in Russia in 1917?
Q2: What was the role of the communist party in the Soviet political system?
Q3: Which military alliance held together the socialist bloc?
Q4: Who initiated the series of reforms in the Soviet Union?
Q5: Which major republics declared the disbandment of the Soviet Union in 1991?
Q6: What was the impact of shock therapy on the Russian currency?
Q7: Name one former Soviet republic that had a violent secessionist movement.
Q8: What did the disintegration of the Soviet Union mean for Cold War confrontations?
Q9: What organizations became powerful advisors to post-communist countries?
Q10: Why did India benefit from its relationship with post-communist countries?
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Explain the key features of the Soviet political system.
Q2: Describe the factors that led to the disintegration of the Soviet Union.
Q3: What were the consequences of shock therapy on the economies and people of the former Soviet bloc?
Q4: How did the end of the Soviet bloc impact the global power dynamics?
Q5: Discuss the relations between India and post-communist countries.
Q6: Explain the role of Mikhail Gorbachev in the reforms of the Soviet Union.
Q7: Why did some former Soviet republics experience conflicts and civil wars after the dissolution of the USSR?
Q8: What were the main goals of shock therapy in post-communist regimes?
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: Explain the internal weaknesses of Soviet political and economic institutions that led to the disintegration of the Soviet Union.
Q2: Examine the consequences of shock therapy on the economies and societies of the former Soviet bloc.
Q3: Explore how the end of the Soviet bloc impacted global power dynamics.
Q4: Evaluate India's strategic relations with post-communist countries and the significance of these relationships in the global context.
You can access the solutions to this worksheet here.
|
34 videos|308 docs|51 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet: The End of Bipolarity - Political Science Class 12 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What is the significance of the end of bipolarity in international relations? |  |
| 2. How did the Cold War contribute to the concept of bipolarity? |  |
| 3. What were some key events that led to the end of bipolarity? |  |
| 4. What impact has the end of bipolarity had on global security? |  |
| 5. How does the concept of multipolarity differ from bipolarity? |  |
















