Important Formulas: Polygons - GMAT PDF Download
Polygon
A polygon is a closed two-dimensional shape having straight line segments. It is not a three-dimensional shape. A polygon does not have any curved surface. A polygon should have at least three sides. Each side of the line segment must intersect with another line segment only at its endpoint. Based on the number of sides of a polygon, we can easily identify the polygon shape.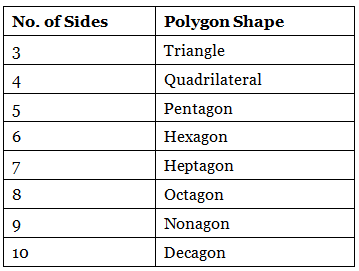
Types of Polygon
Based on the angle measure and the sides of a polygon, the polygon is classified into:
- Regular Polygon – All the interior angles and the sides are equal
- Irregular Polygon – All the interior angles and the sides are of different measure
- Convex polygon – All the interior angles of a polygon are strictly less than 180 degrees
- Concave Polygon – One or more interior angles of a polygon are more than 180 degrees
Perimeter and Area
The perimeter of a polygon is the distance around the outside of the polygon, or the sum of the lengths of the sides of the polygon.
The area of a polygon is the amount of surface that is covered by the polygon.
To find the area of triangles and quadrilaterals, you need two measurements: the base and the height.
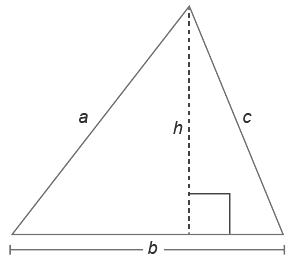
Any of the sides of a triangle can be its base. The height of the triangle is the perpendicular distance from the base to the opposite angle.
For the quadrilaterals listed below, the height of the quadrilateral is the perpendicular distance from the base to the opposite side.
These are the formulas for the perimeter, P, and area, A, of common figures.
Triangle
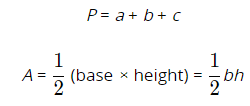
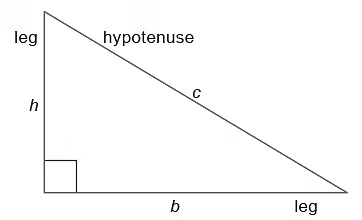
Right Triangle
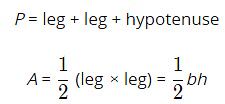
Rectangle
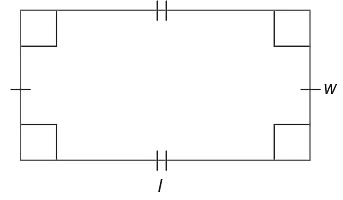
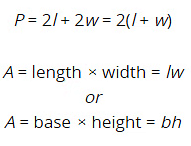 Opposite sides are equal.
Opposite sides are equal.- All angles are equal and are 90°
Square
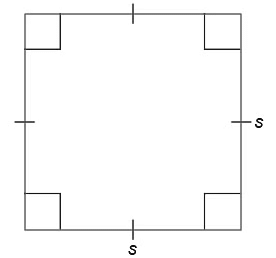
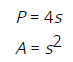
- All sides are equal.
- All angles are equal and are 90°.
Parallelogram
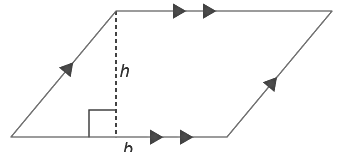
- P = 2l + 2w = 2(l + w)
- A = base × height = bh
- Opposite sides are equal.
- Opposite sides are parallel.
- Opposite angles are equal.
- Adjacent angles add to 180°.
 |
Download the notes
Important Formulas: Polygons
|
Download as PDF |
Rhombus
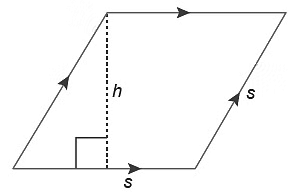
- P = 4s
- A = base × height = bh
- All sides are equal.
- Opposite sides are parallel.
- Opposite angles are equal.
- Adjacent angles add to 180°.
Trapeziod
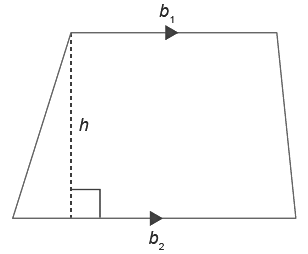
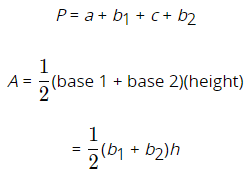
- One pair of opposite sides, the bases, is parallel.
Circle
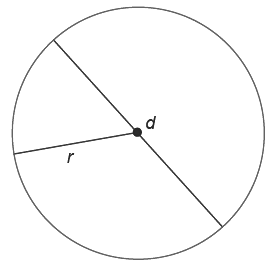
- C = 2πr = πd
- A = πr2
- r = radius, d = diameter, and d = 2r
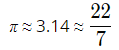
Extra Important Formulas
The important polygon formulas are:
- The sum of interior angles of a polygon with “n” sides =180°(n-2)
- Number of diagonals of a “n-sided” polygon = [n(n-3)]/2
- The measure of interior angles of a regular n-sided polygon = [(n-2)180°]/n
- The measure of exterior angles of a regular n-sided polygon = 360°/n




















