Worksheet: US Hegemony in World Politics | Political Science Class 12 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Match the Column |

|
| Assertion and Reason Based |

|
| Very Short Answers Type Questions |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Long Answers Type Questions |

|
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: Hegemony refers to a situation in which one nation is in a stronger position than __________ nations in the world.
Q2: The collapse of the USSR led to the emergence of US hegemony in__________.
Q3: Operation Desert Storm was another name for the __________.
Q4: The Clinton administration prioritized "soft issues" such as democracy, climate change, and international trade over _________ politics.
Q5: The US launched "Operation Infinite Reach" in retaliation for the bombing of its embassies in ______ and ________.
Q6: The 9/11 attacks involved the hijacking of ________American commercial aircraft.
Q7: George W. Bush succeeded _________ in the US Presidency.
Q8: Operation Enduring Freedom was part of the US's __________.
Q9: The US invasion of Iraq aimed to prevent the development of __________.
Q10: Hegemony includes ________ power, which relates to ideological resources.
Match the Column
Q1:
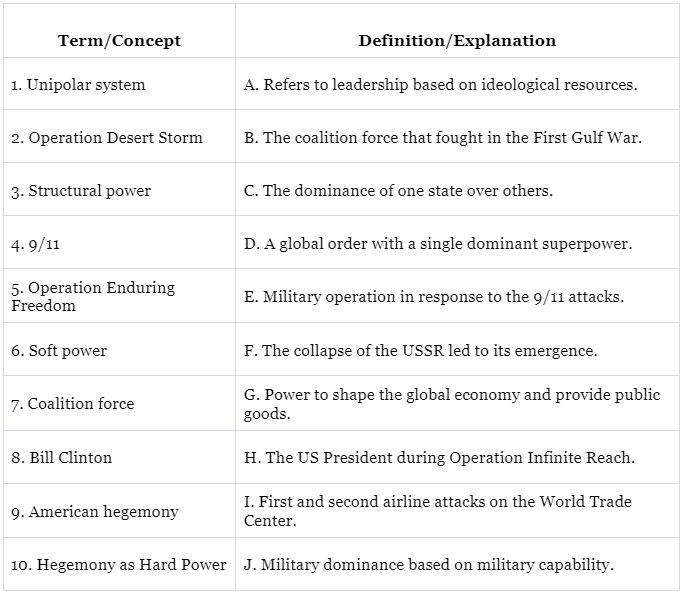
Assertion and Reason Based
Q1: Assertion: The collapse of the USSR led to the emergence of US hegemony.
Reason: With the USSR's collapse, the US's powers remained unchanged.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) The assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) The assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Q2: Assertion: The US invasion of Iraq was a military and political failure.
Reason: The invasion aimed to prevent Iraq from developing Weapons of Mass Destruction (WMD).
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) The assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) The assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Q3: Assertion: Hegemony as Soft Power is based on cultural presence.
Reason: The US used structural power and soft power throughout the Cold War.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) The assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) The assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Very Short Answers Type Questions
Q1: What did the collapse of the USSR lead to in 1991?
Q2: Name the military operation in response to the bombing of US embassies in Nairobi and Dar es Salaam.
Q3: Who succeeded Bill Clinton as US President?
Q4: What was the main goal of the US invasion of Iraq in 2003?
Q5: Define "hegemony as structural power."
Q6: What does "hide strategy" involve in challenging hegemony?
Q7: Name three constraints on American power.
Q8: What is the role of NATO in moderating the exercise of American power?
Q9: What two factors emerged in Indo-US relations in recent years?
Q10: What are the three different strategies for India's relationship with the USA?
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Describe the significance of the collapse of the USSR in the context of US hegemony.
Q2: Explain the main goals and outcomes of Operation Desert Storm.
Q3: What were the key priorities of the Clinton administration in global politics?
Q4: Analyze the impact of 9/11 on US foreign policy and the initiation of the "Global War on Terror."
Q5: Discuss the reasons and consequences of the US invasion of Iraq in 2003.
Q6: Differentiate between hegemony as hard power, structural power, and soft power.
Q7: What are the three constraints on American power, and how do they affect US foreign policy?
Q8: How have India's relations with the USA evolved over time, and what are the recent factors influencing this relationship?
Long Answers Type Questions
Q1: Explain the concept of "hegemony" and how it is associated with the United States, considering its role in politics, economics, and culture. Provide examples.
Q2: Analyze the different strategies proposed in the text for challenging American hegemony, such as the Bandwagon Strategy, Hide Strategy, and the role of non-state entities. Assess their effectiveness and limitations.
Q3: Discuss the factors that have shaped India's relationship with the USA, from its Cold War alignment with the Soviet Union to the recent developments related to technology and the Indian-American diaspora. What strategies are suggested for India's approach to the USA, and how can they be balanced?
Q4: Evaluate the constraints on American power as mentioned in the text, including institutional architecture, domestic factors, and the role of NATO. Explain how these constraints impact the exercise of American power in international relations.
You can access the solutions to this worksheet here.
|
34 videos|308 docs|51 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet: US Hegemony in World Politics - Political Science Class 12 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What is US hegemony in world politics? |  |
| 2. How has US hegemony evolved since World War II? |  |
| 3. What are the main challenges to US hegemony today? |  |
| 4. How does US hegemony impact global economic policies? |  |
| 5. What role does culture play in US hegemony? |  |














