Worksheet Solutions: US Hegemony in World Politics | Political Science Class 12 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Match the Column |

|
| Assertion and Reason Based |

|
| Very Short Answers Type Questions |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Long Answers Type Questions |

|
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: Hegemony refers to a situation in which one nation is in a stronger position than __________ nations in the world.
Ans: other
Hegemony refers to a situation in which one nation is in a stronger position than other nations in the world, indicating a dominant global influence.
Q2: The collapse of the USSR led to the emergence of US hegemony in__________.
Ans: global politics
The collapse of the USSR led to the emergence of US hegemony in global politics, reshaping the international power dynamics after the Cold War.
Q3: Operation Desert Storm was another name for the __________.
Ans: Gulf War
Operation Desert Storm was another name for the Gulf War, a military campaign led by a coalition force, primarily the US, to liberate Kuwait from Iraqi occupation in 1990-1991.
Q4: The Clinton administration prioritized "soft issues" such as democracy, climate change, and international trade over _________ politics.
Ans: traditional
The Clinton administration prioritized "soft issues" such as democracy, climate change, and international trade over traditional politics, emphasizing non-military approaches in global relations.
Q5: The US launched "Operation Infinite Reach" in retaliation for the bombing of its embassies in ______ and ________.
Ans: Nairobi and Dar es Salaam
The US launched "Operation Infinite Reach" in retaliation for the bombing of its embassies in Nairobi and Dar es Salaam, targeting Al-Qaeda bases in Afghanistan and Sudan as a response to the attacks.
Q6: The 9/11 attacks involved the hijacking of ________American commercial aircraft.
Ans: four
The 9/11 attacks involved the hijacking of four American commercial aircraft, leading to coordinated terrorist attacks on the US, notably the World Trade Center and the Pentagon.
Q7: George W. Bush succeeded _________ in the US Presidency.
Ans: Bill Clinton
George W. Bush succeeded Bill Clinton in the US Presidency, taking office after the 2000 presidential election.
Q8: Operation Enduring Freedom was part of the US's __________.
Ans: War on Terror
Operation Enduring Freedom was part of the US's War on Terror, initiated in response to the 9/11 attacks, aiming to combat terrorism globally, primarily focusing on Al-Qaeda and the Taliban regime in Afghanistan.
Q9: The US invasion of Iraq aimed to prevent the development of __________.
Ans: weapons of mass destruction
The US invasion of Iraq aimed to prevent the development of weapons of mass destruction, although no substantial evidence supporting this claim was found, leading to international controversy.
Q10: Hegemony includes ________ power, which relates to ideological resources.
Ans: soft
Hegemony includes soft power, relating to ideological resources and cultural influence, shaping the behavior of other nations through attraction and persuasion.
Match the Column
Q1:
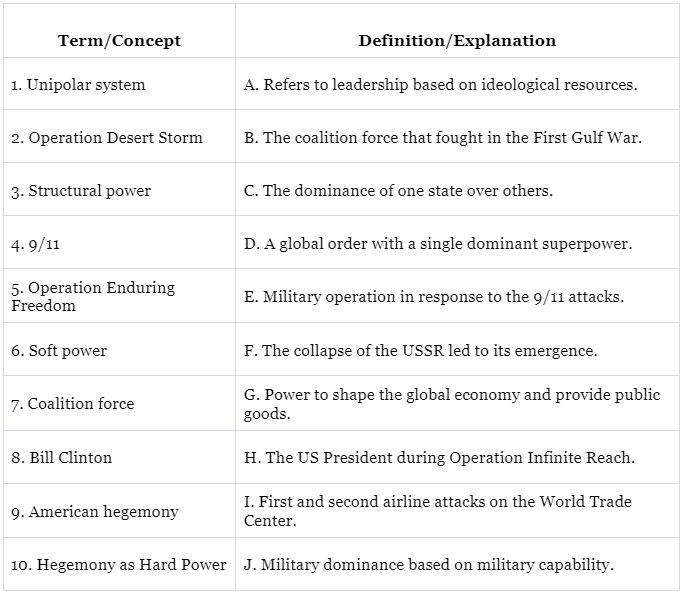 Ans: 1. Unipolar system - D. A global order with a single dominant superpower.
Ans: 1. Unipolar system - D. A global order with a single dominant superpower.
In a unipolar system, there is a single superpower or dominant force in the global order.
2. Operation Desert Storm - B. The coalition force that fought in the First Gulf War.
Operation Desert Storm was the codename for the coalition military operation during the First Gulf War.
3. Structural power - G. Power to shape the global economy and provide public goods.
Structural power involves the ability to shape the international system, including the global economy and public goods.
4. 9/11 - I. First and second airline attacks on the World Trade Center.
The 9/11 attacks involved the first and second hijacked planes crashing into the World Trade Center towers.
5. Operation Enduring Freedom - E. Military operation in response to the 9/11 attacks.
Operation Enduring Freedom was initiated by the US and its allies after the 9/11 attacks.
6. Soft power - A. Refers to leadership based on ideological resources.
Soft power involves influencing others through attraction, culture, and ideology.
7. Coalition force - F. The collapse of the USSR led to its emergence.
The emergence of US hegemony was influenced by the collapse of the USSR.
8. Bill Clinton - H. The US President during Operation Infinite Reach.
Bill Clinton was the US President during Operation Infinite Reach, which targeted Al-Qaeda bases.
9. American hegemony - C. The dominance of one state over others.
American hegemony refers to the US's dominant position in international relations.
10. Hegemony as Hard Power - J. Military dominance based on military capability.
Hegemony as hard power involves military dominance and capabilities.
Assertion and Reason Based
Q1: Assertion: The collapse of the USSR led to the emergence of US hegemony.
Reason: With the USSR's collapse, the US's powers remained unchanged.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) The assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) The assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Ans: (a)
The assertion is true because the collapse of the USSR indeed led to the emergence of US hegemony. The reason is the correct explanation, as the power vacuum created by the USSR's collapse allowed the US to become the dominant global power.
Q2: Assertion: The US invasion of Iraq was a military and political failure.
Reason: The invasion aimed to prevent Iraq from developing Weapons of Mass Destruction (WMD).
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) The assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) The assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Ans: (b)
While the assertion is true that the US invasion of Iraq was a military and political failure, the reason provided (aiming to prevent WMD development) is not the correct explanation. The invasion's failure was due to various factors, including lack of international support and post-invasion challenges in Iraq.
Q3: Assertion: Hegemony as Soft Power is based on cultural presence.
Reason: The US used structural power and soft power throughout the Cold War.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) The assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) The assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Ans: (a)
The assertion is true because hegemony as soft power is indeed based on cultural presence. The reason is the correct explanation, as soft power involves influencing others through cultural, ideological, and social means.
Very Short Answers Type Questions
Q1: What did the collapse of the USSR lead to in 1991?
Ans: The collapse of the USSR in 1991 led to the emergence of US hegemony in world politics.
Q2: Name the military operation in response to the bombing of US embassies in Nairobi and Dar es Salaam.
Ans: The military operation in response to the bombing of US embassies in Nairobi and Dar es Salaam was called "Operation Infinite Reach."
Q3: Who succeeded Bill Clinton as US President?
Ans: George W. Bush succeeded Bill Clinton as US President.
Q4: What was the main goal of the US invasion of Iraq in 2003?
Ans: The main goal of the US invasion of Iraq in 2003 was to prevent the development of Weapons of Mass Destruction (WMD).
Q5: Define "hegemony as structural power."
Ans: "Hegemony as structural power" refers to the ability of a dominant power to shape the global economy and provide essential public goods, influencing international systems.
Q6: What does "hide strategy" involve in challenging hegemony?
Ans: "Hide strategy" involves staying as far removed from the dominant power as possible, avoiding direct involvement or alliances.
Q7: Name three constraints on American power.
Ans: Three constraints on American power are institutional architecture, domestic skepticism, and the moderating influence of NATO.
Q8: What is the role of NATO in moderating the exercise of American power?
Ans: NATO moderates the exercise of American power by providing a platform for collective decision-making and encouraging dialogue among member countries.
Q9: What two factors emerged in Indo-US relations in recent years?
Ans: The two factors in recent Indo-US relations are the technological dimension and the role of the Indian-American diaspora.
Q10: What are the three different strategies for India's relationship with the USA?
Ans: The three different strategies for India's relationship with the USA include maintaining distance, exploring common interests, and leading a coalition of developing countries.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Describe the significance of the collapse of the USSR in the context of US hegemony.
Ans: The collapse of the USSR in 1991 created a power vacuum, allowing the US to become the dominant global power. With no major competing superpower, the international system shifted to a unipolar structure, establishing American hegemony in world politics.
Q2: Explain the main goals and outcomes of Operation Desert Storm.
Ans: Operation Desert Storm was the military operation led by a coalition force of 34 nations, primarily the US, to liberate Kuwait from Iraqi occupation in 1990-1991. The operation aimed to enforce UN Security Council resolutions and restore Kuwait's sovereignty, resulting in the expulsion of Iraqi forces from Kuwait.
Q3: What were the key priorities of the Clinton administration in global politics?
Ans: The Clinton administration prioritized "soft issues" such as the advancement of democracy, climate change, and international trade over "hard politics" like military interventions. This shift reflected a focus on non-coercive diplomacy and global cooperation in addressing pressing global challenges.
Q4: Analyze the impact of 9/11 on US foreign policy and the initiation of the "Global War on Terror."
Ans: The 9/11 attacks on September 11, 2001, prompted a swift and aggressive response from the US. President George W. Bush launched the Global War on Terror, initiating Operation Enduring Freedom. This operation targeted Al-Qaeda and the Taliban regime in Afghanistan, aiming to dismantle terrorist networks responsible for the attacks.
Q5: Discuss the reasons and consequences of the US invasion of Iraq in 2003.
Ans: The US invasion of Iraq in 2003 aimed to prevent the development and use of Weapons of Mass Destruction (WMD) by Saddam Hussein's regime. However, no substantial evidence of WMD was found, leading to international criticism and raising questions about the invasion's true motivations, such as control over Iraqi oilfields.
Q6: Differentiate between hegemony as hard power, structural power, and soft power.
Ans: Hegemony as hard power relates to military capability and the ability to exert military influence over other states. It signifies a nation's military superiority, including technological advancements and defense capabilities. Hegemony as structural power involves shaping the global economy and providing public goods, ensuring the functioning of essential international systems. Hegemony as soft power implies influencing others through cultural, ideological, and social means, creating attraction and shaping behavior.
Q7: What are the three constraints on American power, and how do they affect US foreign policy?
Ans: The three constraints on American power include the institutional architecture of the US, domestic skepticism rooted in American political culture, and the moderating influence of NATO. These constraints limit the unilateral exercise of American power, promoting collective decision-making and checks on military actions.
Q8: How have India's relations with the USA evolved over time, and what are the recent factors influencing this relationship?
Ans: India's relationship with the USA has undergone significant transformations. During the Cold War, India maintained a close friendship with the Soviet Union. However, India's decision to liberalize its economy and integrate into the global economy attracted the interest of the US and other nations. Recent factors influencing the relationship include the technological dimension, fostering collaboration in various sectors, and the role of the Indian-American diaspora, acting as a bridge between the two countries.
Long Answers Type Questions
Q1: Explain the concept of "hegemony" and how it is associated with the United States, considering its role in politics, economics, and culture. Provide examples.
Ans: Hegemony refers to the leadership or predominance of one state over others in terms of military, economic, political power, and cultural superiority. American hegemony, emerging after the collapse of the USSR in 1991, placed the US in a dominant position globally. The US influenced politics, economics, and culture worldwide. For instance, Operation Desert Storm showcased the US military's technological superiority. Hegemony as hard power demonstrated the US's military capabilities. Structural power involved shaping the global economy and providing public goods, such as internet infrastructure. Soft power, based on cultural presence, allowed the US to influence ideological spheres. Throughout the Cold War and beyond, the US utilized various forms of power, making it a global hegemon.
Q2: Analyze the different strategies proposed in the text for challenging American hegemony, such as the Bandwagon Strategy, Hide Strategy, and the role of non-state entities. Assess their effectiveness and limitations.
Ans: Challenging American hegemony involves different strategies. The Bandwagon Strategy suggests benefiting from operating within the existing hegemonic system, extracting advantages rather than opposing it directly. The Hide Strategy advocates staying distant from the dominant power to avoid entanglements, exemplified by China, Russia, and the European Union. Non-state entities, such as NGOs, social movements, and public opinion, can also pose challenges. These entities, in combination, might counterbalance American hegemony. NGOs and global public opinion can influence policy decisions, potentially limiting American influence. Thus, a combination of these strategies, tailored to specific contexts, can effectively challenge hegemonic dominance.
Q3: Discuss the factors that have shaped India's relationship with the USA, from its Cold War alignment with the Soviet Union to the recent developments related to technology and the Indian-American diaspora. What strategies are suggested for India's approach to the USA, and how can they be balanced?
Ans: India's relationship with the USA has undergone significant shifts. Historically aligned with the Soviet Union during the Cold War, India later liberalized its economy, becoming an attractive trading partner. The technological dimension and the role of the Indian-American diaspora have emerged as recent factors shaping relations. India faces three strategic options: maintaining distance from the US, focusing on increasing national power independently; recognizing common interests, aligning with the USA strategically; leading a coalition of developing countries, promoting a multipolar world. Balancing these strategies, India can harness the benefits of collaboration with the USA while safeguarding its national interests and sovereignty.
Q4: Evaluate the constraints on American power as mentioned in the text, including institutional architecture, domestic factors, and the role of NATO. Explain how these constraints impact the exercise of American power in international relations.
Ans: Constraints on American power are crucial in shaping its foreign policy. Institutional architecture provides checks and balances within the US government, preventing unilateral decisions. Domestic skepticism, rooted in American political culture, fosters critical evaluation of governmental actions, limiting unchecked power. Additionally, NATO plays a significant role, acting as a collective security organization. While primarily a military alliance, NATO moderates American power by encouraging dialogue and collective decision-making. These constraints promote responsible global engagement, ensuring that American power is exercised judiciously, considering international opinions and interests.
|
34 videos|305 docs|51 tests
|


















