Worksheet: Contemporary Centres of Power | Political Science Class 12 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Match the column |

|
| Assertion and Reason based |

|
| Very Short Answers Type Questions |

|
| Short Answers Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: The European economy was revived after World War II with extensive financial support from ______________ under the Marshall Plan.
Q2: The Organisation for European Economic Cooperation (OEEC) was founded in ____________ to direct help to West European nations.
Q3: The disintegration of the USSR led to the formation of the ______________ in 1992.
Q4: ASEAN stands for Association of South East Asian Nations, founded in ____________.
Q5: The ASEAN emblem consists of ten rice stalks representing ______________ South East Asian nations.
Q6: China's "Open Door Policy" was announced by ______________ in 1978.
Q7: India experienced a military setback against China in the year ______________.
Q8: The slogan "Hindi-Chini-Bhai Bhai" gained popularity during peaceful relations between ______________ and ______________.
Q9: The ASEAN Economic Community seeks to create a ______________ market and promote regional social and economic development.
Q10: The European Union has the largest economy in the world with a GDP exceeding ______________ in 2005.
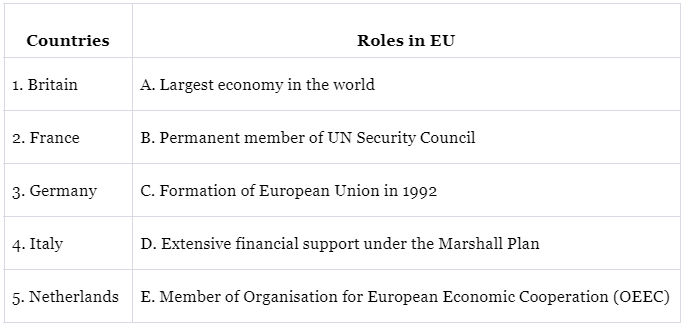
Match the column
Q1:
Assertion and Reason based
Q1: Assertion: The disintegration of the USSR led to the formation of the European Union in 1992.
Reason: European nations wanted to establish a common foreign and security policy.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false.
Q2: Assertion: China's "Open Door Policy" aimed to boost production through foreign investments.
Reason: Special economic zones were established to attract foreign capital and technology.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false.
Q3: Assertion: ASEAN's emblem represents unity with ten rice stalks.
Reason: ASEAN comprises ten South East Asian nations.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false.
Q4: Assertion: India and China had peaceful relations after India's independence.
Reason: The slogan "Hindi-Chini-Bhai Bhai" symbolized the friendship between the two nations.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false.
Very Short Answers Type Questions
Q1: What was the purpose of the Organisation for European Economic Cooperation (OEEC)?
Q2: Name three objectives of ASEAN.
Q3: Who announced China's "Open Door Policy," and what was its goal?
Q4: What does the ASEAN emblem symbolize?
Q5: Which two European countries are permanent members of the UN Security Council?
Q6: What does ASEAN way refer to in the context of interaction?
Q7: When did India and China experience a military dispute, and what was the cause?
Q8: What was the slogan "Hindi-Chini-Bhai Bhai" associated with?
Q9: What are the three pillars of the ASEAN community established in 2003?
Q10: What does China's economy aim to achieve through its Special Economic Zones?
Short Answers Type Questions
Q1: How did the Cold War aid the integration of Europe after 1945?
Q2: Explain the objectives of ASEAN's ASEAN Economic Community.
Q3: How did China's economic policies change after 1978, leading to its growth as a global economic power?
Q4: Describe the founding principles of ASEAN and its approach to international relations.
Q5: How did the Chinese economy evolve since 1978?
Q6: Discuss the impact of the Chinese economy on the global stage.
Q7: Explain the evolution of the European Union from an economic union to a political entity.
Q8: Describe the factors that led to the improvement of relations between India and China in 1988.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: Explain the factors that contributed to the evolution of the European Union from an economic union to a political one. Provide specific examples of this transformation.
Q2: Discuss the founding objectives and principles of ASEAN. How has the ASEAN community evolved over time, and what are its key pillars?
Q3: Explain the key factors and events that contributed to China's rapid economic growth since 1978. How has this growth positioned China globally?
Q4: Examine the historical trajectory of India-China relations, highlighting key events, conflicts, and turning points. How did the relations between the two countries start improving, and what factors contributed to this improvement?
You can access the solutions to this worksheet here.
|
34 videos|305 docs|51 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet: Contemporary Centres of Power - Political Science Class 12 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What are alternative centres of power in the field of humanities/arts? |  |
| 2. How do alternative centres of power contribute to the field of humanities/arts? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of alternative centres of power in the field of humanities/arts? |  |
| 4. How can individuals engage with alternative centres of power in the field of humanities/arts? |  |
| 5. What challenges do alternative centres of power face in the field of humanities/arts? |  |




















