Worksheet Solutions: Election and Representation | Political Science Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Match the Column |

|
| Assertion and Reason Based |

|
| Very Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: When did the Election Commission of India get two more Election Commissioners?
Ans: 1989
The Election Commission of India got two more Election Commissioners in 1989 to make it a multi-member body, ensuring greater accountability and power-sharing.
Q2: FPTP stands for _______.
Ans: First-Past-The-Post
FPTP stands for First-Past-The-Post, which is an electoral system used in India for direct elections to the Lok Sabha and State Legislative Assemblies.
Q3: In the FPTP system, the candidate with the _______ number of votes is declared the winner.
Ans: highest
In the FPTP system, the candidate with the highest number of votes, not necessarily a majority, is declared the winner in a constituency.
Q4: PR stands for _______ _______.
Ans: Proportional Representation
PR stands for Proportional Representation, which is another electoral system that allocates seats in proportion to the percentage of votes a party receives.
Q5: In India, the FPTP system is used for electing members to the _______ _______ and State Legislative Assemblies.
Ans: Lok Sabha
In India, the FPTP system is used for electing members to the Lok Sabha and State Legislative Assemblies.
Q6: The FPTP system is also known as the _______ system.
Ans: Plurality
The FPTP system is also known as the Plurality System, where the candidate with the most votes wins.
Q7: Universal Adult Franchise was introduced in India through the _______ Amendment in 1989.
Ans: 61st
Universal Adult Franchise was introduced in India through the 61st Amendment in 1989, reducing the voting age from 21 to 18.
Q8: The Delimitation Commission is responsible for deciding the reservation of _______.
Ans: constituencies
The Delimitation Commission is responsible for deciding the reservation of constituencies for Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes.
Q9: The Election Commission of India is responsible for conducting elections to _______ _______.
Ans: Parliament, State Legislatures, President, and Vice-President
The Election Commission of India is responsible for conducting elections to Parliament, State Legislatures, President, and Vice-President.
Q10: The Election Commission consists of a Chief Election Commissioner and _______ Election Commissioners.
Ans: two
The Election Commission consists of a Chief Election Commissioner and two Election Commissioners, making it a multi-member body.
Match the Column
Q1: Match the electoral system with its characteristics:
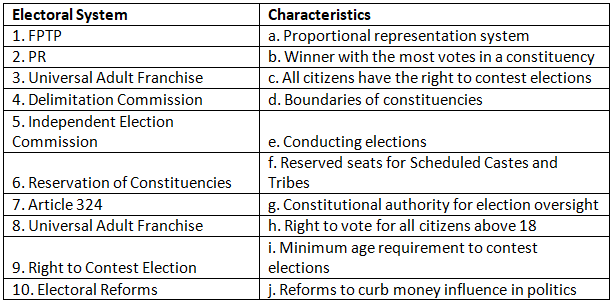 Ans:
Ans: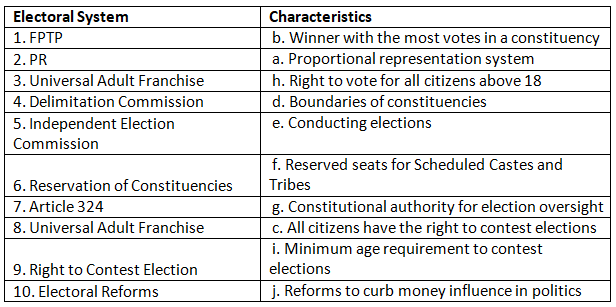
Assertion and Reason Based
Q1: Assertion: Universal Adult Franchise allows all citizens above 21 years to vote.
Reason: It promotes equality and non-discrimination.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct, but Reason is incorrect.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
Ans: (c)
The Assertion is incorrect because Universal Adult Franchise allows all citizens above 18 years to vote, not 21. The Reason is correct, as Universal Adult Franchise promotes equality and non-discrimination.
Q2: Assertion: The FPTP system is popular because of its complexity.
Reason: It ensures proportional representation.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct, but Reason is incorrect.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
Ans: (b)
The Assertion is incorrect. The FPTP system is popular because of its simplicity, not complexity. The Reason is also incorrect, as the FPTP system does not ensure proportional representation.
Q3: Assertion: The Election Commission conducts local body elections.
Reason: The Election Commission is responsible for all elections in India.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct, but Reason is incorrect.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
Ans: (b)
The Assertion is correct. The Reason is also correct in stating that the Election Commission is responsible for all elections in India, but it is not the direct reason for the Assertion.
Q4: Assertion: Independent Election Commissioners have more powers than the Chief Election Commissioner.
Reason: Independent Election Commissioners are appointed by the President.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct, but Reason is incorrect.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
Ans: (c)
The Assertion is incorrect. Independent Election Commissioners do not have more powers than the Chief Election Commissioner. The Reason is also incorrect because Independent Election Commissioners are appointed by the President, but this is not related to their powers.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Explain what the FPTP system stands for.
Ans: The FPTP system stands for "First-Past-The-Post," where the candidate with the most votes in a constituency wins.
Q2: How is the winning candidate determined in the FPTP system?
Ans: In the FPTP system, the winning candidate is determined by having the highest number of votes in a constituency, even if it's not a majority.
Q3: What is Universal Adult Franchise, and when was it introduced in India?
Ans: Universal Adult Franchise allows all citizens above 18 years to vote, promoting equality and non-discrimination.
Q4: What is the role of the Delimitation Commission?
Ans: The Delimitation Commission determines the boundaries of constituencies and decides the reservation of seats.
Q5: What is the significance of the 61st Amendment in the Indian Constitution?
Ans: The 61st Amendment in 1989 reduced the voting age to 18, introducing Universal Adult Franchise.
Q6: What are the minimum age requirements for contesting Lok Sabha or Assembly elections?
Ans: The minimum age requirement to contest Lok Sabha or Assembly elections is 25 years.
Q7: Why was the 42nd Amendment significant regarding the delimitation of seats?
Ans: The 42nd Amendment in 1976 froze the number of seats until the year 2000.
Q8: What is the primary responsibility of the Election Commission of India?
Ans: The primary responsibility of the Election Commission of India is to conduct elections to various offices.
Q9: How are seats reserved for Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes in the legislature?
Ans: Seats reserved for Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes are allocated based on their proportion in the population.
Q10: Why are electoral reforms necessary in India?
Ans: Electoral reforms are necessary to improve the electoral process, ensure transparency, and reduce the influence of money in politics.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Compare and contrast the First-Past-The-Post (FPTP) system and the Proportional Representation (PR) system of elections, highlighting their advantages and disadvantages.
Ans: The First-Past-The-Post (FPTP) system and the Proportional Representation (PR) system are two distinct electoral systems with their advantages and disadvantages. In the FPTP system, each constituency elects one representative, and the candidate with the most votes in that constituency wins, regardless of whether they secure a majority. This system offers simplicity and a direct choice to voters but may not ensure proportional representation. On the other hand, the PR system allocates seats in proportion to the percentage of votes a party receives, promoting fair representation. However, it can lead to more complex election outcomes. While FPTP is used in India for direct elections to the Lok Sabha and State Legislative Assemblies, PR is employed in various countries like Israel and the Netherlands.
Q2: Explain how the reservation of constituencies for Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes is determined in India, and why it is important.
Ans: The reservation of constituencies in India is a crucial aspect of ensuring representation for marginalized communities. The Delimitation Commission, an independent body, determines which constituencies should be reserved for Scheduled Castes (SC) and Scheduled Tribes (ST). The President of India appoints this commission, which works in collaboration with the Election Commission of India. The number of reserved seats in each state is determined based on the proportion of SC and ST residents in that state. For SC seats, the commission selects constituencies with a higher percentage of SC population and disperses them across the state. This is because the SC population is distributed fairly evenly. ST seats are reserved for constituencies with the highest proportion of ST residents. This reservation system is a proactive measure to provide representation and opportunities for historically disadvantaged communities in the legislative bodies.
Q3: Describe the composition and functions of the Election Commission of India. How does it ensure free and fair elections?
Ans: The Election Commission of India is a constitutional authority responsible for conducting elections in India. It was originally a single-member body until two more Election Commissioners were appointed in 1989, making it a multi-member body. The Commission is headed by the Chief Election Commissioner (CEC), who presides over the Election Commission, along with two Election Commissioners. Importantly, all three members have equal powers, and decisions regarding elections are taken collectively. They are appointed by the President of India on the advice of the Council of Ministers and hold office for a term of six years or until they reach the age of 65, whichever comes earlier. To ensure their independence and prevent undue influence, the Constitution provides security of tenure, and the President can only remove the CEC with a special majority recommendation from both Houses of Parliament. The Election Commission's primary responsibilities include overseeing voter lists, determining election schedules, and ensuring free and fair elections.
Q4: Discuss the need for electoral reforms in India, and provide specific suggestions for improving the electoral process and reducing the influence of money in politics.
Ans: Electoral reforms are essential in India to improve the electoral process and strengthen the democratic system.
Some key reforms needed include:
- Introduction of Proportional Representation (PR): Replacing or complementing the FPTP system with PR can ensure fair representation based on vote share.
- Reserving Seats for Women: A provision should be made to ensure the election of at least one-third of women to parliaments and assemblies, promoting gender equality.
- Tighter Regulation of Money in Politics: Establishing tighter regulations to curb the influence of money in electoral politics, such as government-funded election expenses.
- Disqualification of Candidates with Criminal Charges: Candidates with any criminal charges, even if their appeals are pending, should be disqualified from running for office to maintain integrity.
- Prohibition of Caste and Religious Appeals: A complete ban on using caste and religious appeals in political campaigns to foster unity and secularism.
- Regulation of Political Parties: Implementing a law to regulate the functioning of political parties, ensuring transparency and democratic operation.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: Explain the advantages of the First-Past-The-Post (FPTP) system in India, and why it is considered a suitable choice for a stable government.
Ans: The First-Past-The-Post (FPTP) system in India offers several advantages, making it a suitable choice for a stable government. First, it is simple and easy for voters to understand. In a constituency-based system like FPTP, voters know who their representative is, which promotes accountability. Voters have a clear choice between specific candidates and parties, allowing them to express their preferences. The FPTP system encourages candidates to connect with the community, as candidates must be members of the group for which the seat is reserved. This system fosters diversity and representation.
Moreover, in a diverse country like India, FPTP encourages voters from various social groups to come together to win local elections. Additionally, seats in the Lok Sabha and State Legislative Assemblies are reserved for Scheduled Castes and Tribes, ensuring representation for historically disadvantaged communities. The simplicity, accountability, and community-based representation of the FPTP system make it a good choice for ensuring a stable government.
Q2: Discuss the significance of Universal Adult Franchise in the Indian electoral system and its role in promoting democracy and equality.
Ans: Universal Adult Franchise is a fundamental pillar of democracy and plays a crucial role in the Indian electoral system. It grants the right to vote to all adult citizens, regardless of wealth, income, gender, social status, race, ethnicity, or other restrictions, subject only to minor exceptions. The reduction of the voting age to 18 through the 61st Amendment in 1989 introduced Universal Adult Franchise, allowing all citizens to participate in the selection of their representatives.
Universal Adult Franchise is essential because it upholds the principles of equality and non-discrimination, ensuring that every citizen's voice is heard. It promotes inclusivity and represents the diversity of the Indian population. It empowers individuals to participate in the democratic process, holding elected representatives accountable. This universal right to vote strengthens the democratic fabric of India, fostering political engagement and giving each citizen a say in the governance of the nation. It ensures that the government is truly "of the people, by the people, and for the people."
Q3: Elaborate on the role and significance of the Delimitation Commission in India, and its impact on fair representation.
Ans: The Delimitation Commission plays a vital role in the Indian electoral system by determining the boundaries of constituencies and deciding the reservation of seats for Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes. The Commission is an independent body appointed by the President of India and collaborates with the Election Commission of India. Its primary functions are to ensure fair and effective representation of constituencies and to address population shifts and changes.
When it comes to the reservation of constituencies, the Delimitation Commission examines the population composition of each constituency after drawing the boundaries. Seats are reserved for constituencies with a higher proportion of Scheduled Castes or Scheduled Tribes residents. For Scheduled Castes, the Commission disperses these constituencies throughout the state since the SC population is evenly distributed. For Scheduled Tribes, seats are reserved for constituencies with the highest proportion of ST residents.
The Delimitation Commission's work is crucial for upholding the principles of social justice and representation for marginalized communities, ensuring their voices are heard in the legislative bodies.
Q4: Provide a comprehensive list of electoral reforms that you believe would improve the Indian electoral process, ensuring transparency, fairness, and better representation.
Ans: Electoral reforms are imperative in India to enhance the electoral process, increase transparency, and reduce the influence of money in politics. Here are some key reforms:
- Introduction of Proportional Representation (PR): India should consider replacing or complementing the First-Past-The-Post (FPTP) system with PR. PR allocates seats based on the percentage of votes each party receives, providing a more accurate reflection of the people's choices.
- Reservation of Seats for Women: A special provision should be made to ensure the election of at least one-third of women to parliaments and assemblies, promoting gender equality and women's representation in politics.
- Tighter Regulations on Campaign Finance: To curb the influence of money in politics, stricter regulations should be imposed on campaign financing. A government-funded special fund can cover the expenses of elections, reducing the role of private funding.
- Disqualification of Candidates with Criminal Charges: Candidates with pending criminal charges should be disqualified from running for office. This step ensures that individuals with criminal backgrounds do not enter positions of power.
- Prohibition of Caste and Religious Appeals: A comprehensive ban on using caste and religious appeals in campaigns can promote a more inclusive and secular political landscape.
- Regulation of Political Parties: A law should be enacted to regulate the functioning of political parties, ensuring they operate transparently, democratically, and with accountability.
|
43 videos|268 docs|39 tests
|




















