Worksheet Solutions: Federalism | Political Science Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Match the Column |

|
| Assertion and Reason Based |

|
| Very Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Short Answers Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: Federalism is a system of government that divides power between a central authority and ____________.
Ans: constituent political units
Federalism involves sharing power between a central authority and smaller political units, such as states or provinces.
Q2: In some federal countries, there is a system of ____________ citizenship.
Ans: dual
Dual citizenship means that individuals can hold citizenship in both the central nation and their specific state or region.
Q3: Federalism in Nigeria has faced challenges due to ____________ and disputes over oil resources.
Ans: religious divisions
Religious divisions and conflicts over control of oil resources have been significant sources of contention in Nigeria's federal system.
Q4: The Indian Constitution divides powers into three lists: the Union List, the State List, and the ____________ List.
Ans: Concurrent List
These lists specify which subjects are under the exclusive control of the central government, the state governments, and those on which both can legislate.
Q5: The Governor in India has the power to recommend the dismissal of a ____________ government.
Ans: State
Governors have a role in maintaining the state government's stability and can recommend its dismissal under certain circumstances.
Q6: President's rule in India can be imposed when the State government cannot function according to the provisions of the ____________.
Ans: Constitution
President's rule is imposed when there's a breakdown in the constitutional machinery in a State.
Q7: In Indian federalism, certain States have been granted special provisions due to their unique ____________ and historical backgrounds.
Ans: social
These special provisions are often granted to address the unique cultural, linguistic, or historical characteristics of specific States.
Q8: Jammu and Kashmir's autonomy is granted under ____________ of the Indian Constitution.
Ans: Article 370
Article 370 provides a special status to Jammu and Kashmir and grants it certain autonomy.
Q9: One difference between Jammu and Kashmir and other Indian States is that no ____________ emergency can be declared without the State's concurrence.
Ans: emergency due to internal disturbances
Jammu and Kashmir has unique provisions that require its consent for the imposition of certain types of emergencies.
Q10: The Constitution makers in India believed that a strong central government was necessary to address issues like ____________, illiteracy, and wealth inequality.
Ans: poverty, illiteracy, and wealth inequality
The framers of the Indian Constitution believed that a strong central government was required to address social and economic challenges and ensure national unity.
Match the Column
Q1: Match the terms from Column A with their corresponding descriptions in Column B.
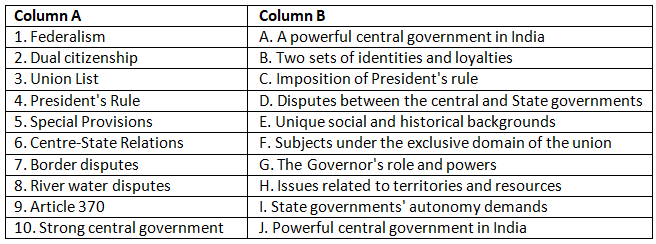 Ans: 1. Federalism - (B) Two sets of identities and loyalties
Ans: 1. Federalism - (B) Two sets of identities and loyalties
Federalism allows individuals to identify both with their region (state) and with the nation as a whole.
2. Dual citizenship - (A) A powerful central government in India
This statement is not an accurate match for dual citizenship. Dual citizenship pertains to individuals' legal status, not the nature of the central government.
3. Union List - (F) Subjects under the exclusive domain of the union
The Union List includes subjects on which the central government has exclusive legislative authority.
4. President's Rule - (C) Imposition of President's rule
President's Rule is the provision allowing the central government to take control of a state's governance under specific circumstances.
5. Special Provisions - (E) Unique social and historical backgrounds
Special provisions are granted to states with distinct social, cultural, or historical characteristics.
6. Centre-State Relations - (G) The Governor's role and powers
Centre-State relations encompass various aspects, including the role and powers of the Governor.
7. Border disputes - (H) Issues related to territories and resources
Border disputes often revolve around territorial claims and resource allocation between neighboring states.
8. River water disputes - (I) State governments' autonomy demands
River water disputes often become contentious as they affect state autonomy and control over essential resources.
9. Article 370 - (J) Powerful central government in India
Article 370 addresses the special status of Jammu and Kashmir and its relationship with the central government.
10. Strong central government - (D) Disputes between the central and State governments
Disputes between the central and state governments can arise in a federal system, but this option doesn't directly match the term "strong central government."
Assertion and Reason Based
Q1: Assertion: Federalism in Nigeria faced challenges due to conflicts among different ethnic groups.
Reason: The Yoruba, Ibo, and Hausa-Fulani groups sought to expand their power into other regions.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but Reason is true.
Ans: (a)
The assertion correctly identifies that conflicts among different ethnic groups have posed challenges to federalism in Nigeria. The reason also provides a correct explanation, as the expansion of power by these dominant ethnic groups into other regions has often led to tension and instability in the country.
Q2: Assertion: The Indian Constitution centralizes economic and financial powers in the hands of the central government.
Reason: This centralization was considered necessary due to India's vast size, diversity, and social issues.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but Reason is true.
Ans: (a)
The assertion correctly states that economic and financial powers are centralized in the Indian Constitution. The reason is also valid because centralization is indeed a response to India's vast size, diversity, and the need to address socio-economic disparities and challenges across the country.
Q3: Assertion: President's rule can be imposed in a state without the testing of its majority.
Reason: The Constitution grants the central government the authority to dismiss a state government at its discretion.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but Reason is true.
Ans: (a)
The assertion is accurate as President's rule can indeed be imposed without testing the majority in a state. The reason provides the correct explanation, as the Constitution grants the central government the discretionary authority to dismiss a state government when it deems necessary, even if the state government enjoys a majority.
Q4: Assertion: Special provisions in the Indian Constitution primarily apply to north-eastern states.
Reason: These states have a sizeable indigenous tribal population with distinct history and culture.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but Reason is true.
Ans: (a)
The assertion correctly identifies that special provisions primarily apply to north-eastern states. The reason is also correct, as these states have significant indigenous tribal populations with unique histories and cultures, necessitating special protection and autonomy measures.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: What is the role of a Governor in Indian federalism?
Ans: The role of a Governor in Indian federalism is to act as the ceremonial head of a state and represent the President of India at the state level.
Q2: Why do border disputes between States often occur in federal systems?
Ans: Border disputes between states often occur in federal systems due to ambiguities in the distribution of powers and resources, leading to conflicting claims.
Q3: What is the primary reason for President's rule in India?
Ans: The primary reason for President's rule in India is the breakdown of constitutional machinery in a state, usually due to political instability or failure of the state government to function.
Q4: Name one State in India with special provisions and explain the reason behind it.
Ans: Jammu and Kashmir is a state in India with special provisions under Article 370, granting it a high degree of autonomy in various matters, except defense, foreign affairs, and communications. This provision aimed to respect the region's unique circumstances and history.
Q5: What is the significance of the Union List in the Indian Constitution?
Ans: The Union List in the Indian Constitution contains subjects on which only the central government can make laws, ensuring uniformity and national cohesion in matters like defense, foreign affairs, and currency.
Q6: How does dual citizenship work in some federal countries?
Ans: Dual citizenship in some federal countries allows citizens to hold both national and subnational (state or provincial) citizenship, subject to varying rules and conditions.
Q7: What challenges has federalism in Nigeria faced?
Ans: Federalism in Nigeria has faced challenges such as ethnic and regional tensions, resource distribution disputes, and a history of military interventions in governance.
Q8: Explain the importance of culture and ideology in the functioning of federations.
Ans: Culture and ideology play a vital role in federations as they influence political preferences, policy-making, and regional identity, impacting the functioning of the system.
Q9: What is the significance of the Concurrent List in the Indian Constitution?
Ans: The Concurrent List in the Indian Constitution contains subjects on which both the central and state governments can legislate, providing flexibility and cooperation in areas like education and health.
Q10: How do financial autonomy demands relate to Indian federalism?
Ans: Financial autonomy demands in Indian federalism relate to states seeking greater control over their finances, including revenue generation and expenditure management, to reduce dependence on central funds.
Short Answers Type Questions
Q1: Explain the historical background of federalism in Nigeria and its impact on the country.
Ans: Nigeria's federalism has its roots in British colonial administration. It has contributed to both unity and division in the country due to its diverse ethnic and regional composition.
Q2: Describe the division of powers between the central government and State governments in Indian federalism.
Ans: Powers in Indian federalism are divided into Union, State, and Concurrent Lists. The central government handles Union List subjects, while state governments manage State List subjects, with Concurrent List subjects being jointly managed.
Q3: Discuss the challenges and conflicts associated with border disputes in Indian federalism.
Ans: Border disputes in India result from unclear territorial demarcations and resource competition, leading to inter-state tensions. Resolution often requires central government intervention or judicial decisions.
Q4: Elaborate on the role of special provisions in the Indian Constitution and provide examples.
Ans: Special provisions in the Indian Constitution accommodate unique circumstances in certain states or regions. For example, Article 370 granted special autonomy to Jammu and Kashmir, but it was abrogated in 2019, leading to significant controversy.
Q5: Analyze the power and role of Governors in Indian federalism and their impact on State governments.
Ans: Governors in India serve as the ceremonial head of a state and represent the President. They play a role in the state's administration by issuing orders and maintaining constitutional stability.
Q6: What are the reasons behind demands for greater autonomy by State governments in India?
Ans: State governments seek greater autonomy to control their finances, resources, and governance. This allows them to address local needs and reduce dependence on central funds.
Q7: Discuss the significance of a strong central government in Indian federalism and the reasoning behind it.
Ans: A strong central government is essential to maintain national unity, oversee critical subjects like defense and foreign affairs, and ensure uniformity in the country's legal and administrative framework.
Q8: Explain the concept of President's rule in India, its implications, and the controversies surrounding it.
Ans: President's rule is imposed when the constitutional machinery in a state breaks down due to political instability or governance failure. It allows the central government to take over the state's administration temporarily. Controversies surround its use, often raising questions of federalism and state sovereignty.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: Discuss the historical background and evolution of federalism in Nigeria. How has this impacted the country's stability?
Ans: Federalism in Nigeria evolved as a response to the country's diverse ethnic and regional composition, dating back to British colonial rule. The federal structure was intended to accommodate these differences and promote unity. However, it has also been a source of tension, with power struggles, ethnic rivalries, and resource disputes often leading to instability and even civil conflicts, as seen in the Nigerian Civil War (1967-1970). The historical background of federalism in Nigeria has both contributed to the country's stability and posed significant challenges to its unity.
Q2: Compare and contrast the division of powers and responsibilities between the central government and State governments in Indian federalism. Highlight key differences.
Ans: In Indian federalism, powers and responsibilities are divided between the central government and state governments as outlined in the Seventh Schedule of the Constitution. The central government handles subjects in the Union List, which includes areas like defense, foreign affairs, and currency. State governments have authority over subjects in the State List, such as police, public health, and agriculture. Concurrent List subjects, such as education and forests, are managed jointly. Key differences include the dominance of the central government in key areas and state autonomy in others, with cooperative efforts required for concurrent subjects.
Q3: Examine the issues surrounding border disputes and river water sharing in Indian federalism. How can these conflicts be effectively resolved?
Ans: Border disputes in India often result from unclear territorial demarcations, historical grievances, and competition for resources. These conflicts create inter-state tensions and hinder efficient governance. River water sharing disputes, like the Cauvery and Krishna river disputes, stem from competition over water resources, leading to legal battles and political conflicts. Effective resolution requires cooperation, negotiations, and possibly the involvement of national institutions.
Q4: Explain the concept of special provisions in the Indian Constitution, focusing on the unique status of Jammu and Kashmir under Article 370. Discuss the implications and controversies related to Article 370.
Ans: Special provisions in the Indian Constitution are designed to accommodate unique circumstances in specific states or regions. Article 370 provided special autonomy to Jammu and Kashmir, allowing the state to have its own constitution and considerable independence in various matters, except defense, foreign affairs, and communications. The abrogation of Article 370 in 2019 was met with controversy, as it ended Jammu and Kashmir's special status. It raised questions about constitutional changes, federalism, and the rights of the region's residents, leading to ongoing debates and tensions in Indian politics.
|
43 videos|201 docs|39 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet Solutions: Federalism - Political Science Class 11 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What is federalism? |  |
| 2. What are the advantages of federalism? |  |
| 3. How does federalism promote democracy? |  |
| 4. What are the challenges of federalism? |  |
| 5. How does federalism impact policy-making? |  |





















