Worksheet Solutions: Local Governments | Political Science Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Match the Column |

|
| Assertion and Reason Based |

|
| Very Short Answers Type Questions |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: Local government is the government closest to the __________.
Ans: people
Local government operates at the grassroots level and directly interacts with the citizens.
Q2: The growth of local government in India started with the formation of __________.
Ans: sabhas
Sabhas were self-governing village communities in ancient India, which laid the foundation for local governance.
Q3: The three-tier structure of Panchayati Raj includes Gram Panchayat, Mandal, and __________.
Ans: Zilla Panchayat
This structure represents the levels of local government in rural areas, with Gram Panchayat at the base, Mandal at the intermediate level, and Zilla Panchayat at the apex.
Q4: The Gram Sabha comprises all the adult members registered as __________ in the Panchayat area.
Ans: voters
Gram Sabha includes all eligible voters and plays a vital role in local decision-making.
Q5: The 73rd Amendment of the Constitution deals with __________ local governments.
Ans: rural
The 73rd Amendment focuses on Panchayati Raj Institutions in rural areas.
Q6: The 74th Amendment of the Constitution deals with __________ local governments.
Ans: urban
The 74th Amendment pertains to municipalities and urban governance.
Q7: The Government of India Act, 1919, established village panchayats in several __________.
Ans: provinces
This Act played a significant role in promoting local self-governance in India.
Q8: __________ subjects were transferred to the Panchayati Raj Institutions as per the 73rd Amendment.
Ans: Twenty-nine
This transfer of subjects from the State list to Panchayati Raj Institutions empowered them to manage various local issues.
Q9: The 74th Amendment includes a 'Twelfth Schedule' related to __________.
Ans: municipalities
The Twelfth Schedule lists subjects that are under the purview of urban local bodies.
Q10: In case of dissolution, fresh elections must be held within __________ months.
Ans: six
This provision ensures that local governance remains continuous, even if there is a dissolution of the governing body.
Match the Column
Q1: Match the provisions of the 73rd Amendment with their descriptions.
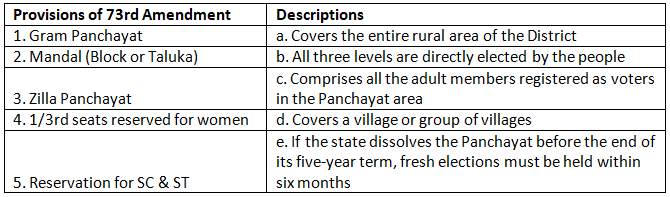 Ans: 1. Gram Panchayat - d. Covers a village or group of villages
Ans: 1. Gram Panchayat - d. Covers a village or group of villages
Gram Panchayat covers a village or a group of villages. It is the basic level of the Panchayati Raj system.
2. Mandal (Block or Taluka) - e. If the state dissolves the Panchayat before the end of its five-year term, fresh elections must be held within six months
The Mandal, also known as the Block or Taluka, covers the entire rural area of the district. It is a larger administrative unit than the Gram Panchayat.
3. Zilla Panchayat - a. Covers the entire rural area of the District
Zilla Panchayat encompasses all the adult members registered as voters in the Panchayat area. It is at the district level and plays a significant role in local governance.
4. 1/3rd seats reserved for women - b. All three levels are directly elected by the people
This provision ensures that at least one-third of the seats in Panchayati Raj institutions are reserved for women. It promotes gender equality and participation in local governance.
5. Reservation for SC & ST - c. Comprises all the adult members registered as voters in the Panchayat area
The amendment also provides for the reservation of seats for Scheduled Castes (SC) and Scheduled Tribes (ST) in Panchayati Raj institutions. This is aimed at ensuring representation and empowerment of these marginalized communities.
Assertion and Reason Based
Q1: Assertion: The 73rd Amendment of the Constitution deals with rural local governments.
Reason: The 73rd Amendment includes provisions for the three-tier Panchayati Raj system.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Ans: (b)
The assertion is true because the 73rd Amendment primarily focuses on rural local governments, while the reason is also true but doesn't directly explain the assertion.
Q2: Assertion: The 74th Amendment of the Constitution focuses on rural local governments.
Reason: The 74th Amendment includes provisions related to the Twelfth Schedule.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Ans: (d)
Both the assertion and reason are incorrect. The 74th Amendment primarily deals with urban local governments and introduces the Twelfth Schedule for municipalities.
Q3: Assertion: The Gram Sabha comprises all the adult members registered as voters in the Panchayat area.
Reason: The Gram Sabha has a limited role and function in local governance.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Ans: (a)
The assertion is true, and the reason is also true because the Gram Sabha does include all eligible voters. The reason correctly explains the assertion.
Q4: Assertion: The 73rd and 74th Amendments aim at strengthening local governments and ensuring uniformity in their structure.
Reason: These amendments gave local governments a constitutional status.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Ans: (a)
Both the assertion and the reason are true, and the reason correctly explains the assertion. These amendments indeed aimed to strengthen local governance and provided constitutional recognition.
Very Short Answers Type Questions
Q1: Why is local government considered essential for democratic decision-making?
Ans: Local government is considered essential for democratic decision-making because it operates at the grassroots level, involving citizens directly in governance, and is closest to their needs.
Q2: What were the self-governing village communities in India called in ancient times?
Ans: In ancient times, self-governing village communities in India were called sabhas.
Q3: Who initiated the creation of elected local self-governing bodies in modern India?
Ans: Elected local self-governing bodies were created in modern India at the initiative of Lord Rippon, the then Viceroy of India.
Q4: What was the primary concern of Jawaharlal Nehru regarding local government?
Ans: Jawaharlal Nehru was concerned that extreme localism could threaten the unity and integration of the nation.
Q5: What are the three tiers of Panchayati Raj as per the 73rd Amendment?
Ans: The three tiers of Panchayati Raj as per the 73rd Amendment are Gram Panchayat, Mandal (Block or Taluka), and Zilla Panchayat.
Q6: What is the significance of reservations in local government institutions?
Ans: Reservations in local government institutions ensure representation for marginalized sections, such as women and SC/ST categories.
Q7: How were subjects transferred to Panchayati Raj Institutions as per the 73rd Amendment?
Ans: Subjects were transferred to Panchayati Raj Institutions as per the 73rd Amendment, as listed in the Eleventh Schedule of the Constitution.
Q8: What is the Twelfth Schedule of the Indian Constitution related to?
Ans: The Twelfth Schedule of the Indian Constitution is related to the functions and responsibilities of urban local bodies.
Q9: When did the 73rd and 74th Amendments come into force?
Ans: The 73rd and 74th Amendments came into force in 1993.
Q10: What was the primary purpose of the 74th Amendment Act?
Ans: The primary purpose of the 74th Amendment Act was to strengthen urban local governments and provide them with constitutional recognition.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Explain the historical development of local government in India.
Ans: The historical development of local government in India can be traced back to ancient times when self-governing village communities or 'Gram Sabhas' existed. However, the modern evolution of local government began during British colonial rule with the introduction of institutions like Municipalities and District Boards. After gaining independence in 1947, India continued to develop its local government structure. The 73rd and 74th Amendments in 1992 marked a significant milestone in decentralizing power to rural and urban local bodies, establishing the Panchayati Raj system and Municipalities, respectively.
Q2: Why did only a few states initially adopt the three-tier Panchayati Raj system?
Ans: Initially, only a few states adopted the three-tier Panchayati Raj system because the decision to implement it was left to the discretion of the state governments. Some states were hesitant due to political, administrative, and financial reasons. They were concerned about relinquishing power to local bodies, while others lacked the resources and administrative capacity to implement the system. Over time, the success stories of the early adopter states encouraged others to follow suit.
Q3: Discuss the provisions of the 73rd Amendment related to reservations.
Ans: The 73rd Amendment introduced provisions related to reservations, including reserving seats for Scheduled Castes (SCs), Scheduled Tribes (STs), and women. It mandates that approximately one-third of the seats be reserved for women in Panchayati Raj institutions, and a proportion of seats should be reserved for SCs and STs based on their population in a particular area.
Q4: What is the significance of the Eleventh Schedule of the Constitution?
Ans: The Eleventh Schedule of the Constitution contains a list of 29 subjects that are under the domain of Panchayati Raj institutions. This schedule outlines the functions and responsibilities of Panchayats, ensuring that they have a clear mandate to govern in these areas, which range from agriculture and rural development to education and social justice.
Q5: Describe the main provisions of the 74th Amendment Act and its similarities to the 73rd Amendment.
Ans: The main provisions of the 74th Amendment Act pertain to urban local governance. Like the 73rd Amendment, it mandates the establishment of Municipalities and delineates their powers and functions. It also includes provisions for reservations, and a Municipal Corporation is the highest body at the city level. The 74th Amendment shares similarities with the 73rd Amendment in terms of decentralization and empowering local governments.
Q6: How did the 73rd and 74th Amendments standardize local government institutions in India?
Ans: The 73rd and 74th Amendments standardized local government institutions in India by providing a common framework for the establishment and functioning of Panchayati Raj institutions and Municipalities in all states. They ensured that a three-tier structure of Panchayats and Municipalities was uniformly adopted across the country. These amendments also provided constitutional status and clear guidelines for the organization and functioning of local governments, promoting decentralization and local self-governance.
Q7: Explain the impact of seat reservations for women in local government bodies.
Ans: Seat reservations for women in local government bodies have had a significant impact by enhancing gender representation in decision-making. They have increased the participation of women in local governance and encouraged their active involvement in community development, social welfare, and resource management. This has contributed to a more inclusive and equitable approach to local development, addressing issues that affect women and marginalized communities.
Q8: How have women contributed to local governance and resource management?
Ans: Women have made substantial contributions to local governance and resource management by bringing a unique perspective and focusing on issues such as health, education, sanitation, and women's empowerment. Their participation has led to the formulation of policies and programs that address the specific needs of women and marginalized groups. Moreover, women's involvement has resulted in better utilization of resources and improved service delivery in areas like healthcare and education, leading to overall development in local communities.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: Discuss the advantages of local government and its importance in India's democratic system.
Ans: Advantages of Local Government and its Importance in India's Democratic System:
Local government plays a vital role in India's democratic system and offers several advantages:
- Proximity to the People: Local government is the government closest to the people, making it convenient for citizens to access authorities and resolve issues quickly and cost-effectively.
- Involvement in Decision Making: It allows common citizens to participate in decision-making concerning their lives, needs, and development. Local knowledge and local interests are essential for democratic decision-making.
- Effective in Protecting Local Interests: Local government can effectively protect the local interests of the people by addressing region-specific concerns and issues.
- Efficient and People-Friendly Administration: It ensures more efficient and people-friendly administration as it can cater to local needs and challenges effectively.
- Grassroots Development: Local governments contribute to grassroots development by addressing issues related to agriculture, education, healthcare, infrastructure, and more.
- Fostering Civic Engagement: They encourage civic engagement and political awareness by involving citizens in governance, which is crucial for the health of any democracy.
- Decentralization and Empowerment: Local government promotes decentralization of power and empowers local leaders to take charge of their communities' development.
- Faster Response to Crises: In times of crises like natural disasters or public health emergencies, local governments can respond more swiftly due to their proximity to the affected areas.
The importance of local government in India's democratic system is immense. It fosters democratic values by involving citizens in governance, ensures accountability, and creates a sense of ownership and responsibility among people. It also aligns with the principle of subsidiarity, which suggests that matters should be handled by the smallest, lowest, or least-centralized competent authority. Local government exemplifies this principle and is instrumental in the success of Indian democracy.
Q2: Examine the reasons why local governments and Panchayats did not receive adequate importance in the Constitution initially.
Ans: Reasons for the Delay in Adopting the Three-Tier Panchayati Raj System:
The adoption of the three-tier Panchayati Raj system in India faced delays due to various reasons:
- Limited Powers and Functions: Initially, local bodies did not have enough powers and functions to effectively address local development. They were highly dependent on State and Central governments for financial assistance, which hindered their autonomy and effectiveness.
- Perception of Unnecessity: Some states did not consider it necessary to establish elected local bodies. They believed that government officers could manage local administration more efficiently.
- Indirect Elections: In many states, local bodies had indirect elections, which were perceived as less democratic and less representative of the people's will.
- Election Postponement: Elections to local bodies were often postponed, further delaying the establishment of elected local governments.
- Strong Unitary Inclination: The turmoil due to the Partition of India resulted in a strong unitary inclination in the Constitution, which initially reduced the emphasis on local governance.
- Concerns About Factionalism: Dr. B.R. Ambedkar was concerned about the factional and caste-ridden nature of rural society, which he believed could undermine the noble purpose of local government.
Overcoming these challenges required a shift in perspective, leading to the adoption of constitutional amendments like the 73rd Amendment. These amendments aimed to empower local governments, ensure their constitutional status, and promote decentralization, ultimately enhancing the effectiveness of the three-tier Panchayati Raj system.
Q3: Analyze the reasons for the delay in adopting the three-tier Panchayati Raj system in some states and the challenges faced.
Ans: Impact of Seat Reservations for Women in Local Government Bodies:
The reservation of seats for women in local government bodies, as mandated by the 73rd and 74th Amendments, has had a significant impact on India's governance landscape:
- Enhanced Representation: Reservations have increased women's representation in local bodies, ensuring that their voices are heard in decision-making processes.
- Empowerment of Women: Women who were previously marginalized or confined to traditional roles gained empowerment and self-confidence through political participation.
- Fresh Perspective: Women brought a fresh perspective and a more empathetic outlook to discussions in local bodies. They often prioritize issues like healthcare, education, and social welfare.
- Independent Decision-Making: Many women in local government became independent decision-makers rather than being proxies for male family members who sponsored their election.
- Improved Governance: The participation of women has led to more inclusive and comprehensive governance. They focus on issues that affect women and children, thus contributing to overall welfare.
- Change in Social Norms: Women's participation has challenged traditional social norms and stereotypes, inspiring others to break free from gender constraints.
- Enhanced Resource Management: Women's involvement in local governance has improved resource management, particularly in areas related to social welfare, health, and education.
- Accountability and Transparency: The increased participation of women has led to greater accountability and transparency in local governance.
- Social Development: With more women in power, local bodies have been more responsive to the social development needs of their communities.
- Inspiration for Future Generations: Women in local government serve as role models for future generations, encouraging more women to participate in politics.
The reservation of seats for women in local government bodies has not only improved women's representation but has also enriched the quality of governance by diversifying perspectives and priorities. It has been a significant step toward gender equality and the overall development of local communities.
Q4: Evaluate the impact of the 73rd and 74th Amendments on the empowerment of women in local government institutions in India.
Ans: The 73rd and 74th Amendments to the Indian Constitution, which came into force in 1993, mandated the reservation of seats for women in local government institutions, both in rural Panchayati Raj bodies and urban Nagarpalikas. These amendments aimed to empower women, promote gender equality, and enhance their participation in the decision-making process. The impact of these amendments on the empowerment of women in local government institutions in India has been substantial.
- Increased Representation: The most immediate and visible impact has been the increase in the number of women participating in local governance. The reservation of one-third of the seats for women at all levels (General, SC, ST, OBC) ensured their presence in decision-making bodies.
- Enhanced Participation: These amendments encouraged women to actively engage in local politics. Many women who were previously on the periphery of political activity have become active participants and leaders in their communities.
- Political Empowerment: Women who assumed leadership roles in local government gained political empowerment. They have had the opportunity to influence policies, advocate for gender-sensitive initiatives, and exercise authority over resources.
- Improved Social Welfare: The participation of women in local bodies has led to a greater focus on issues related to social welfare, healthcare, education, and child development. They have often advocated for projects and policies that directly benefit women and children.
- Resource Allocation: Women representatives have played a crucial role in allocating resources for gender-specific programs, ensuring that women and children receive equitable support in areas such as health, education, and economic development.
- Gender-Sensitive Decision Making: The presence of women in local bodies has brought a gender-sensitive approach to governance. They are more attuned to the needs and challenges faced by women, which has led to more inclusive and comprehensive decision-making.
- Accountability and Transparency: The inclusion of women has resulted in increased accountability and transparency in local governance. Their active participation has ensured that the actions and decisions of local bodies are scrutinized and made more accessible to the public.
- Challenging Stereotypes: Women leaders in local government have challenged traditional stereotypes and norms. Their presence has acted as a catalyst for social change by demonstrating that women can effectively lead and govern.
- Increased Civic Awareness: The involvement of women has also led to a rise in civic awareness among women in rural and urban areas. It has encouraged other women to actively participate in the political process.
- Role Models: Women in local government have become role models for future generations, inspiring young girls to aspire to leadership positions and engage in politics. Their success stories have far-reaching effects on women's aspirations and ambitions.
In conclusion, the 73rd and 74th Amendments have had a profound and positive impact on the empowerment of women in local government institutions in India. These women are not only actively participating in decision-making but are also advocating for gender-sensitive policies and social welfare programs. Their presence has challenged traditional gender roles and stereotypes and has significantly contributed to the overall development of local communities. These amendments have not only increased the quantity of women in local governance but have also improved the quality of governance through diverse perspectives and priorities.
|
43 videos|223 docs|39 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet Solutions: Local Governments - Political Science Class 11 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What is the role of local governments in humanities/arts? |  |
| 2. How do local governments support local artists? |  |
| 3. What are the benefits of local government support for humanities/arts? |  |
| 4. How can individuals engage with local government initiatives in humanities/arts? |  |
| 5. How can local governments ensure equal access to humanities/arts for all community members? |  |
















