Worksheet: Social Justice | Political Science Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Match the Column |

|
| Assertion and Reason Based |

|
| Very Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: The concept of justice has been interpreted differently across various __________ and traditions.
Q2: In ancient India, justice was linked to __________ and the responsibility of maintaining a just social order was placed on the shoulders of __________.
Q3: According to Immanuel Kant, every human being has inherent __________, and justice demands that all individuals have equal opportunities to develop their abilities and pursue their chosen __________.
Q4: Discrimination on the basis of class, caste, race, or gender violates the principle of treating equals __________.
Q5: Proportionate justice considers factors such as the level of __________, skills required, and potential risks involved in the work while distributing rewards.
Q6: The principle of taking into account special needs of individuals extends the principle of treating equals equally to accommodate individuals with special __________ or __________.
Q7: Social justice involves the fair distribution of goods and services within a society, as well as between __________.
Q8: John Rawls suggests that rational thinking, rather than __________, could lead to fair and impartial judgment regarding the distribution of benefits and burdens in a society.
Q9: Social justice does not necessitate absolute equality in the way people __________.
Q10: Supporters of free markets believe that unregulated markets ensure a fair distribution of benefits and __________ in society.
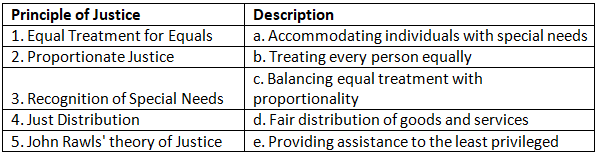
Match the Column
Q1: Match the principles of justice with their descriptions.
Assertion and Reason Based
Q1: Assertion: Social justice necessitates absolute equality in the way people live.
Reason: Different methods have been developed to determine people's basic necessities.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Q2: Assertion: John Rawls' theory of justice involves thinking under a "veil of ignorance."
Reason: Rawls believes that rational thinking, rather than morality, leads to fair judgment of benefit distribution.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Q3: Assertion: Free markets ensure a fair distribution of benefits and responsibilities in society.
Reason: Supporters of free markets believe in complete state intervention to guarantee a basic minimum standard of living.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: What is the responsibility of a democratic government towards its citizens?
Q2: Define the principle of treating equals equally.
Q3: Explain the principle of proportionate justice.
Q4: Give an example of a situation where recognizing special needs is important.
Q5: What does social justice entail?
Q6: What is the "veil of ignorance" theory put forward by John Rawls?
Q7: What are some key rights granted in liberal democracies to ensure equal opportunities for all?
Q8: What is one of the responsibilities of a democratic government regarding people's basic necessities?
Q9: Why do some advocates of free markets support state intervention?
Q10: Why are disagreements regarding issues of distribution and justice beneficial in a democratic society?
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Explain how the principle of equal treatment for equals is related to the concept of justice.
Q2: Describe John Rawls' theory of justice and the idea of thinking under a "veil of ignorance."
Q3: Discuss the role of social justice in ensuring a fair distribution of resources within a society.
Q4: What are some key principles of justice, and how do they contribute to a just distribution of resources and opportunities?
Q5: Compare and contrast the arguments for free markets and state intervention in achieving social justice.
Q6: How do governments and international organizations determine people's basic necessities in the context of social justice?
Q7: Provide an example of a policy or program in India that aims to assist marginalized sections of the population.
Q8: Why is it important for a democratic society to engage in political negotiations to resolve disagreements related to distribution and justice?
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: Explain the historical perspectives on justice in ancient India, China, and Greece, and how they have influenced contemporary notions of justice.
Q2: Discuss the concept of social justice and its significance in addressing economic and social inequalities within a society. Provide examples to illustrate the need for social justice.
Q3: Explore John Rawls' theory of justice in detail, including the concept of thinking under a "veil of ignorance." How does this theory contribute to a fair and just society?
Q4: Analyze the debate between proponents of free markets and state intervention in achieving social justice. What are the arguments on both sides, and how can these differing perspectives be reconciled in a democratic society?
You can access the solutions to this worksheet here.
|
43 videos|268 docs|39 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet: Social Justice - Political Science Class 11 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What is the significance of social justice in today's society? |  |
| 2. How can individuals contribute to social justice efforts in their communities? |  |
| 3. What are some common misconceptions about social justice? |  |
| 4. How does social justice relate to human rights? |  |
| 5. What are some key movements or figures in the history of social justice? |  |















