Worksheet Solutions: Social Justice | Political Science Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Match the Column |

|
| Assertion and Reason Based |

|
| Very Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: The concept of justice has been interpreted differently across various __________ and traditions.
Ans: cultures
The text mentions that the notion of justice has been interpreted differently across various cultures and traditions.
Q2: In ancient India, justice was linked to __________ and the responsibility of maintaining a just social order was placed on the shoulders of __________.
Ans: dharma, kings
The text highlights that in ancient India, justice was associated with the concept of dharma, and kings were responsible for upholding it.
Q3: According to Immanuel Kant, every human being has inherent __________, and justice demands that all individuals have equal opportunities to develop their abilities and pursue their chosen __________.
Ans: objectives
Immanuel Kant's view is summarized in the text, emphasizing that justice mandates equal opportunities for individuals to pursue their objectives.
Q4: Discrimination on the basis of class, caste, race, or gender violates the principle of treating equals __________.
Ans: equally
The principle of treating equals equally implies that individuals should not be discriminated against based on factors like class, caste, race, or gender.
Q5: Proportionate justice considers factors such as the level of __________, skills required, and potential risks involved in the work while distributing rewards.
Ans: effort
The text describes proportionate justice as a principle that takes into account various factors, including effort, skills, and risks, when distributing rewards.
Q6: The principle of taking into account special needs of individuals extends the principle of treating equals equally to accommodate individuals with special __________ or __________.
Ans: needs or disabilities
This principle acknowledges the need to accommodate individuals with special needs or disabilities, broadening the concept of treating equals equally.
Q7: Social justice involves the fair distribution of goods and services within a society, as well as between __________.
Ans: nations
Social justice encompasses both the distribution of resources within a society and the distribution between nations.
Q8: John Rawls suggests that rational thinking, rather than __________, could lead to fair and impartial judgment regarding the distribution of benefits and burdens in a society.
Ans: morality
John Rawls emphasizes rational thinking rather than morality as the basis for achieving fair and impartial distribution in society.
Q9: Social justice does not necessitate absolute equality in the way people __________.
Ans: live
The text clarifies that social justice doesn't require everyone to live in absolute equality.
Q10: Supporters of free markets believe that unregulated markets ensure a fair distribution of benefits and __________ in society.
Ans: responsibilities
The text mentions that supporters of free markets believe that unregulated markets can ensure a fair distribution of benefits and responsibilities.
Match the Column
Q1: Match the principles of justice with their descriptions.
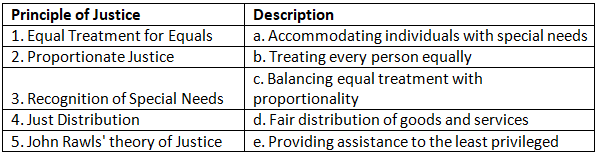 Ans: 1. Equal Treatment for Equals - b. Treating every person equally
Ans: 1. Equal Treatment for Equals - b. Treating every person equally
This principle emphasizes treating every person equally.
2. Proportionate Justice - c. Balancing equal treatment with proportionality
Proportionate justice involves balancing equal treatment with proportionality based on factors like effort and skills.
3. Recognition of Special Needs - a. Accommodating individuals with special needs
This principle acknowledges the need to accommodate individuals with special needs.
4. Just Distribution - d. Fair distribution of goods and services
Just distribution involves the fair allocation of goods and services within a society.
John Rawls' theory of Justice - e. Providing assistance to the least privileged
John Rawls' theory of justice suggests providing assistance to the least privileged in society.
Assertion and Reason Based
Q1: Assertion: Social justice necessitates absolute equality in the way people live.
Reason: Different methods have been developed to determine people's basic necessities.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Ans: (b)
The assertion that "Social justice necessitates absolute equality in the way people live" is not entirely accurate. Social justice aims for fairness and equal opportunities but does not necessarily require absolute equality in the way people live. The reason, on the other hand, is true. Different methods have been developed to determine people's basic necessities, which are used to address economic and social inequalities. However, the reason does not fully explain the assertion, so the correct answer is (b).
Q2: Assertion: John Rawls' theory of justice involves thinking under a "veil of ignorance."
Reason: Rawls believes that rational thinking, rather than morality, leads to fair judgment of benefit distribution.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Ans: (a)
Both the assertion and the reason are correct, and the reason correctly explains the assertion. John Rawls' theory indeed involves the concept of thinking under a "veil of ignorance," where individuals make decisions about societal organization without knowing their own position. Rawls emphasizes that rational thinking under this veil of ignorance leads to fair and impartial judgments regarding the distribution of benefits and burdens in society.
Q3: Assertion: Free markets ensure a fair distribution of benefits and responsibilities in society.
Reason: Supporters of free markets believe in complete state intervention to guarantee a basic minimum standard of living.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Ans: (c)
The assertion that "Free markets ensure a fair distribution of benefits and responsibilities in society" is not entirely accurate. Free markets may not guarantee a fair distribution of benefits and responsibilities, as they often favor those who are already privileged. The reason is also not entirely accurate because supporters of free markets typically do not believe in complete state intervention but may accept some state intervention to ensure a basic minimum standard of living. Therefore, both the assertion and the reason are partially true, and they do not provide a clear explanation of each other, making option (c) the correct choice.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: What is the responsibility of a democratic government towards its citizens?
Ans: The responsibility of a democratic government towards its citizens is providing citizens with their basic needs, like healthcare, education, and safety. This ensures the well-being of the population.
Q2: Define the principle of treating equals equally.
Ans: The principle of treating equals equally means that every individual, regardless of factors like race or gender, should receive equal treatment and opportunities.
Q3: Explain the principle of proportionate justice.
Ans: Proportionate justice considers factors like effort, skills, and risks in the distribution of rewards, ensuring fairness in outcomes.
Q4: Give an example of a situation where recognizing special needs is important.
Ans: Special needs include accommodating individuals with unique requirements, such as those with physical disabilities, to provide equal opportunities.
Q5: What does social justice entail?
Ans: Social justice entails the fair distribution of resources, opportunities, and rights to achieve equity in society.
Q6: What is the "veil of ignorance" theory put forward by John Rawls?
Ans: The "veil of ignorance" theory by John Rawls is a situation where people have no knowledge of their position or status in society, which helps in making impartial decisions.
Q7: What are some key rights granted in liberal democracies to ensure equal opportunities for all?
Ans: Civil rights, political rights, and social rights are key rights granted in liberal democracies to ensure equal opportunities for all citizens.
Q8: What is one of the responsibilities of a democratic government regarding people's basic necessities?
Ans: One of the responsibilities of a democratic government regarding people's basic necessities is to ensure access to healthcare, education, and basic living conditions for all citizens.
Q9: Why do some advocates of free markets support state intervention?
Ans: Some advocates of free markets support state intervention to guarantee a basic minimum standard of living, ensuring fair competition for all.
Q10: Why are disagreements regarding issues of distribution and justice beneficial in a democratic society?
Ans: Politics in a democratic society is about negotiating disagreements about issues of distribution and justice through debate and discussion.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Explain how the principle of equal treatment for equals is related to the concept of justice.
Ans: The principle of equal treatment for equals is related to the concept of justice because it emphasizes that individuals who share common characteristics as human beings should be treated equally. This principle ensures that people are not discriminated against based on factors like race, caste, or gender, contributing to a just society.
Q2: Describe John Rawls' theory of justice and the idea of thinking under a "veil of ignorance."
Ans: John Rawls' theory of justice involves thinking under a "veil of ignorance," where individuals make decisions about society without knowing their own position. This approach is helpful for those born into disadvantaged sections of society because it ensures impartial decision-making, benefiting even the least privileged. It encourages people to make choices that they believe are in their own interest, which leads to a fair and impartial society.
Q3: Discuss the role of social justice in ensuring a fair distribution of resources within a society.
Ans: Social justice plays a crucial role in ensuring a fair distribution of resources within a society. It requires not only equal treatment under the law and policies but also a basic equality of life conditions and opportunities. Disagreements about resource distribution and access to education and jobs can lead to strong opinions and even violence. John Rawls' theory supports the idea that assistance should be provided to the least privileged members of society to achieve social justice.
Q4: What are some key principles of justice, and how do they contribute to a just distribution of resources and opportunities?
Ans: Key principles of justice include equal treatment for equals, proportionate justice, and recognition of special needs. Equal treatment ensures fairness by treating people with common characteristics equally. Proportionate justice balances equal treatment with considering effort, skills, and risks in distributing rewards. Recognition of special needs extends equal treatment to accommodate individuals with unique requirements, such as those with disabilities. These principles contribute to a just distribution of resources and opportunities by ensuring fairness and addressing individual needs.
Q5: Compare and contrast the arguments for free markets and state intervention in achieving social justice.
Ans: The debate between free markets and state intervention in achieving social justice is multifaceted. Supporters of free markets argue that unregulated markets efficiently distribute benefits, offering choices and high-quality services. However, they can be criticized for favoring the already privileged, potentially leading to inequalities. State intervention, on the other hand, ensures basic living standards for all, promoting fairness. However, the cost of such services may be high, making them inaccessible to the poor.
Q6: How do governments and international organizations determine people's basic necessities in the context of social justice?
Ans: Governments and international organizations determine people's basic necessities in the context of social justice through various methods, including assessments, data analysis, and policy development. They often set standards for essentials such as healthcare, education, and living conditions based on the best available research and expert recommendations. For instance, organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) establish guidelines for healthcare access, while governments may develop poverty lines or minimum wage standards to ensure basic economic well-being.
Q7: Provide an example of a policy or program in India that aims to assist marginalized sections of the population.
Ans: An example of a policy or program in India aimed at assisting marginalized sections of the population is the "Reservation System." The reservation system in India is designed to provide opportunities for individuals from historically disadvantaged groups, including Scheduled Castes (SC), Scheduled Tribes (ST), and Other Backward Classes (OBC), in education and employment. These reservations involve setting aside a certain percentage of seats in educational institutions, government jobs, and legislative bodies for these groups.
Q8: Why is it important for a democratic society to engage in political negotiations to resolve disagreements related to distribution and justice?
Ans: It is crucial for a democratic society to engage in political negotiations to resolve disagreements related to distribution and justice for several reasons. Firstly, democratic societies are diverse, with varying interests, perspectives, and needs. Political negotiations provide a platform for different groups to voice their concerns and interests, ensuring that a wide range of views is considered.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: Explain the historical perspectives on justice in ancient India, China, and Greece, and how they have influenced contemporary notions of justice.
Ans: In ancient India, China, and Greece, justice was interpreted differently and has influenced contemporary notions of justice. In India, justice was linked to dharma, where the responsibility of maintaining a just social order rested with kings. In China, Confucius emphasized that rulers should uphold justice by punishing wrongdoers and rewarding the virtuous. In Greece, Plato explored justice in "The Republic," discussing the concept of justice and how it pertains to individuals and society. These historical perspectives influenced contemporary justice concepts, emphasizing the importance of fairness, rule of law, and moral principles in achieving justice.
Q2: Discuss the concept of social justice and its significance in addressing economic and social inequalities within a society. Provide examples to illustrate the need for social justice.
Ans: Social justice involves the fair distribution of goods and services within a society, addressing economic and social inequalities. It seeks to ensure equal treatment under the law and equal opportunities for all citizens. For example, it may require redistributing resources to bridge economic disparities and providing equal access to education and jobs. The significance of social justice lies in fostering an equitable, inclusive, and harmonious society. It prevents marginalization, reduces social tensions, and promotes overall well-being. Without social justice, societies can face divisions, conflicts, and a lack of basic human rights.
Q3: Explore John Rawls' theory of justice in detail, including the concept of thinking under a "veil of ignorance." How does this theory contribute to a fair and just society?
Ans: John Rawls' theory of justice involves imagining a society where individuals make decisions behind a "veil of ignorance." They don't know their own position or characteristics in that society, making decisions impartial. Rawls argues that in such a situation, people would act in their own interest but also consider the interests of the least privileged because they could be in that position. This rational approach leads to fair and just societal arrangements. While it may be difficult to imagine oneself under a veil of ignorance, Rawls believes that rational thinking, rather than morality, can guide people to make fair decisions. This theory aims to ensure fairness and equity, particularly for the least advantaged.
Q4: Analyze the debate between proponents of free markets and state intervention in achieving social justice. What are the arguments on both sides, and how can these differing perspectives be reconciled in a democratic society?
Ans: The debate between free markets and state intervention in achieving social justice is complex. Supporters of free markets argue that unregulated markets can distribute benefits efficiently, offering choices and high-quality services. However, it's often criticized for favoring those already privileged and may lead to inequalities. State intervention, on the other hand, can ensure basic living standards for all, promoting fairness. The cost of such services might be high, making them inaccessible to the poor. The resolution lies in finding a balance. Many now support regulated markets, ensuring a minimum standard of living, so everyone can compete on equal terms. In a democratic society, these debates are essential as they encourage diverse perspectives and rational discussions to address complex issues of justice and distribution.
|
43 videos|268 docs|39 tests
|




















