Worksheet Solutions: Rights | Political Science Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Match the Column |

|
| Assertion and Reason Based |

|
| Very Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: Rights are legal, social, or ethical principles of ______ or entitlement.
Ans: freedom
Rights encompass the concept of freedom and entitlement, allowing individuals to exercise certain privileges or protections.
Q2: According to political theorists in the 17th and 18th centuries, rights are derived from ______ law.
Ans: natural
Natural law is a foundational concept in early political theory, suggesting that rights are inherent in human beings and not granted by any specific authority.
Q3: The three natural rights identified by early political theorists are the right to life, right to liberty, and right to ______.
Ans: property
These three rights are considered the foundational natural rights from which other rights are derived.
Q4: The term "human rights" has become more popular than "natural rights" because of its ______ acceptability.
Ans: radical
The idea of natural law, which underpins natural rights, is often seen as radical in modern society, leading to the preference for the term "human rights."
Q5: Rights are necessary for leading a life of ______ and dignity.
Ans: respect
Rights are essential for ensuring that individuals are treated with respect and dignity and have access to basic freedoms and entitlements.
Q6: A bill of rights is a list of a country's most important rights granted to its ______.
Ans: citizens
A bill of rights outlines the fundamental rights granted to the citizens of a country, often found in a constitution.
Q7: Economic rights encompass basic needs such as food, shelter, clothing, and ______.
Ans: health
Economic rights include the right to access basic necessities, including healthcare, to ensure a decent standard of living.
Q8: Cultural rights aim at ensuring the enjoyment of culture and its components in conditions of ______, human dignity, and non-discrimination.
Ans: equality
Cultural rights focus on ensuring that all individuals and communities can access and participate in their cultural heritage on an equal basis.
Q9: Rights require individuals to respect the rights of ______.
Ans: others
Rights come with the responsibility to respect the rights of others, ensuring that individual freedoms are balanced with the rights of the broader community.
Q10: Citizens must be vigilant about restrictions that may be placed on their rights, as they are the foundation of a ______ society.
Ans: democratic
Citizens must remain watchful of any potential limitations on their rights, as these rights are central to the functioning of a democratic society.
Match the Column
Q1: Match the following types of rights with their descriptions:
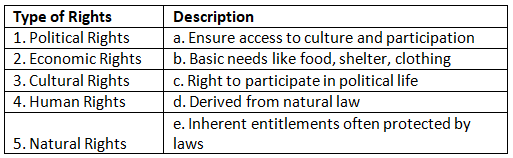 Ans: 1. Political Rights (c) - Right to participate in political life
Ans: 1. Political Rights (c) - Right to participate in political life
Political rights grant individuals the ability to participate in the political processes of a society. This includes the right to vote, stand for office, engage in political activities, and express political opinions. These rights are fundamental to democratic systems, as they ensure active citizenship and people's involvement in the government's decision-making.
2. Economic Rights (b) - Basic needs like food, shelter, clothing
Economic rights focus on providing individuals with access to essential economic resources necessary for a decent quality of life. This encompasses the right to basic needs such as food, shelter, clothing, healthcare, and education. Economic rights aim to address social and economic inequalities.
3. Cultural Rights (a) - Ensure access to culture and participation
Cultural rights safeguard the right of individuals and communities to engage in their cultural practices, preserve their cultural heritage, and actively participate in cultural life. These rights are vital for the protection of cultural diversity and the promotion of cultural expression.
4. Human Rights (d) - Derived from natural law
Human rights are considered to be inherent entitlements that all individuals possess simply because they are human beings. They are not reliant on specific legal systems or governments but are viewed as universal and inalienable. The concept of human rights is rooted in the principles of natural law.
5. Natural Rights (e) - Inherent entitlements often protected by laws
Natural rights are fundamental entitlements that individuals are believed to inherently possess, often grounded in moral or philosophical principles. These rights are commonly acknowledged and protected by legal systems, becoming integral parts of legal frameworks that ensure individual freedoms and rights.
Assertion and Reason Based
Q1: Assertion: Human rights are more commonly used today than natural rights.
Reason: The idea of natural law appears radical and unacceptable in modern society.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct.
(b) Assertion is correct, but the Reason is not.
(c) Assertion is not correct, but the Reason is.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
Ans: (a)
Human rights have gained prominence as they are seen as more acceptable in contemporary society compared to the radical concept of natural law.
Q2: Assertion: Economic rights include the right to participate in political life.
Reason: Economic rights are essential for leading a life of respect and dignity.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct.
(b) Assertion is correct, but the Reason is not.
(c) Assertion is not correct, but the Reason is.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
Ans: (b)
Economic rights focus on basic needs, while political rights are related to political participation.
Q3: Assertion: Rights spell out what the government must do but not what it must avoid.
Reason: Legal recognition is the basis for asserting rights.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct.
(b) Assertion is correct, but the Reason is not.
(c) Assertion is not correct, but the Reason is.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
Ans: (c)
Rights specify both government actions and restrictions, and legal recognition is important but not the sole basis for asserting rights.
Q4: Assertion: Rights require individuals to respect the rights of others.
Reason: Balancing conflicting rights is not a requirement in a democratic society.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct.
(b) Assertion is correct, but the Reason is not.
(c) Assertion is not correct, but the Reason is.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
Ans: (b)
Rights do require individuals to respect the rights of others, and balancing conflicting rights is often necessary in a democratic society.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: What are rights?
Ans: Rights are legal, social, or ethical principles that grant individuals or groups specific freedoms or entitlements.
Q2: Name three natural rights.
Ans: The three natural rights are the right to life, the right to liberty, and the right to property.
Q3: Why are human rights more popular today than natural rights?
Ans: Human rights are more popular because they are perceived as more acceptable in modern society compared to the radical concept of natural law.
Q4: How do political rights contribute to democracy?
Ans: Political rights allow individuals to participate in the political life of a society, ensuring that governments are accountable to the people and promoting democratic governance.
Q5: Provide an example of an economic right.
Ans: An example of an economic right is the right to access affordable healthcare.
Q6: What do cultural rights aim to ensure?
Ans: Cultural rights aim to ensure that people and communities have access to their cultural heritage and can participate in their chosen culture with equality and dignity.
Q7: What is the basis for asserting rights?
Ans: The basis for asserting rights can include legal recognition, ethical principles, or social norms, depending on the context.
Q8: Give an example of a situation where rights conflict.
Ans: A situation where rights conflict is when an individual's right to freedom of expression clashes with another individual's right to privacy, such as taking unauthorized photos and sharing them online.
Q9: Why is vigilance necessary to protect rights?
Ans: Vigilance is required to protect rights because governments and organizations may attempt to restrict or infringe upon these rights, and constant monitoring ensures that rights are upheld.
Q10: What is the role of rights in a democratic society?
Ans: In a democratic society, rights play a crucial role in protecting individual freedoms, ensuring equality, and holding the government accountable to the people.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Explain the difference between natural rights and human rights.
Ans: Natural rights are considered inherent and derived from natural law, while human rights are more contemporary and encompass a broader range of rights that are often legally protected.
Q2: How do political rights and civil liberties contribute to the democratic system of government?
Ans: Political rights allow citizens to participate in the political process, while civil liberties protect individual freedoms, both of which are essential for democratic governance.
Q3: Describe the concept of a bill of rights and its purpose.
Ans: A bill of rights is a list of fundamental rights granted to citizens in a constitution, aiming to protect these rights from infringement by public officials and private citizens.
Q4: Discuss the importance of economic rights in democratic societies.
Ans: Economic rights, which include access to basic needs like food and shelter, are vital in democratic societies as they ensure a decent standard of living and promote social welfare.
Q5: Provide examples of cultural rights and their significance.
Ans: Cultural rights include the right to education in one's mother tongue and the right to establish cultural institutions, ensuring cultural diversity and preservation.
Q6: Why is it essential for individuals to respect the rights of others?
Ans: Respecting the rights of others is essential to maintain social harmony, prevent conflicts, and ensure that the principles of equality and justice are upheld.
Q7: Give an example of a situation where individuals must balance their rights.
Ans: Individuals may need to balance their right to free expression with another individual's right to privacy, especially in cases involving sharing personal information without consent.
Q8: What are the challenges associated with protecting rights in the name of national security?
Ans: Protecting rights in the name of national security can lead to potential abuses and overreach by governments, impacting individual freedoms and civil liberties.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: Discuss the historical development of the concept of rights, from natural rights to human rights.
Ans: The concept of rights has evolved over time, starting with natural rights derived from natural law and progressing to contemporary human rights recognized globally. This evolution reflects changing societal values and legal frameworks.
Q2: Explain the role of rights and responsibilities in a democratic society, emphasizing their interdependence.
Ans: Rights and responsibilities are intertwined in a democratic society, as rights come with the responsibility to respect the rights of others and contribute to the common good, ensuring social balance.
Q3: Analyze the current global challenges to human rights and how they are addressed.
Ans: Contemporary global challenges to human rights include issues like discrimination, environmental degradation, and digital privacy. These challenges require international cooperation and legal frameworks to address effectively.
Q4: Provide a critical assessment of the limitations and constraints on rights in the name of national security, considering their impact on democratic societies.
Ans: Balancing national security with the protection of individual rights is a complex issue, and it requires careful evaluation of the potential impact on democratic values, freedoms, and civil liberties.
|
43 videos|268 docs|39 tests
|




















