Worksheet: India's External Relations | Political Science Class 12 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Match the Column |

|
| Assertion and Reason Based |

|
| Very Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: India's foreign policy aimed at upholding peace and security through _____________ of all countries.
Q2: The first summit of the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) was held in ____________ in September 1961.
Q3: The Paonchsheel Agreement outlined the "five principles of peaceful coexistence" between India and ____________.
Q4: The India-Pakistan Indus Waters Treaty was signed in ____________.
Q5: India conducted its first nuclear explosion in ____________.
Q6: The Bandung Conference, where NAM was founded, took place in the city of ____________ in 1955.
Q7: The Shimla Agreement was signed between India and ____________ in 1972.
Match the Column
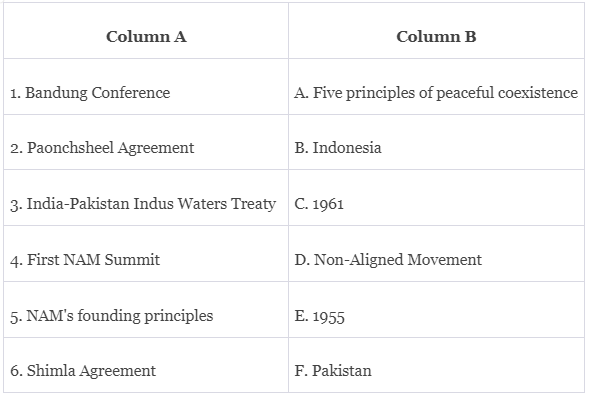
Q1:
Assertion and Reason Based
Q1: Assertion: India refused to sign the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT) of 1968.
Reason: India considered NPT as discriminatory.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but the Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but the Reason is true.
Q2: Assertion: The Bandung Conference in 1955 laid the foundation for the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM).
Reason: NAM was formed to counter the dominance of the superpower blocs led by the US and USSR.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but the Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but the Reason is true.
Q3: Assertion: The Shimla Agreement in 1972 resolved all the issues between India and Pakistan permanently.
Reason: The Shimla Agreement led to peaceful coexistence and normalized relations between the two countries.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but the Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but the Reason is true.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Who was in charge of India's foreign policy from 1946 to 1964?
Q2: When was the Bandung Conference held?
Q3: Name one of the territories over which China has territorial claims in India.
Q4: Which Indian leader gave asylum to the Dalai Lama in 1959?
Q5: Who signed the Shimla Agreement on behalf of Pakistan in 1972?
Q6: What did the Paonchsheel Agreement outline?
Q7: Which Indian state faced armed attacks by Pakistan in 1965?
Q8: Which country hosted the first NAM summit in 1961?
Q9: Who signed the India-Pakistan Indus Waters Treaty in 1960?
Q10: Why did India conduct nuclear tests in 1998?
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Describe India's foreign policy goals after independence.
Q2: How did India handle its relations with the US and the USSR during the Cold War era?
Q3: Explain the significance of the Bandung Conference in 1955.
Q4: What were the consequences of the Sino-Indian conflict in 1962?
Q5: Detail the events leading to the India-Pakistan conflict in 1971.
Q6: Explain India's stance on the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT).
Q7: What were the main principles outlined in the Paonchsheel Agreement of 1954?
Q8: How did the Shimla Agreement in 1972 impact India-Pakistan relations?
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: Explain India's Policy of Non-Alignment during the Cold War era.
Q2: Discuss the Impact of the Sino-Indian Conflict in 1962 on India's Foreign Relations.
Q3: Describe the Factors Leading to the India-Pakistan Conflict in 1971 and Its Aftermath.
Q4: Evaluate India's Nuclear Policy and Its Stance on the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT).
You can access the solutions to this worksheet here.
|
34 videos|305 docs|51 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet: India's External Relations - Political Science Class 12 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What are the key components of India's external relations? |  |
| 2. How does India's foreign policy impact its economy? |  |
| 3. What role does India play in regional organizations like SAARC and ASEAN? |  |
| 4. How has India's relationship with neighboring countries evolved over the years? |  |
| 5. What are the challenges faced by India in its external relations? |  |















