Worksheet: Nationalism | Political Science Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Match the Column |

|
| Assertion and Reason Based |

|
| Very Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: Nationalism has played a significant role in shaping history over the past __________ centuries.
Q2: In the 19th century, nationalism led to the unification of small kingdoms into larger __________ in Europe.
Q3: Nationalists in India invoked its ancient cultural heritage and __________.
Q4: Nations identify with a particular __________ that they claim as their own.
Q5: The aspiration for a homeland has been a major cause of __________ in the world.
Q6: National self-determination refers to a nation's right to __________ themselves.
Q7: After World War I, the Treaty of Versailles led to the establishment of several small, newly independent __________.
Q8: Most states in the world have multiple ethnic and cultural communities within their __________.
Q9: Creating new states may not be the solution; instead, making existing states more __________ and equitable is key.
Q10: Some countries have granted group rights to safeguard the language, cultures, and religion of __________ groups.
Match the Column
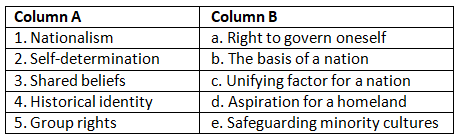
Q1: Match the terms in Column A with their corresponding definitions in Column B.
Assertion and Reason Based
Q1: Assertion: Nationalism has played a significant role in shaping history.
Reason: It has been a source of both unity and division among people.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) The assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) Both assertion and reason are false.
Q2: Assertion: The right to self-determination has led to border conflicts and violence in many countries.
Reason: Creating new states is the only solution to issues of self-determination.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) The assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) Both assertion and reason are false.
Q3: Assertion: Many movements strive for the recognition of group identities, using the language of nationalism.
Reason: In a democratic system, political identity should encompass various identities.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) The assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) Both assertion and reason are false.
Q4: Assertion: Granting independent statehood to every distinct cultural group would be practical and wise.
Reason: It ensures the protection of cultural diversity.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) The assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) Both assertion and reason are false.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Define nationalism.
Q2: What is the basis of a nation's historical identity?
Q3: How does territory contribute to a sense of collective identity?
Q4: Explain the concept of "one culture, one state."
Q5: What is the right to self-determination?
Q6: What challenges do minority communities within states often face?
Q7: Why is creating new states not always the solution to self-determination issues?
Q8: What are group rights in the context of nationalism?
Q9: Why is it important to recognize different groups as part of the national community?
Q10: Why is it risky to allow intolerant and homogenizing forms of identity and nationalism to emerge in a democratic system?
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Discuss the role of nationalism in shaping history and its impact on unity and division.
Q2: Explain the concept of an "imagined" community as it relates to nations.
Q3: Describe the historical basis of a nation and how it is invoked by nationalists.
Q4: Discuss the challenges that arise when multiple cultural groups lay claim to the same territory.
Q5: Analyze the consequences of the "one culture, one state" ideal in Europe after World War I.
Q6: How has the right to self-determination led to conflicts and migrations in the world?
Q7: What is the paradox concerning self-determination and nation-states?
Q8: Why is making existing states more democratic and equitable considered a solution to self-determination issues?
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: Provide a detailed explanation of the different elements that constitute a nation, including shared beliefs, history, territory, shared political ideals, and common political identity.
Q2: Discuss the challenges faced by minority communities within states and the importance of accommodating them as equal citizens.
Q3: Explain why granting independent statehood to every distinct cultural group is considered impractical and unwise. Provide examples.
Q4: In the context of the right to self-determination, discuss the idea that creating new states may not be the ultimate solution and how making existing states more democratic and equitable can address the issues.
You can access the solutions to this worksheet here.
|
44 videos|399 docs|50 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet: Nationalism - Political Science Class 11 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What is nationalism and how does it manifest in different cultures? |  |
| 2. How did nationalism contribute to historical events like the French Revolution? |  |
| 3. What are the positive and negative effects of nationalism? |  |
| 4. How does globalization impact nationalism today? |  |
| 5. What role does education play in fostering nationalism? |  |



















