Worksheet Solutions: The Crisis of Democratic Order | Political Science Class 12 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Match the Column |

|
| Assertion and Reason Based |

|
| Very Short Answers Type Question |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: In the 1970s, India experienced political turmoil and tensions between the government and the _________.
Ans: judiciary
In the 1970s, India experienced political turmoil and tensions between the government and the judiciary, leading to a crisis in democratic order.
Q2: Jai Prakash Narayan led a call for a total revolution in the social, economic, and political spheres in _________.
Ans: Bihar
Jai Prakash Narayan led a call for a total revolution in the social, economic, and political spheres in Bihar, mobilizing mass protests against corruption and rising prices.
Q3: The Naxalite movement aimed to end the political and capitalist system through _________.
Ans: guerrilla warfare
The Naxalite movement aimed to end the political and capitalist system through guerrilla warfare, advocating for the overthrow of existing structures through armed rebellion.
Q4: The railway strike of 1974, led by George Fernandez, halted the country's _________ system.
Ans: Traffic
The railway strike of 1974, led by George Fernandez, halted the country's traffic system, bringing the transportation network to a standstill.
Q5: During the Emergency, freedom of press and some fundamental rights of citizens were _________.
Ans: Suspended
During the Emergency, freedom of press and some fundamental rights of citizens were suspended, suppressing dissent and limiting personal freedoms.
Q6: The Shah Commission estimated that nearly _________ people were arrested under preventive detention laws during the Emergency.
Ans: one lakh
The Shah Commission estimated that nearly one lakh people were arrested under preventive detention laws during the Emergency, highlighting the extent of political repression.
Q7: The Janata Party won _________ seats in the 1977 Lok Sabha elections.
Ans: 330
The Janata Party won 330 seats in the 1977 Lok Sabha elections, securing a decisive victory over the Congress Party and its allies.
Match the Column
Q1:
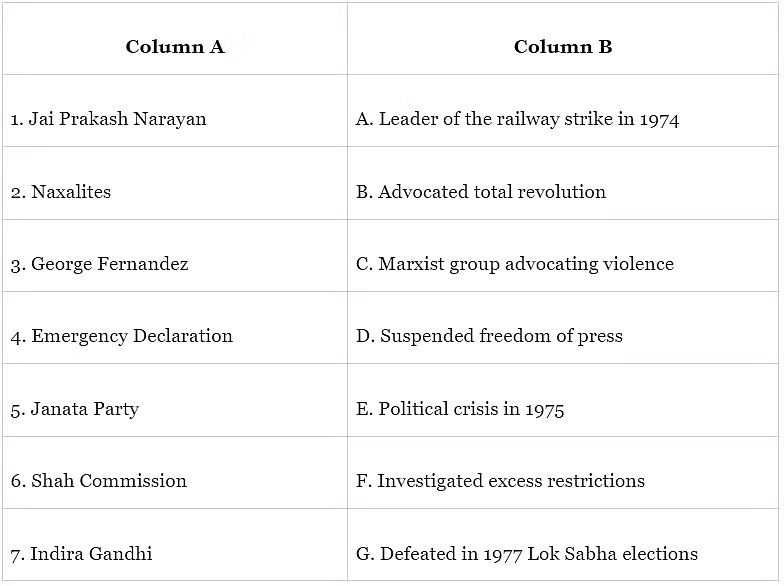 Ans: Jai Prakash Narayan (B): Jai Prakash Narayan advocated total revolution in the social, economic, and political spheres during the political crisis of 1975.
Ans: Jai Prakash Narayan (B): Jai Prakash Narayan advocated total revolution in the social, economic, and political spheres during the political crisis of 1975.
Naxalites (C): Naxalites were a Marxist group advocating violence and guerrilla warfare to end the political system and capitalist structure.
George Fernandez (A): George Fernandez led the railway strike in 1974, which halted the country's traffic system.
Emergency Declaration (D): The Emergency Declaration suspended freedom of press and curtailed various fundamental rights of citizens.
Janata Party (G): The Janata Party, along with its allies, defeated Indira Gandhi's Congress Party in the 1977 Lok Sabha elections.
Shah Commission (F): The Shah Commission investigated excess restrictions and human rights violations imposed during the Emergency.
Indira Gandhi (E): Indira Gandhi, the Prime Minister during the 1975 political crisis, faced a political crisis that led to the declaration of Emergency. She was also defeated in the 1977 Lok Sabha elections.
Assertion and Reason Based
Q1: Assertion: The Emergency was imposed to suppress opposition parties and maintain stability.
Reason: The government believed that opposition parties were taking non-parliamentary routes to remove Indira Gandhi from power.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but Reason is true.
Ans: (b)
While both the assertion and reason are true, the reason provided doesn't correctly explain the assertion. The Emergency was imposed primarily to maintain stability, but the fact that opposition parties were taking non-parliamentary routes to remove Indira Gandhi was one of the contributing factors, not the main explanation for the Emergency.
Q2: Assertion: The Naxalite movement aimed to end the political system and capitalist structure through guerrilla warfare.
Reason: Naxalites believed in peaceful protests and non-violence to achieve their goals.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but Reason is true.
Ans: (c)
The assertion is correct; the Naxalite movement did aim to end the political system and capitalist structure through guerrilla warfare. However, the reason is false. Naxalites were known for their use of violence, not peaceful protests or non-violence.
Q3: Assertion: The Emergency directly affected the lives of common people, leading to widespread protests.
Reason: The government argued that opposition parties must allow the ruling party to govern according to its policies in a democracy.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but Reason is true.
Ans: (a)
Both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason correctly explains the assertion. During the Emergency, the lives of common people were directly affected due to the suspension of fundamental rights, and the government did argue that opposition parties should allow the ruling party to govern according to its policies to maintain stability.
Q4: Assertion: The Janata Party's victory in the 1977 Lok Sabha elections marked the end of Congress Party's rule.
Reason: The Janata Party formed a stable government under the leadership of Morarji Desai.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but Reason is true.
Ans: (a)
Both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason correctly explains the assertion. The Janata Party's victory in 1977 indeed marked the end of Congress Party's rule, and they formed a government under the leadership of Morarji Desai, which initially brought stability and ended Congress's uninterrupted rule.
Very Short Answers Type Question
Q1: What did Jai Prakash Narayan advocate for in Bihar in 1975?
Ans: Jai Prakash Narayan advocated for total revolution in the social, economic, and political spheres.
Q2: What was the objective of the Naxalite movement?
Ans: The objective of the Naxalite movement was to end the political and capitalist system through guerrilla warfare.
Q3: Who led the railway strike in 1974?
Ans: George Fernandez led the railway strike in 1974.
Q4: What constitutional article was used to proclaim Emergency?
Ans: Article 352 was used to proclaim Emergency.
Q5: Why did the government impose press censorship during Emergency?
Ans: The government imposed press censorship during Emergency to control the publication of articles and matters.
Q6: Who led the Janata Party to victory in the 1977 Lok Sabha elections?
Ans: The Janata Party and its allies led the Janata Party to victory in the 1977 Lok Sabha elections.
Q7: Who became the Prime Minister after the 1977 elections?
Ans: Morarji Desai became the Prime Minister after the 1977 elections.
Q8: What was the focus of politics after the Emergency?
Ans: The focus of politics after the Emergency was the welfare of backward castes and reservations for 'other backward classes'.
Q9: What did the Shah Commission investigate?
Ans: The Shah Commission investigated the excess restrictions imposed during the Emergency.
Q10: What was the outcome of the 1977 Lok Sabha elections for the Congress Party?
Ans: The Congress Party was defeated, winning only 154 seats.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Explain the impact of the Emergency on civil liberties and freedom of press.
Ans: Civil liberties and fundamental rights were suspended, leading to a loss of personal freedom. Freedom of press was curtailed, and press censorship was enforced, restricting the media's ability to report freely. Describe the factors that contributed to the downfall of the Janata Party government. Internal conflicts and power struggles among leaders weakened the party's unity.
Q2: Differences in ideologies and policies led to divisions within the party.
Ans: Internal conflicts and power struggles among leaders weakened the party's unity. Differences in ideologies and policies led to divisions within the party. Inability to manage economic challenges and address public expectations resulted in dissatisfaction.
Q3: Discuss the role of Jai Prakash Narayan during the political crisis of 1975.
Ans:
- Jai Prakash Narayan called for a total revolution, mobilizing masses against the government.
- He led a massive march to the Parliament in 1975, protesting against rising prices and corruption.
- His leadership amplified the opposition against the government, contributing to the political turmoil.
Q4: Explain the ideological differences that escalated within the Congress during the 1970s.
Ans:
- Differences emerged between supporters of Indira Gandhi and her opponents within the Congress.
- Ideological divisions were sharpened, leading to internal conflicts over party policies and leadership.
- These differences deepened the political crisis within the Congress party.
Q5: Describe the consequences of the railway strike in 1974.
Ans:
- The strike, led by George Fernandez, brought the country's traffic system to a halt.
- The demands of the strikers were rejected by the government, leading to increased discontent.
- The strike highlighted the growing unrest and dissatisfaction among various sections of society.
Q6: Explain the significance of the Shah Commission's investigation during the Emergency.
Ans:
- The Shah Commission investigated excess restrictions imposed during the Emergency.
- It revealed instances of misuse of power and violations of civil liberties.
- The findings raised awareness about the government's actions and the need to protect democratic values.
Q7: Discuss the impact of the Bangladesh war on India's economy in the 1970s.
Ans:
- The war led to an influx of about 8 million refugees into India, putting immense pressure on the economy.
- Economic resources were diverted to manage the refugee crisis, affecting development projects.
- The war strained India's resources, contributing to economic challenges and slowing growth.
Q8: Explain the significance of the 1977 Lok Sabha elections in Indian political history.
Ans:
- The elections marked a decisive victory for the opposition, ending Congress Party's uninterrupted rule since independence.
- The Janata Party and its allies secured a clear majority, forming the government.
- It reflected the people's discontent with the Emergency and their desire for political change, ushering in a new era in Indian politics.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: Discuss the background and circumstances that led to the imposition of the Emergency in India in 1975.
Ans:
- Political turmoil and tensions with the judiciary due to ideological differences within Congress.
- Economic challenges caused by the Bangladesh war and influx of refugees.
- Rising inflation, unemployment, and slowing economic growth.
- Agitations, strikes, and protests by various groups, including the railway strike.
- Conflict between the government and judiciary over constitutional changes.
- Indira Gandhi's election being declared invalid by the Allahabad High Court.
- All these factors contributed to the government's decision to impose Emergency to maintain stability and suppress opposition voices.
Q2: Examine the consequences of the Emergency on Indian society and politics.
Ans:
- Suspension of civil liberties and fundamental rights, leading to loss of personal freedom.
- Curtailed freedom of press and press censorship, limiting media's ability to report freely.
- Widespread arrests and preventive detention of political workers and opposition leaders.
- Impact on common people's lives due to suppressed dissent and fear.
- The rise of opposition against the government's actions and authoritarianism.
- The realization of the value of civil liberties and democratic rights among citizens.
- The aftermath of the Emergency influencing the 1977 Lok Sabha elections, leading to Congress Party's defeat and the formation of a new government.
Q3: Describe the role of Jai Prakash Narayan and the JP Movement during the political crisis of 1975.
Ans:
- Jai Prakash Narayan's call for a total revolution against corruption and rising prices.
- Leadership in organizing massive protests, including the march to the Parliament.
- Mobilizing public support against the government, amplifying the opposition's voice.
- His role in galvanizing various sections of society and unifying the opposition forces.
- Impact of the JP Movement in raising awareness about democratic values and citizen's rights.
- Contribution to the eventual end of the Emergency and restoration of democracy in India.
Q4: Discuss the political scenario in India after the 1977 Lok Sabha elections and the implications of Janata Party's victory.
Ans:
- Congress Party's defeat in the elections, marking the end of its uninterrupted rule.
- Formation of the Janata Party-led government, with Morarji Desai as the Prime Minister.
- Initial optimism and challenges faced by the new government.
- Internal conflicts within the Janata Party, leading to the government's downfall.
- Implications of the Janata Party's victory in shaping the subsequent political landscape.
- The importance of this period in Indian political history, reflecting the strength of democratic institutions and the people's power to bring about political change.
|
34 videos|308 docs|51 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet Solutions: The Crisis of Democratic Order - Political Science Class 12 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What is the crisis of democratic order? |  |
| 2. What are the causes of the crisis of democratic order? |  |
| 3. How does the crisis of democratic order impact society? |  |
| 4. What are the potential solutions to address the crisis of democratic order? |  |
| 5. Are there any successful examples of overcoming the crisis of democratic order? |  |















