| Table of contents |

|
| What are Profit and Loss? |

|
| Terms used in Profit and Loss |

|
| Profit and Loss Formulas |

|
| Profit Percentage and Loss Percentage |

|
What are Profit and Loss?
Profit is the difference amount when a person sells a product at a higher rate than cost price & loss is the difference amount when a person sells a product at a lower rate than cost price. Every commodity, product or item has a cost price and selling price and depending on the values of these prices, we compute the profit gained or the loss incurred for an individual product.
Profit: When a person sells a product at a higher rate than the cost price, then the difference between both amounts.
Profit Formula = Selling price – Cost price
Loss: When a person sells a product at a lower rate than the cost price, then the difference between both amounts.
Loss = Cost Price – Selling Price
Terms used in Profit and Loss
- Cost Price: Cost price is the price at which a person purchases a product. For example, if Ahana purchased a book for 250 rupees, this is the cost price for that particular book. Cost price is abbreviated as C.P.
- Selling Price: Selling price is the price at which a person sells a product. For example, if Ankur sold a book for 350 rupees, then this is thought to be the selling price of the book. The selling price is abbreviated as S.P.
- Market Price: It is the price that is marked on an article or commodity. It is also known as list price or tag price. If there is no discount on the marked price, then the selling price is equal to the marked price.
- Markup: It is the amount by which cost price is increased to reach market price. Markup = market price – cost price
- Discount: The reduction offered by a merchant on a marked price is called a discount.
- Successive Discount: If an article is sold at two discounts then it is said that it is sold after two successive discounts.
- Dishonest Dealing: In it, a person/shopkeeper sells any product at the wrong weight and earns a profit. This can be done either by using false weight or by false reading.
- A shopkeeper claims to sell rice at a cost price but uses a false weight of 900gm instead of 1000gm.
- A person sells cloth to a customer but uses false reading and gives 90 meters of cloth instead of 100 meters.
- Successive Selling: In it, a product is sold for more than one time from one person to another person at some profit or loss. For example – A sold a pen to B at 10% profit and then B sold the pen to C at 20% profit.
- Sales Tax: When purchasing any product we have to give a certain tax to the government. This additional payment is known as sales tax. Tax is always calculated on the selling price of a product.
Profit and Loss Formulas
Profit and loss formula is employed in maths to determine the price of an entity in the market and comprehend how advantageous a business is.
If the selling price > cost price, then the difference between the S.P. and C.P. is called profit.
Similarly, if the selling price < cost price, then the difference between the C.P. and the S.P. is called loss.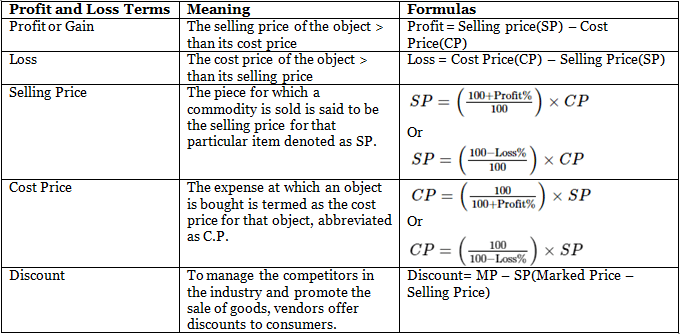
Profit Percentage and Loss Percentage
The profit percentage (%), as well as the loss percentage (%), is obtained with the help of the below-mentioned formulas. Along with the profit percentage (%) and loss percentage (%) other percentage-related formulas are also discussed below: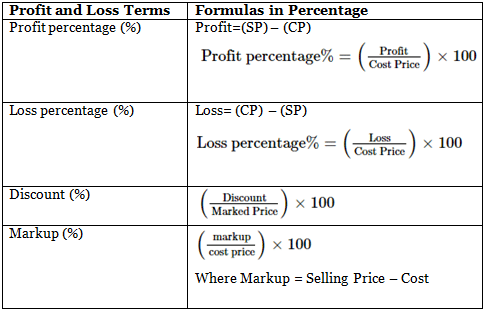
Solved Examples of Profit and Loss
Example 1: Marked price of a cricket bat is Rs 1000 and it is sold at Rs 800. Find the discount percentage.
Sol: Discount = MP – SP = 1000 – 800 = Rs 200
Discount Percentage = (D/MP) × 100 = (200/1000) × 100 = 20%.
Example 2: Marked price of a product is Rs 240 and 25% discount is provided on it. Find the selling price.
Sol: Discount = SP × 25% = 240 × (25/100) = Rs 60
Selling price = MP – Discount = 240 – 60 = Rs 180.
Alternate Method: Selling Price = (100 – D %) × MP/100 = (100 – 25) × 240/100 = Rs 180.
Example 3: A T-shirt is sold after providing two successive discounts of 20%. If the marked price of a T-shirt is Rs 200 then find the selling price.
Sol: Discount 1 = 200 × 20/100 = Rs 40
Selling price after 1st discount = 200 – 40 = Rs 160 Discount 2 = 160 × 20/100 = Rs 32
Selling price after 2nd discount = 160 – 32 = Rs 128
Alternate Method: Effective discount = 20 + 20 – (20 × 20)/100 = 36% Discount = 200 × 36/100 = Rs 72
Selling price = 200 – 72 = Rs 128.
Example 4: A man gains 30% by selling an article for a certain price. If he sells it at double the current selling price, then what will be the profit percentage?
Sol: Let, the cost price be Rs. x.
∴ Selling price = Rs. 1.3x
Now, new SP = Rs. 2.6x
∴ Profit % = [(2.6x− x )] × 100 = 160%
Example 5: If A bought an article at Rs.200 and sold it to B at 20% profit. Again B sold the article at 10% profit to C. Find the amount paid by C.
Sol: Price paid by B = 200 + (200/100 × 20) = 200 + 40 = Rs. 240
∴ Price paid by C = 240 + (240/100 × 10) = 240 + 24 = Rs. 264
Alternate Method: Net profit = 20 + 10 + 20 × 10/100 = 32%
Hence, amount paid by C = 200 + (200/100 × 32) = Rs. 264.
FAQs on Profit, Loss and Discount Important Notes - CAT
| 1. What is the difference between profit and loss? |  |
| 2. What are some common terms used in Profit and Loss statements? |  |
| 3. What are the formulas for calculating Profit and Loss? |  |
| 4. How do you calculate Profit Percentage and Loss Percentage? |  |
| 5. What are some important notes to remember about Profit, Loss, and Discount? |  |














