Worksheet: Living Organisms and Their Surroundings | Basic Science for JSS 2 PDF Download
Q1: Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
(i) What is a habitat?
(a) A natural home for living things.
(b) A human-made structure.
(c) A place for picnics.
(d) A type of soil.
(ii) Which of the following is not a biotic component of a habitat?
(a) Trees
(b) Birds
(c) Soil
(d) Grasses
(iii) In a tropical rainforest, what forms a thick canopy blocking sunlight from reaching the forest floor?
(a) Large animals
(b) Trees with broad leaves
(c) Rain clouds
(d) Desert plants
(iv) Which animal can live without food and water for several days and has adaptations for a desert habitat?
(a) Polar bear
(b) Camel
(c) Kangaroo rat
(d) Elephant
(v) In which habitat are pine trees and juniper trees found?
(a) Sandy desert
(b) Tropical rainforest
(c) Grassland
(d) Mountain regions
Q2: Fill in the Blanks
(i) A habitat is the ____________ of a living thing.
(ii) In a desert, desert plants have small leaves to prevent water loss through ____________.
(iii) Mangrove swamps protect coastal regions from natural disasters like ____________ and ____________.
(iv) Animals in the mountainous regions have thick fur to keep warm and more ____________ to obtain oxygen from thin air at high altitudes.
(v) Aquatic plants have air sacs in their stems and leaves, helping them to ____________.
Q3: Match the Column (in a Table)
Match the habitats (Column A) with their characteristics (Column B).
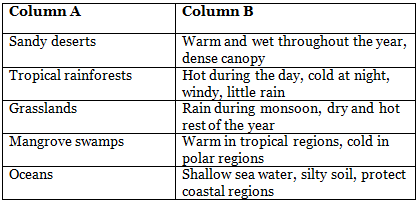
Q4: True or False
(i) Desert plants have large leaves to collect more sunlight.
(ii) Camels can store food in their humps.
(iii) In a tropical rainforest, the forest floor receives ample sunlight.
(iv) Mangrove swamps reduce the force of ocean waves and can protect coastal regions during cyclones and tsunamis.
(v) Animals in high mountain regions have less red blood cells to adapt to low oxygen levels.
You can access the solutions to this worksheet here.
|
44 videos|157 docs|54 tests
|
















