Worksheet: National Income Accounting- 2 | Economics Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
MCQ Questions
Q1: Combined factor income, which can’t be separated into various income components is known as ……… .
(a) Mixed income of self-employed
(b) Compensation of employees
(c) Deferred income
(d) Any of the above
Q2: Other things remaining the same, when foreign currency becomes cheaper, the effect on national income is likely to be
(a) positive
(b) negative
(c) Both positive and negative
(d) No effect
Q3: Which of the following is not a ‘factor payment’?
(a) Free uniform for defence personnel
(b) Salaries to members of Parliament
(c) Rent paid to the owner of the building
(d) Scholarship given to the students
Q4: If Real GDP is `R.s. 200 and the Price Index (with base =100) is 110, calculate Nominal GDP.
(a) Rs 33
(b) Rs 220
(c) Rs 200
(d) Rs 100
Q5: Let us assume that the GDP of some country was R.s.100 at current prices in 2012-13 and that was R.s. 90 in 2011-12; and that the GDP at constant 2004-05 prices was R.s. 59 in 2012-13 and that was R.s. 56.1 in 2011-12, then in GDP of 2011-12 at 2012-13 (constant) prices would be
(a) Rs 59.1
(b) Rs 90
(c) Rs 95.08
(d) Rs 100
Q6: Which of the given statements is incorrect?
(a) GDPMP = GDPFC + NIT
(b) NNPMP = NNP - FC
(c) GNPMP = GDPMP + NFIA
(d) NNPFC = National Income
Q7. If in an economy, all production is undertaken by firms and the recorded sales of all firms in a year are less than their respective recorded costs, then which of the following statements is necessarily true?
(a) At least some firms must have made accounting errors
(b) The economy’s GDP of that year was negative
(c) The total purchases of intermediates by firms were more than their total sales
(d) None of the above
Q8: With a positive externality
(a) there is under-consumption in the free market.
(b) there is overconsumption in the free market.
(c) the government may tax to decrease production.
(d) society could be made better off if less was produced.
Q9: Given the following data for an economy Gross domestic product at market prices `R.s.20,000 Gross domestic capital formation `R.s. 5,000 Depreciation ` R.s.4,000 Net exports (–) ` R.s.2,000 Net factor incomes from abroad ` 5,000 The economy’s net domestic capital formation is
(a) Rs 1,000
(b) Rs 5,000
(c) Rs 3,000
(d) (–) Rs 1,000
Q10: Which of the following statements is/are correct?
(i) Capital formation is a stock variable.
(ii) A car covering a distance of 400 km in 5 hours includes both stock as well as flow variables.
Alternatives
(a) Both are true
(b) Both are false
(c) (i) is true, but (ii) is false
(d) (i) is false, but (ii) is true
Q11: Depreciation of fixed capital assets refers to
(a) normal wear and tear
(b) foreseen obsolescence
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) unforeseen obsolescence
Q12: Money flows are reciprocal of
(a) monetary flows
(b) real flows
(c) circular flow
(d) inventory flows
Q13: A thousand rupee note is an example of
(a) stock variable
(b) flow variable
(c) Either stock or flow
(d) Neither stock nor flow
Q14: Circular flow of income is based upon which of the following assumptions?
(a) All sectors are self-sufficient and independent
(b) Income generated in one sector is consumed within the same sector
(c) One person’s expenditure is another person’s income
(d) All economies are closed economies
Q15: In which of the following cases would the purchase of rice be included while calculating the GDP of India from the expenditure side?
(a) A resident Indian purchases rice to make a dosa which he sells to his neighbour. He then pockets the money received.
(b) A resident Indian purchases rice to make dosa which he sells to his neighbour. He donates the money received to a charity.
(c) A foreign citizen visiting India purchases rice to make a dosa which he sells to another foreign citizen visiting India.
(d) A non-resident Indian visiting India purchases rice, goes back to his country of residence, makes a dosa and then sells it to his neighbour.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: "Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is not the best indicator of the economic welfare of a country.’’ Defend or refute the given statement with valid reasons.
Q2: Explain how ‘non-monetary exchanges’ act as a limitation in taking GDP as an index of welfare.
Q3: Differentiate Between Nominal and Real GDP with Examples.
Q4: The Government incurs expenditure to popularise yoga among the masses. Analyse its impact on the Gross Domestic Product and welfare of the people.
Q5: From the following data, calculate net value added at factor cost 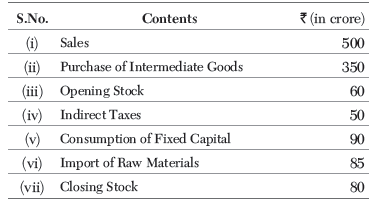
Q6: What steps are taken while estimating national income by income method?
Q7: What precautions should be taken while estimating national income by income method?
Q8: What steps are taken while estimating national income by expenditure method?
Q9: (a) Estimate the value of all above components of final expenditure incurred by all economic units within the domestic territory of the country in a year and their sum will estimate GDPMP.
(b) From the estimates of GDPMP, the value of depreciation and NIT are subtracted and NFIA is added to get NNPFC (National Income).
(c) Explain the components of domestic factor income.
Q10: Define NFIA. What are the components?
Q11: What is meant by expenditure method?
Q12: Define nominal GDP.
Q13: What is depreciation?
Q14: Define depreciation reserve fund.
Q15: Why does an entrepreneur make a provision for the consumption of fixed capital?
Q16: What is fixed investment?
Q17: What do you mean by inventory investment?
Q18: Define capital loss.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: How will the following be treated while estimating the national income of India? Give reasons.
(i) Dividend received by a foreigner from investment in shares of an Indian company.
(ii) Expenditure on education of children by a family in Uttar Pradesh.
(iii) Remittances from non-resident Indians to their families in India.
Q2: Explain the precautions that are taken while estimating national income by value-added method.
You can access the solutions to this worksheet here.
|
64 videos|308 docs|51 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet: National Income Accounting- 2 - Economics Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What is national income accounting? |  |
| 2. What are the components of national income? |  |
| 3. How is national income calculated? |  |
| 4. What is GDP and how is it related to national income? |  |
| 5. Why is national income accounting important? |  |





















