Worksheet Solutions: Production and Costs- 1 | Economics Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions |

|
| Match the Following |

|
| True or False |

|
| Very Short Answers |

|
| Short Answers |

|
| Long Answers |

|
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1: Which of the following is NOT a factor of production?
(a) Land
(b) Money
(c) Labor
(d) Entrepreneurship
Ans: (b) Money
Q2: What is the primary goal of production in economics?
(a) Maximizing Costs
(b) Maximizing Profits
(c) Minimizing Labor
(d) Minimizing Production
Ans: (b) Maximizing Profits
Q3: Which cost remains constant regardless of the level of production?
(a) Variable Cost
(b) Total Cost
(c) Fixed Cost
(d) Marginal Cost
Ans: (c) Fixed Cost
Q4: What does the Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns state?
(a) Marginal cost decreases as production increases
(b) Marginal cost remains constant as production increases
(c) Marginal cost increases as production increases
(d) Marginal cost is unrelated to production
Ans: (c) Marginal cost increases as production increases
Q5: Which market structure is characterized by a large number of sellers and buyers, similar products, and easy entry and exit?
(a) Monopoly
(b) Oligopoly
(c) Perfect Competition
(d) Monopolistic Competition
Ans: (c) Perfect Competition
Match the Following
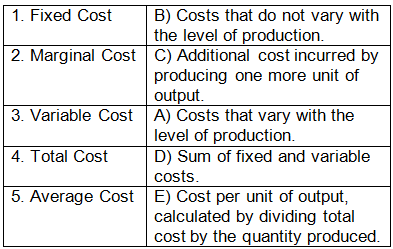
Q1: Match the production term with its corresponding definition:
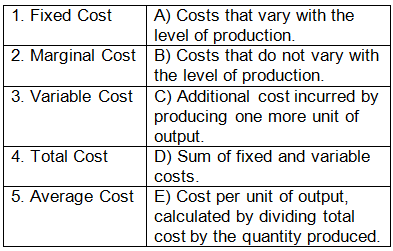
Ans:
True or False
Q1: Total cost is the sum of fixed and variable costs.
Ans: True
Q2: Marginal cost is the change in total cost when one more unit is produced.
Ans: True
Q3: Average variable cost decreases as production increases.
Ans: False
Q4: Economic costs include both explicit and implicit costs.
Ans: True
Q5: In perfect competition, firms have control over the market price.
Ans: False
Very Short Answers
Q1: Define Production Function.
Ans: Production function represents the relationship between inputs (factors of production) and output (quantity of goods and services) produced by a firm.
Q2: What is Economies of Scale?
Ans: Economies of scale occur when a firm experiences cost savings as it increases its level of production.
Q3: Explain Opportunity Cost.
Ans: Opportunity cost is the value of the next best alternative that must be forgone when a decision is made to allocate resources to a particular choice.
Q4: Differentiate between Fixed Costs and Variable Costs.
Ans: Fixed costs remain constant regardless of the level of production, while variable costs vary with the quantity of output produced.
Q5: What is a Production Possibility Curve?
Ans: A production possibility curve illustrates the maximum combinations of two goods that a society can produce given its available resources and technology.
Short Answers
Q1: Explain the Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns.
Ans: As a firm increases the quantity of one input while keeping other inputs constant, the additional output produced per unit of the input will eventually decrease.
This occurs due to inefficiencies, lack of coordination among inputs, and resource constraints, leading to diminishing returns.
Q2: Discuss the Relationship between Average Cost and Marginal Cost.
Ans:
- When marginal cost is less than average cost, average cost decreases.
- When marginal cost is equal to average cost, average cost remains constant.
- When marginal cost is greater than average cost, average cost increases.
- This relationship is essential for firms to make production decisions and optimize their costs.
Q3: Explain the Concept of Break-Even Point.
Ans: The break-even point is the level of output where total revenue equals total cost, resulting in neither profit nor loss.
Below the break-even point, the firm incurs losses; above the break-even point, the firm earns profits.
It helps firms determine the minimum quantity they need to produce to cover all their costs.
Q4: Discuss the Characteristics of Perfectly Competitive Markets.
Ans: There are numerous buyers and sellers in the market.
- Products are homogenous (identical).
- Firms have no control over the market price; they are price takers.
- There is free entry and exit of firms in the industry.
- Perfect information is available to all market participants.
Q5: Explain the Concept of Short-Run and Long-Run Production.
Ans: In the short run, at least one input is fixed, and the firm can only vary the quantity of the variable inputs. It operates within a limited production scale.
- In the long run, all inputs are variable, and the firm can adjust its production scale, technology, and resources. There are no fixed inputs in the long run.
- Firms can make optimal decisions regarding input usage and scale of operations in the long run, leading to efficient production.
Long Answers
Q1: Discuss the Factors Influencing Production Decisions.
Ans:
- Resource Availability: The availability of inputs such as labor, capital, and raw materials affects production decisions. Scarcity of resources may limit production.
- Technology: Advancements in technology enhance production efficiency, reduce costs, and increase output. Firms adopt new technologies to improve their productivity.
- Market Demand: Production decisions are influenced by consumer demand. Firms produce goods and services that are in demand to maximize sales and profits.
- Government Regulations: Regulations related to environmental standards, labor laws, and safety measures impact production processes and costs. Firms must comply with these regulations.
- Economic Conditions: Economic factors such as inflation, interest rates, and economic growth influence production decisions. Uncertain economic conditions can affect investment and production planning.
Q2: Explain the Concept of Economies and Diseconomies of Scale.
Ans:
- Economies of Scale: Economies of scale occur when a firm experiences cost advantages as it increases its scale of production. Larger firms can spread their fixed costs over a larger output, leading to lower average costs. This results in efficient production and higher profitability.
- Diseconomies of Scale: Diseconomies of scale occur when a firm's costs per unit increase as it expands its production scale. This can be due to inefficiencies in large organizations, communication challenges, and coordination issues. Diseconomies of scale lead to higher average costs and reduced profitability.
Q3: Discuss the Role of Production Function in Business Decision-Making.
Ans: The production function represents the relationship between inputs and outputs in a business.
- It helps firms determine the most efficient combination of inputs to produce a given level of output or to minimize costs.
- Firms use production functions to analyze the impact of changes in input quantities, technology, and resources on their output and costs.
- By understanding the production function, businesses can optimize their production processes, improve efficiency, and make informed decisions regarding input usage and production levels.
Q4: Explain the Concept of Opportunity Cost with Examples.
Ans:
- Opportunity cost is the value of the next best alternative forgone when a decision is made. It reflects the cost of choosing one option over others.
- For example, if a student decides to attend a part-time job instead of studying for an exam, the opportunity cost is the potential grade improvement lost due to lack of study time.
- In business, if a company allocates resources to produce one product over another, the opportunity cost is the potential profit from the foregone product.
- Understanding opportunity cost helps individuals and businesses make rational decisions by evaluating the trade-offs involved in various choices.
Q5: Discuss the Impact of Production Costs on Pricing Strategies.
Ans: Production costs directly influence pricing strategies. Firms need to cover their costs to ensure sustainability and profitability.
- Cost-Plus Pricing: Some firms add a markup percentage to their production costs to determine the selling price. This ensures that costs are covered and provides a margin for profit.
- Competitive Pricing: Firms analyze competitors' prices and set their prices competitively. If production costs are high, firms might opt for differentiation and justify higher prices through product quality or unique features.
- Elasticity of Demand: Firms consider the price elasticity of demand. If demand is elastic (responsive to price changes), firms might lower prices to increase sales volume and cover costs. If demand is inelastic (insensitive to price changes), firms can set higher prices to maximize revenue.
- Discounts and Promotions: Firms use discounts and promotions strategically to boost sales. Discounts can attract price-sensitive customers, allowing the firm to sell products even if prices are high.
- Cost Efficiency: Firms aim to optimize production processes to reduce costs. Cost-efficient operations enable firms to offer competitive prices and maintain profitability in the market.
|
59 videos|222 docs|43 tests
|




















