Worksheet Solutions: The Theory of the Firm under Perfect Competition- 1 | Economics Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions |

|
| Match the Following |

|
| True or False |

|
| Very Short Answers |

|
| Short Answers |

|
| Long Answers |

|
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1: Which market structure is characterized by numerous buyers and sellers, homogeneous products, and perfect information?
(a) Perfect Competition
(b) Monopoly
(c) Oligopoly
(d) Monopolistic Competition
Ans: a
Q2: What is the primary goal of a firm operating under perfect competition?
(a) Maximize Profit
(b) Increase Market Share
(c) Minimize Costs
(d) Set the Highest Price Possible
Ans: a
Q3: In perfect competition, which of the following is true regarding the demand curve faced by a firm?
(a) Perfectly Elastic
(b) Downward Sloping
(c) Upward Sloping
(d) Horizontal at Market Price
Ans: a
Q4: What happens to the price and output level of a firm in the short run if it incurs losses?
(a) Price Decreases, Output Decreases
(b) Price Increases, Output Decreases
(c) Price Increases, Output Increases
(d) Price Decreases, Output Increases
Ans: a
Q5: Which of the following statements is true about a firm in perfect competition in the long run?
(a) Firms can earn economic profit in the long run.
(b) Firms can only cover their explicit costs in the long run.
(c) Firms can earn normal profit in the long run.
(d) Firms can only survive if they make supernormal profit.
Ans: c
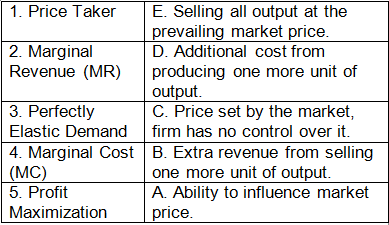
Match the Following
Q: Match the following terms with their correct definitions:
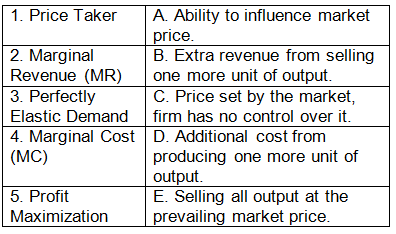
Ans:
True or False
Q1: Perfectly competitive firms can freely enter or exit the market.
Ans: True
Q2: In perfect competition, each firm has some degree of market power.
Ans: False
Q3: Perfectly elastic demand curve implies that the firm can sell any quantity of output at the market price.
Ans: True
Q4: Firms in perfect competition can engage in non-price competition to increase sales.
Ans: False
Q5: Normal profit is the minimum level of profit necessary to keep a firm in operation.
Ans: True
Very Short Answers
Q1: Explain the concept of perfect competition in one sentence.
Ans: Perfect competition is a market structure characterized by a large number of small firms producing homogeneous products, with perfect information, and ease of entry and exit.
Q2: Define Marginal Revenue (MR).
Ans: Marginal Revenue (MR) is the additional revenue earned by a firm from selling one more unit of output.
Q3: Why is the demand curve facing a perfectly competitive firm perfectly elastic?
Ans: The demand curve facing a perfectly competitive firm is perfectly elastic because the firm can sell any quantity of output at the prevailing market price.
Q4: What is the significance of the price being equal to marginal cost for a firm in perfect competition?
Ans: When price equals marginal cost, the firm maximizes its profit because it produces at the point where the additional cost of production equals the additional revenue from selling one more unit of output.
Q5: State one condition necessary for a firm to achieve profit maximization in perfect competition.
Ans: For profit maximization in perfect competition, a firm must produce at the level where marginal cost equals marginal revenue and where price equals marginal cost.
Short Answers
Q1: Profit Maximization in Perfect Competition
Ans: Determine the level of output where marginal cost (MC) equals marginal revenue (MR).
- Find the corresponding price from the demand curve.
- Produce and sell the quantity of output at this price to maximize profit.
Q2: Role of Perfect Competition in Promoting Consumer Welfare
Ans: Perfect competition ensures that consumers have access to a variety of products at competitive prices.
- Firms are compelled to produce efficiently, leading to lower production costs and affordable prices for consumers.
- Consumers benefit from the optimal allocation of resources and the availability of choices in the market.
Q3: Short-Run and Long-Run Equilibrium of a Firm in Perfect Competition
Ans: In the short run, a firm may experience profits or losses based on market conditions.
- In the long run, firms enter or exit the market based on profitability.
- Long-run equilibrium occurs when all firms earn only normal profit, and price equals both average total cost and marginal cost.
Q4: Importance of Price Elasticity of Demand for Perfectly Competitive Firms
Ans: Perfectly competitive firms face perfectly elastic demand, meaning they can sell any quantity at the market price.
- Price elasticity of demand is irrelevant for individual firms in perfect competition as they cannot influence the market price.
Q5: Challenges Faced by Firms in Perfect Competition
Ans: Fierce competition from other firms in the market.
- Inability to set prices due to the perfectly elastic demand curve.
- Continuous need for efficiency to survive in the long run.
- Limited ability to differentiate products, leading to a focus on cost leadership.
Long Answers
Q1: Market Entry and Exit in Perfect Competition
Ans: Market Entry:
- Firms enter the market attracted by potential profits.
- New firms bring additional supply, leading to price reduction until normal profit is earned.
- If firms continue to earn economic profit, more firms enter the market, increasing supply until profit normalizes.
Market Exit:
- Firms exit the market if they incur losses.
- High costs or low demand can lead to losses, prompting firms to leave the industry.
- Exiting reduces supply, increasing prices until remaining firms earn normal profit.
Q2: Efficiency of Perfectly Competitive Markets
Ans: Perfectly competitive markets achieve allocative and productive efficiency.
- Allocative efficiency occurs because price equals marginal cost, ensuring resources are allocated where they are most valued.
- Productive efficiency is achieved as firms produce at the minimum average total cost, utilizing resources efficiently.
Q3: Price Determination in Perfect Competition
Ans: Prices are determined through the interaction of market demand and supply.
- Individual firms are price takers and sell at the prevailing market price.
- Market forces adjust supply and demand until the equilibrium price is reached, where quantity demanded equals quantity supplied.
Q4: Benefits of Perfect Competition for Consumers and Society
Ans: Consumers benefit from low prices and a wide variety of goods and services.
- Efficient resource allocation ensures products are available to satisfy consumer preferences.
- Society benefits from the optimal utilization of resources, leading to overall economic welfare.
Q5: Importance of Perfect Competition in the Economy
Ans: Encourages innovation and efficiency as firms compete to reduce costs and improve products.
- Promotes consumer welfare by offering diverse products at competitive prices.
- Acts as a benchmark for evaluating other market structures, aiding policymakers in economic decisions.
|
59 videos|222 docs|43 tests
|




















