Floral Families: Compositae, Graminae - NEET PDF Download
What is Compositae?
The Compositae or Asteraceae family, commonly known as the aster, daisy, or sunflower family, is the largest family of flowering plants in terms of the number of species. It includes about 1,620 genera and over 23,600 species. The family is characterized by its composite inflorescences, known as capitula or heads, which are often mistaken for single flowers.
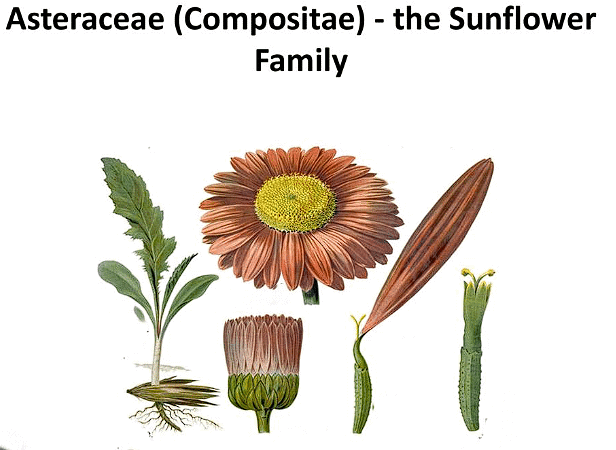
This family is also known as Daisy family. Members of this family are found in a wide range of habitats across the globe and include many ornamental plants, weeds, and crops.
Vegetative Characters of Compositae Family
(a) Stem: Stems in the Compositae family can be herbaceous or woody, erect, prostrate, or climbing. They are often grooved and can be hollow in some species.
(b) Leaves: Leaves of Compositae plants are usually alternate, though they can be opposite or whorled in some genera. They can be simple or compound, with a wide range of shapes and margins. The leaves are often sessile or have a petiole.
Floral Characters of Compositae Family
(a) Inflorescence
The inflorescence is a capitulum (head), which is a compact cluster of numerous small florets arranged on a receptacle, often surrounded by bracts (phyllaries) forming an involucre. Each capitulum can resemble a single flower.
(b) Flower
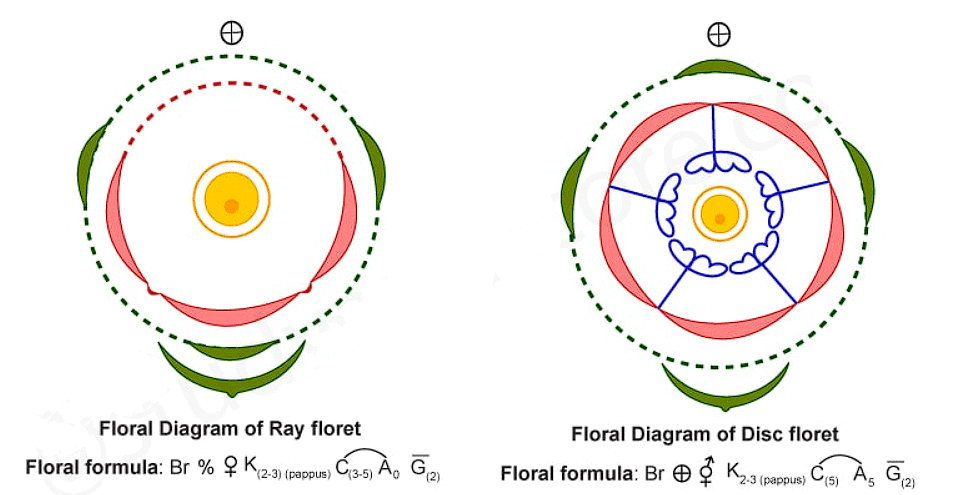
The florets within a capitulum can be of two types: ray florets (sterile, ligulate, and often petal-like) and disk florets (fertile, tubular). Some capitula contain only one type, while others have both.
(c) Calyx
The calyx is modified into a structure called a pappus, which can be a ring of scales, bristles, or absent. It aids in seed dispersal.
(d) Corolla
The corolla can be tubular (in disk florets) or ligulate (in ray florets). They are usually fused at the base, forming a tube or a strap-shaped structure.
(e) Androecium
The androecium typically consists of five stamens, which are fused by their anthers, forming a tube through which the style grows.
(f) Gynoecium
The gynoecium is composed of two carpels fused to form a single ovary, which is inferior. It typically has one locule with one ovule.
(g) Fruits
The fruit is an achene, which is a small, dry, one-seeded fruit that does not open at maturity. The pappus is often attached to the achene.
(h) Seeds
The seed is contained within the achene and is usually small with a thin seed coat. It lacks endosperm, as the cotyledons store the nutrients.
Floral Formula of Compositae Family
A typical floral formula for the Compositae family is:
This represents a flower with a corolla of five fused petals, five stamens fused by their anthers, and an inferior ovary with two carpels.
Economic Importance of Compositae Family
The Compositae family has significant economic value due to its diverse applications:
(a) Food Crops: Some species are cultivated for food, including lettuce (Lactuca sativa), artichoke (Cynara scolymus), and sunflower (Helianthus annuus) for its seeds and oil.
(b) Ornamental Plants
Many species are popular ornamentals, such as daisies, chrysanthemums, asters, and marigolds.
(c) Medicinal Uses
Several members have medicinal properties, like Echinacea for immune support and Arnica for topical pain relief.
(d) Industrial Uses: Some species are used for their natural latex (e.g., rubber from Taraxacum species) and as biofuels.
(e) Environmental and Ecological Importance: Members of the Compositae family play a crucial role in ecosystems as sources of nectar and pollen for pollinators.
What is Graminae?
The Gramineae or Poaceae family, commonly known as the grass family, is one of the largest and most important plant families. It includes about 780 genera and over 12,000 species. Grasses are found worldwide in diverse habitats and are particularly known for their economic importance in agriculture. They are the primary source of calories for humans and livestock, mainly through cereals like wheat, rice, and maize.
Vegetative Characters of Graminae
(a) Stem: The stem, or culm, is typically cylindrical, hollow, and jointed, with solid nodes. It can be erect, decumbent, or creeping. Some grasses have rhizomes or stolons.
(b) Leaves: Leaves are usually alternate, arranged in two ranks. They consist of a sheath that encloses the stem, a ligule at the junction of the sheath and blade, and a flat or rolled blade. The venation is parallel.
Floral Characters of Graminae
(a) Inflorescence: The inflorescence is typically a spike, raceme, or panicle composed of units called spikelets. Each spikelet consists of one to many florets, each with a pair of bracts called glumes at the base.
(b) Flower: The flowers, or florets, are usually small and not showy. They lack a distinct calyx and corolla, having instead modified structures called lodicules, lemma, and palea.
(c) Calyx: The calyx is absent in grass flowers. The role of the calyx is assumed by the glumes at the base of the spikelet.
(d) Corolla: The corolla is also absent. Instead, two or three small scales called lodicules are present, which swell at flowering and help in the opening of the floret.
(e) Androecium: The androecium typically consists of three stamens, but the number can vary. The anthers are usually large and well-exposed for wind pollination.
(f) Gynoecium: The gynoecium is composed of a single carpel, forming a superior ovary. It usually has two feathery stigmas to catch pollen grains.
(g) Fruits: The fruit is a caryopsis, a type of dry fruit where the seed coat is fused to the ovary wall.
(h) Seed: The seed is contained within the caryopsis and is usually small. It contains endosperm, which is a significant food reserve.
(i) Floral Formula
A typical floral formula for the Gramineae family is:
This represents a flower with no perianth, six stamens, and a superior ovary with two carpels.
Economic Importance Graminae
The Gramineae family has immense economic value due to its diverse applications:
(a) Food Production: Cereals like wheat, rice, maize, barley, and oats are staple foods for a large portion of the world's population.
(b) Fodder: Grasses are a primary source of fodder for livestock, providing essential nutrients for animals.
(c) Biofuels: Some grasses, like switchgrass and miscanthus, are used in the production of biofuels.
(d) Construction and Crafts: Bamboo, a member of the grass family, is used extensively in construction, furniture, and crafts.
(e) Soil Conservation: Grasses play a crucial role in soil conservation, erosion control, and land rehabilitation.
(f) Ornamental Use: Many grasses are used for ornamental purposes in landscaping and garden design.
FAQs on Floral Families: Compositae, Graminae - NEET
| 1. What is Compositae? |  |
| 2. What are the vegetative characters of the Compositae family? |  |
| 3. What are the floral characters of the Compositae family? |  |
| 4. What is the floral formula of the Compositae family? |  |
| 5. What is the economic importance of the Compositae family? |  |















