Worksheet Solutions: Presentation of Data - 2 | Economics Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1: Which of the following method(s) of statistics is followed by collection of primary data in a statistical enquiry?
(a) Classification
(b) Organisation
(c) Presentation
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Ans: d
Q2: Frequency polygon can be drawn
(a) with histogram only
(b) without histogram only
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Neither (a) nor (b)
Ans: c
Q3: The systematic presentation of raw data in row and column is called tabulation.
Choose from the options below.
(a) True
(b) False
(c) Partially true
(d) Incomplete statement
Ans: a
Q4: Horizontal bar graphs are also known as
(a) Complex bar graph
(b) Simple bar graph
(c) Derived bar graph
(d) None of these
Ans: b
Q5: General purpose table is also referred to as
(a) Repository table
(b) Original table
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Neither (a) nor (b)
Ans: a
Q6: Accuracy is not required while drawing the diagrams. Choose from the options below.
(a) True
(b) False
(c) Partially true
(d) Incomplete statement
Ans: b
Q7: Which of the following is/are part(s) of a table?
(a) Stubs
(b) Captions
(c) Title
(d) All of these
Ans: d
Q8: Which of the following are methods of presentation of data?
(i) Text presentation
(ii) Semi-tabular presentation
(iii) Tabular presentation
(iv) Pictorial presentation
Choose from the options below.
(a) (i), (ii), (iii)
(b) (ii), (iii), (iv)
(c) (i), (iii), (iv)
(d) (i), (ii), (iii), (iv)
Ans: d
Q9: On the basis of construction, which of the following are types of table?
(a) Simple table
(b) Complex table
(c) Derived table
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Ans: d
Q10: The main part of table is known as
(a) Body
(b) Heading
(c) Footnote
(d) None of these
Ans: a
Q11: Histogram always starts from the origin.
Choose from the options below.
(a) True
(b) False
(c) Partially true
(d) Incomplete statement
Ans: c
Q12: The most accurate mode of presentation for comparison and computation is the ____ .
(a) diagram
(b) table
(c) text
(d) All of these
Ans: b
Q13: A simple bar graph can be drawn
(a) vertically
(b) horizontally
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Neither (a) nor (b)
Ans: c
Q14: Tabulation makes the data complex.
Choose from the options below.
(a) True
(b) False
(c) Partially true
(d) Incomplete statement
Ans: b
Q15: Which of the following is/are essentials of a good classification?
(a) It should comprised of all the items of the population
(b) It should be simple and clear
(c) It should be comprised of all related instruction of understanding
(d) All of the above
Ans: d
50 students were asked to choose their Favourite sport these are the results. 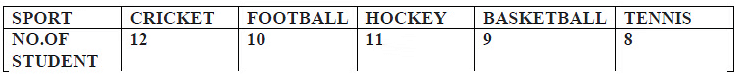
The data is to be illustrated in a pie chart.
Q16: In which form a data presented in a pie diagram?
(a) percentage
(b) Degrees
(c) Absolute values
(d) table
Ans: A
Q17: What angle should be used for football.
(a) 36̊
(b) 72̊
(c) 90̊
(d) 10̊
Ans: a
Q18: What angle should be used for tennis.
(a) 8̊
(b) 57.6̊
(c) 28.8̊
(d) 64̊
Ans: b
Q19: In a pie diagram/circle 1% is equal to ____.
(a) 1
(b) 3.6
(c) 36
(d) 10
Ans: b
Answer the following questions based on the histogram Given below.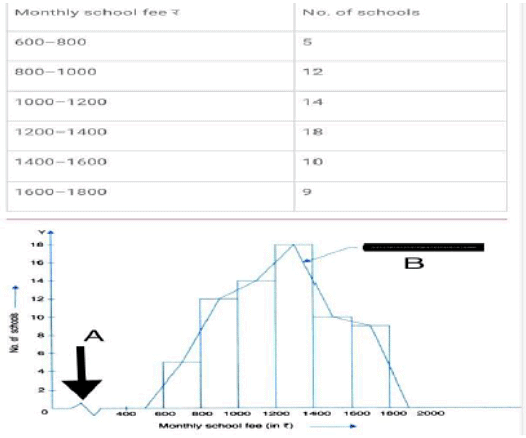
Q20: Which group contains maximum monthly school fee?
(a) 1000-1200
(b) 1200-1400
(c) 1400-1600
(d) 800-1000
Ans: b
Q21: What A denotes in the above diagram.
(a) Jagged line
(b) horizontal line
(c) Broken line
(d) Both A and C
Ans: c
Q22: How many schools charge monthly school fee between 1200 to 1800?
(a) 44
(b) 37
(c) 42
(d)18
Ans: b
Q23: A --------------------- becomes a ----------------- if we Draw a line joining mid points of the tops of all rectangular.
(a) Histogram, Frequency polygon
(b) Frequency polygon, Histogram
(c) Frequency ,Histogram
(d) Histogram, Frequency distribution
Ans: a
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: Define or explain briefly.
(a) Statistical Table
(b) Tabulation
(c) Time series
(d) Pie Diagram
Ans: (a) Statistical Table:
A statistical table is a structured arrangement of data in rows and columns. It is used to present and organize numerical information in a clear and systematic manner, making it easier to analyze and interpret data. Statistical tables often include headings, labels, and units of measurement to provide context for the data they contain.
(b) Tabulation:
Tabulation is the process of systematically organizing and presenting data in the form of tables. It involves categorizing and summarizing data into rows and columns, with each row representing a specific category or variable and each column representing a particular aspect of the data. Tabulation is essential for data analysis and helps in drawing meaningful conclusions from the data.
(c) Time Series:
A time series is a sequence of data points or observations collected or recorded at regular intervals over a period of time. Time series data is used to analyze trends, patterns, and variations over time. It is often represented graphically using line charts or plotted on a graph with time on the x-axis and the variable of interest on the y-axis.
(d) Pie Diagram:
A pie diagram, also known as a pie chart, is a circular chart divided into sectors or slices to represent data as a percentage of a whole. Each sector's size is proportional to the quantity it represents in the dataset. Pie charts are typically used to display the composition of a whole or the distribution of a categorical variable.
Q2: Name 4 types of presentation
Ans: Four Types of Presentation:
- Verbal Presentation: Communicating information using spoken or written words, such as speeches, reports, or written documents.
- Visual Presentation: Presenting information through visual aids, such as charts, graphs, and diagrams.
- Multimedia Presentation: Combining various media elements, including text, images, videos, and audio, to convey information effectively.
- Interactive Presentation: Engaging the audience by allowing them to actively participate or interact with the presentation, often seen in workshops or software demonstrations.
Q3: Give 2 object of Presentation
Ans: Two Objectives of Presentation:
- To convey information effectively: The primary objective of a presentation is to communicate information, ideas, or data clearly and comprehensively to the audience.
- To engage and persuade the audience: Presentations often aim to persuade or influence the audience's opinions, decisions, or actions by presenting information in a compelling and convincing manner.
Q4: Ogives are also know as
Ans: Ogives are also known as cumulative frequency curves. They are graphical representations of cumulative frequency distributions and are used to show the cumulative frequency of data points at or below specific values.
Q5: Discuss the following :
(a) Objectives of Tabulation
(b) Parts of a Table (with diagram)
(c) Type of Tables
(d) Importance of graphs and diagrams
(e) Various types of one dimensional diagram
(f) Limitations of Diagrammatic Presentation
(g) Point to keep in mind while preparing a table.
Ans: (a) Objectives of Tabulation:
Tabulation has several objectives, including:
- Summarizing and simplifying complex data.
- Facilitating easy comparison and analysis of data.
- Aiding in the presentation of data in a clear and organized manner.
- Providing a basis for making inferences and drawing conclusions from data.
(b) Parts of a Table:
A typical table consists of the following parts:
- Title or Heading: Describes the content of the table.
- Stub: Contains row labels or categories.
- Body: Contains the data arranged in rows and columns.
- Caption: Explains the table's content and any additional information.
- Footnotes: Provide additional notes or explanations for specific data points.
(c) Types of Tables:
There are various types of tables, including:
- Frequency Distribution Table
- Cross-tabulation Table
- Comparative Table
- Time Series Table
- Cause-and-Effect Table
(d) Importance of Graphs and Diagrams:
Graphs and diagrams are essential for visualizing data because they:
- Simplify complex data.
- Highlight patterns and trends.
- Facilitate quick understanding and interpretation.
- Aid in making data-driven decisions.
(e) Various Types of One-Dimensional Diagrams:
One-dimensional diagrams include bar charts, histograms, frequency polygons, and line charts, which represent data along a single axis.
(f) Limitations of Diagrammatic Presentation:
- May oversimplify complex data.
- May not be suitable for all types of data.
- Can be misinterpreted if not properly labeled and scaled.
(g) Points to Keep in Mind While Preparing a Table:
- Use clear and concise headings.
- Ensure the data is organized logically.
- Include appropriate units of measurement.
- Label rows and columns accurately.
- Use consistent formatting and layout.
Q6: Differentiate between:
(a) Graphs/ Diagrams
(b) Stub /Caption
(c) Subdivided/ Percentage Bar diagram
(d) Deviation /Broken Bar Diagram
Ans: (a) Graphs/Diagrams: Graphs are a broader category that includes various types of visual representations of data, including diagrams. Diagrams are specific types of graphs that use symbols and shapes to convey information.
(b) Stub/Caption: The stub is the row labels or categories in a table, while the caption is an explanatory title or note that provides context for the entire table.
(c) Subdivided/Percentage Bar Diagram: Subdivided bar diagrams represent data within categories as subdivisions or segments of bars. Percentage bar diagrams show the percentage distribution of data within each category.
(d) Deviation/Broken Bar Diagram: Deviation bar diagrams compare data points to a reference point or average, often using bars that extend above and below the reference line. Broken bar diagrams use gaps or breaks in bars to represent data with discontinuities or missing values.
Q7: How will a histogram be drawn if
(a) Class intervals are uneqnal
(b) Class intervals are inclusive
Ans: (a) If Class Intervals Are Unequal:
- Adjust the width of each bar according to the class interval's width.
- The height of each bar represents the frequency or relative frequency of the corresponding class.
(b) If Class Intervals Are Inclusive:
- Ensure that each data point is appropriately assigned to the corresponding class interval, considering inclusivity.
- Construct the histogram with the class intervals on the x-axis and the frequency or relative frequency on the y-axis.
Q8: Give alternative terms for
(a) Multiple Bar Diagram
(b) Angular Diagram
(c) Sub-Divided Bar Diagram
(d) Time Series
Ans: (a) Multiple Bar Diagram: Clustered Bar Chart
(b) Angular Diagram: Radial Diagram
(c) Sub-Divided Bar Diagram: Stacked Bar Chart
(d) Time Series: Temporal Data Series
|
58 videos|215 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet Solutions: Presentation of Data - 2 - Economics Class 11 - Commerce
| 1. What are the different methods of presenting data? |  |
| 2. How do you choose the appropriate method for presenting data? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages of using visual representations, such as graphs and charts, to present data? |  |
| 4. How can data be presented effectively to ensure clarity and comprehension? |  |
| 5. What are some common mistakes to avoid when presenting data? |  |






















