Glycolysis | Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Introduction
- Carbohydrates are the major source of energy for the living cells. The major function of carbohydrates in metabolism is as a fuel to be oxidized and provide energy for other metabolic processes.
- The 3 principal monosaccharides resulting from digestive processes are glucose, fructose, and galactose.
- However, Glucose is the central molecule in carbohydrate metabolism since all the major pathways of carbohydrate metabolism are connected with it.
What is Glycolysis?
- Glycolysis is derived from the Greek words (glycose – sweet or sugar and lysis – dissolution).
- Glycolysis the sequence of 10 enzyme-catalyzed reactions that convert glucose into pyruvate with the simultaneous production of ATP.
- lt is a universal pathway in the living
- It is frequently referred to as Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas or EMP pathway, in honor of these pioneer workers i.e Gustave Embden(1874-1933), Otto Meyerhof (1883-1951) and Jacob Parnas in the field.
- Glycolysis takes place in all cells of the body. The enzymes of this pathway are present in the cytosomal fraction of the of the cell.
Salient feature of Glycolysis
- Glycolysis is the central pathway of glucose catabolism.
- It takes place in all cells of the body. The enzymes of this pathway are present in the cytosomal fraction of the cell.
- It is a major pathway for ATP synthesis in tissues lacking mitochondria, g. erythrocytes, cornea, lens etc.
- Glycolysis occurs in the absence of oxygen(anaerobic) or in the presence of oxygen (aerobic). Lactate is the end product under anaerobic condition. In the aerobic condition, pyruvate is formed, which is then oxidized to CO2 and H2O.
- The glucose in brain has to undergo glycolysis before it is oxidized to CO2 and H2O so glycolysis is very essential for the brain which is dependent on glucose for energy.
- Glycolysis is a central metabolic pathway with many of its intermediates providing branch point to other pathways. Thus, the intermediates of glycolysis are useful for the synthesis of amino acids and fat.
- Reversal of glycolysis along with the alternate arrangements at the irreversible steps will result in the synthesis of glucose (gluconeogenesis).
Reactions of Glycolysis

During glycolysis, the 6-carbon glucose is broken down into two moles of 3-carbon pyruvate via 10 enzyme-catalyzed sequential reactions as shown in the above figure.
- Glucose is phosphorylated at C6 to yield Glucose 6-phosphate by Hexokinase or Glucokinase (both are isoenzymes). This is an irreversible reaction, dependent on ATP and Mg2+. The enzyme Hexokinase is present in almost all the lt catalyzes the phosphorylation of various hexose and is inhibited by Glucose 6-phosphate. Glucokinase present in liver catalyzes the phosphorylation of only glucose.
- Glucose 6-phosphate is reversibly isomerized to Fructose 6-phosphate by Phosphoglucoisomerase in presence of Mg2+. This reaction involves a shift in the carbonyl oxygen from C1 to C2, thus converting an aldose into a ketose.
- Fructose 6-phosphate is phosphorylated by ATP to produce Fructose 1, 6-bisphosphate in the presence of another inducible allosteric enzyme Phosphofructokinase (PFK). The enzyme catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group from ATP to Fructose 6-phosphate at C1 to yield Fructose 1, 6-bisphosphate. This is an irreversible and a regulatory step in glycolysis.
- Fructose 1, 6-bisphosphate is a molecule with phosphate group on both ends, it splits in the middle into two different triose phosphates, Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate(an aldose) and Dihydroxyacetone phosphate(a ketose) so named as Glycolysis. This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase (simply called aldolase) which cleaves the Fructose 1, 6-bisphosphate molecule between C3 and C4. Carbon atoms 4, 5 and 6 appear in glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and 1, 2 and 3 in dihydroxyacetone phosphate.
- The enzyme Phosphotriose isomerase catalyzes the reversible interconversion of Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and Dihydroxyacetone phosphate. Thus, two molecules of Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate are obtained from one molecule of Glucose.
- Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase converts Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate to 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate by dehydrogenation. This step is important as it is involved in the formation of NADH+ H+ and a high energy compound 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate. lodoacetate and Arsenate inhibit the enzyme Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. ln aerobic condition, NADH passes through the Electron Transport Chain and 6 ATP (2 x 3 ATP) are synthesized by oxidative phosphorylation.
- This is the first ATP-generating reaction in glycolysis. It involves the transfer of high-energy phosphate group from the carboxylic group of 3-Phosphoglycerate phosphate to ADP by the enzyme Phosphoglycerate kinase, thus producing ATP and leaving 3-Phosphoglycerate. This step is a good example of Substrate Level Phosphorylation since ATP is synthesized from the substrate without the involvement of Electron Transport Chain. Phosphoglycerate kinase reaction is reversible, a rare example among the kinase reactions
- The 3-Phosphoglycerate is converted into 2-Phosphoglycerate due to the intramolecular shift of phosphoryl group from C3 to C2, by the enzyme Phosphoglycerate mutase. This is an isomerization
- The high energy compound Phosphoenolpyruvate is generated by dehydration of 2-Phosphoglycerate by the enzyme Enolase. This enzyme requires Mg2+ or Mn2+ and is inhibited by Fluoride.
- Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) is converted into pyruvate in enol form (i.e. enolpyruvate) by the inducible allosteric enzyme Pyruvate kinase(PK). The enzyme catalyzes the transfer of a phosphoryl group from PEP to ADP, thus forming ATP. Pyruvate kinase requires K+ and either Mg2+ or Mn2+. This is the second ATP-generating reaction in glycolysis. This step also is a substrate level phosphorylation. This reaction is irreversible.
The overall reaction of Glycolysis can be summarized as:
Glucose + 2NAD+ + 2ADP + 2Pi → 2Pyruvate + 2[NADH++H+] + 2ATP + 2H2O
Thus, three things happen simultaneously in glycolysis :
- Glucose is oxidized to pyruvate.
- NAD+ is reduced to NADH.
- ADP is phosphorylated to form ATP.
There can be no EMP pathway without all 3 events which means that NAD+, ADP, and Pi, as well as glucose, must be present.
Muscle or Anaerobic Glycolysis
- The fate of pyruvate produced in glycolysis depends on the presence or absence of oxygen in the cells.
- Under aerobic conditions, the pyruvate is the product of glycolysis and NADH, formed by the dehydrogenation of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, is then reoxidized to NAD+ by oxygen.
- Under anaerobic conditions, the NADH generated in glycolysis cannot be reoxidized by oxygen but must be reoxidized to NAD+ by the pyruvate itself, converting pyruvate into lactate. The reaction is catalyzed by Lactate
- Such type of glycolytic sequence actively occurs in contracting skeletal muscles during strenuous exercise where oxygen supply is very limited. Glycolysis in the erythrocytes leads to lactate production, since mitochondria, the centers for aerobic oxidation are absent.
- Besides these a large number of microorganisms, the lactic acid bacteria (Lactobacilli, Bacilli, Streptococci, and Clostridia) also follow the same path for the reduction of pyruvate to lactate. Such type of fermentation that yields lactate as the sole product is termed homolactic fermentation.
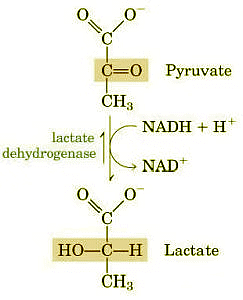 Fig: Anaerobic conversion of Pyruvate into Lactate
Fig: Anaerobic conversion of Pyruvate into Lactate
Energy Yield in Glycolysis
The details of ATP generation in glycolysis (from glucose) are given in the table given below. Under anaerobic conditions, 2 ATP are synthesized while, under aerobic conditions, 8 ATP are synthesized.

Note:
- (-) the sign refers to the utilization of ATP in the reaction
- (*) NADH so produced(6) or utilized(anaerobic glycolysis) undergo ETC to produce ATP i.e. 1NADH=3ATP
Regulation of Glycolysis
The three enzymes namely hexokinase (glucokinase), phosphofructokinase and pyruvate kinase, catalyzing the irreversible reactions regulate glycolysis.
Phosphofructokinase:
- Phosphofructokinase is the most important control element in the glycolytic pathway.
- It is an allosteric enzyme that catalyzes the rate-limiting step.
- The enzyme is regulated by allosteric effectors.
- High levels of ATP allosterically inhibit the enzyme in the liver, thus lowering its affinity for fructose 6-phosphate. Other allosteric inhibitors are citrate and H+ ions (low pH).
- Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate, ADP, AMP and Pi are the allosteric
Hexokinase:
- It is inhibited by glucose 6-phosphate.
- This enzyme prevents the accumulation of glucose 6-phosphate due to product inhibition. High concentrations of this molecule signal that the cell no longer requires glucose for energy and the glucose will be left in the blood.
- Glucokinase, which specifically phosphorylates glucose, is inducible. The substrate glucose, probably through the involvement of insulin, induces glucokinase.
Pyruvate kinase:
- Pyruvate kinase also regulates glycolysis.
- This enzyme is inhibited by ATP and activated by fructose 1,6-bisphosphate.
Note:
- Phosphofructokinase has a greater regulatory effect than Hexokinase. The reason becomes evident as glucose 6-phosphate is not solely a glycolytic intermediate. Glucose 6-phosphate can also be converted into glycogen or it can be oxidized by the pentose phosphate pathway to form NADPH.
- The first irreversible reaction unique to the glycolytic pathway, the committed step, is the phosphorylation of fructose 6-phosphate to fructose 1,6-bisphosphate. Thus, it is highly appropriate for phosphofructokinase to be the primary control site in glycolysis.
- In general, the enzyme catalyzing the committed step in a metabolic sequence is the most important control element in the pathway.
Lactic acidosis
- Lactic acidosis is a form of metabolic acidosis that begins in the kidneys. People with lactic acidosis have kidneys that are unable to remove excess acid from their body.
- Lactic acid is 3 carbon hydroxy acid. There are two types of lactic acid: L-lactate and D-lactate. Most forms of lactic acidosis are caused by too much L-lactate.
- If lactic acid builds up in the body more quickly than it can be removed, acidity levels in bodily fluids — such as blood — spike. This buildup of acid causes an imbalance in the body’s pH level, which should always be slightly alkaline instead of acidic.
- Lactic acid buildup occurs when there’s not enough oxygen in the muscles to break down glucose and glycogen. This is called anaerobic metabolism. Elevation of lactic acid in the circulation (normal plasma 4-1 5 mg/dl) may occur due to its increased production or decreased utilization.
- The term oxygen debt refers to the excess amount of 02 required to recover. In clinical practice, measurement of plasma lactic acid is useful to know about the oxygen debt and monitor the patient’s recovery.
Cancer and Glycolysis
- Cancer cells display increased uptake of glucose and glycolysis.
- As the tumors grow rapidly, the blood vessels are unable to supply adequate oxygen, and thus a condition of hypoxia exists. Due to this, anaerobic glycolysis predominantly occurs to supply energy.
- The cancer cells get adapted to hypoxic glycolysis through the involvement of a transcription factor namely hypoxia-inducible transcription factor (HIF). HIF increases the synthesis of glycolytic enzymes and the glucose transporter.
- However, the cancer cells cannot grow and survive without proper vascularization. One of the modalities of cancer treatment is to use drugs that can inhibit vascularization of tumors.
|
181 videos|346 docs
|
FAQs on Glycolysis - Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is glycolysis? |  |
| 2. What are the salient features of glycolysis? |  |
| 3. What are the reactions involved in glycolysis? |  |
| 4. What is muscle or anaerobic glycolysis? |  |
| 5. How much energy is yielded in glycolysis? |  |

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|

















