Worksheet Solutions: Financial Statements - I | Accountancy Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Fill in The Blanks |

|
| Match The Following |

|
| Objective Questions |

|
| Very Short Answer Type Question |

|
Fill in The Blanks
Q1: Under ____ concept, provision for doubtful debts is made.
Ans: Prudence or Conservatism
Q2: Closing stock is valued at ____ or ____ whichever is lower.
Ans: Cost price or market price
Q3: While making final accounts, prepaid expenses is subtracted from respective expenses in order to show ____ year expenses.
Ans: Current
Q4: Motor car of Rs. 1,00,000 was purchased on 1st October, 2018. Rate of Depreciation is 10%. Amount of depreciation to be shown in profit & Loss Account is Rs. ____
Ans: Rs. 5,000
Q5: Withdrawal of Goods by proprietor will be ____ from Purchases in trading account.
Ans: Deducted
Q6: Annual Insurance premium paid Rs. 10,000 on 1st October, 2017. Amount of insurance premium to be shown in profit & Loss account for the year ended 31st March, 2018 is Rs. ____ .
Ans: 5,000
Q7: Outstanding salary is Shown in balance sheet ____ Side.
Ans: Liabilities
Q8: Debtors of Rs. 8,60,000; Provision is to be created for doubtful debts @10%. Amount of provision in profit & Loss account will be Rs: ____ .
Ans: 86,000
Q9: Goods lost by theft will be deducted from ____ .
Ans: Purchase
Q10: A manager is entitled for a commission of 8% on net profit before charging such commission. Net profit before charging commission is Rs. 5,00,000. Amount of manager’s commission debited to profit & loss account is Rs____ .
Ans: 40,000
Q11: Sales is Rs. 1,20,000; Profit is 33 1/3 on cost. Amount of cost of goods sold will be Rs. ____ .
Ans: 90,000
Q12: Gross profit is Rs. 1,50,000. Selling expenses Rs. 10,000, commission paid Rs. 5,000, office expenses Rs. 20,000. Operating profit will be Rs ____ .
Ans: 1,15,000
Match The Following
Q1: Match the following expenses with their clarification
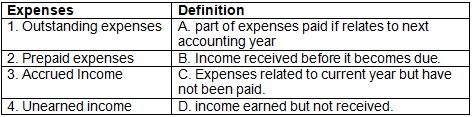
Ans: 1-C, 2-A, 3-D, 4-B
Q2: Match the items in their respective category:
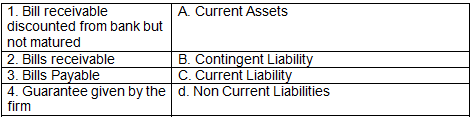
Ans: 1-B, 2-A, 3-C 4-B
Q3: Match the following transaction with their treatment in accounts:
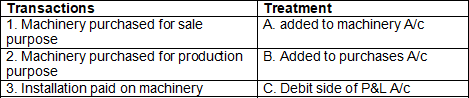
Ans: 1-B, 2&3-A
Q4: Match the following:
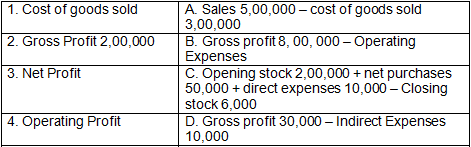
Ans: 1-C, 2-A, 3-D, 4-B
Q5: Match the following:
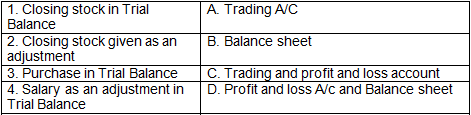
Ans: 1-B, 2-a&B 3-A, 4-D
Q6: Match the taxes levied on type of sales:

Ans: 1-D, 2-C, 3-B, 4-A
Q7: Match the effect of transaction on net profit:
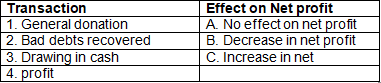
Ans: 1-B, 2- C, 3-A
Objective Questions
Q1: Provision for Doubtful Debts, in excess of the required provision, is credited to
(a) Debtors Account.
(b) Trading Account.
(c) Profit and Loss Account.
(d) Capital Account.
Ans: (c)
Q2: Final Accounts are prepared :
(a) At the end of calendar year
(b) At the end of Assessment year
(c) On every Diwali
(d) At the end of Accounting year
Ans: (d)
Q3: Following information is extracted from the Trial Balance of a business: Sales: Rs. 1,00,000; Purchase: Rs. 60,000; Wages Rs. 21,000.
Closing stock was Rs. 3,000 more than opening stock. One third of the wages was charged to cost of goods sold in the Trading Account. What was the Gross Profit?
(a) Rs. 30,000.
(b) Rs. 33,000.
(c) Rs. 36,000.
(d) Rs. 40,000.
Ans: (c)
Q4: In the Trial Balance, Sundry Debtors are shown at Rs. 2,25,000, Bad Debts Rs. 25,000 and Provision for Doubtful Debts Rs. 5,000. 5% Provision for Doubtful Debts is to be maintained and 2% Provision for Discount on debtors is to be made. The amount of Provision for Discount on Debtors would be
(a) Rs. 4,293.
(b) Rs. 4,500.
(c) Rs. 2,925.
(d) Rs. 4,275.
Ans: (c)
Q5: Trading and Profit and Loss Account is prepared :
(a) For a particular period
(b) On a particular date
(c) For the whole year
(d) None of above
Ans: (a)
Q6: Accrued Income, if given in the Trial Balance, is shown in
(a) Trading Account, as addition to the respective income.
(b) Profit and Loss Account, as addition to the respective income.
(c) Profit and Loss Account, as addition to the respective income and in the Balance Sheet, as an asset.
(d) Balance Sheet as an asset.
Ans: (d)
Q7: Balance Sheet is prepared :
(a) For a particular period
(b) On a particular date
(c) For the whole year
(d) None of the above
Ans: (b)
Q8: On 1st April, 2019 M/s Omega Bros., had a Provision for Doubtful Debts of Rs. 6,500. During 2019-20, Rs. 4,200 proved irrecoverable and it was decided to maintain the Provision for Doubtful Debts @ 5% on debtors which stood at Rs. 1,96,500 before writing off bad debts. Amount of net provision debited to Profit and Loss Account will be
(a) Rs. 9,500.
(b) Rs. 8,200.
(c) Rs. 6,500.
(d) Rs. 7,315.
Ans: (d)
Q9: Prepaid Expenses, if given in the Trial Balance, is shown in
(a) Trading Account, as deduction from the respective expense.
(b) Profit and Loss Account, as deduction from the respective expense.
(c) Trading and Profit and Loss Account, as deduction from the respective expense and in the Balance Sheet, as an asset.
(d) Balance Sheet.
Ans: (d)
Q10: Cost of Goods Sold Rs. 1,50,000; Closing Stock Rs.40,000; Opening Stock Rs.60,000; Amount of purchase will be
(a) Rs. 1,30,000
(b) Rs. 1,70,000
(c) Rs.50,000
(d) None of these
Ans: (a)
Q11: Income received in advance is deducted from the income because of
(a) Revenue Recognition Concept.
(b) Accrual Concept.
(c) Matching Concept.
(d) Prudence Concept.
Ans: (c)
Q12: Opening Stock Rs.8,500
Purchases Rs.30,700
Direct Wages Rs.4,800
Interest on Loan Rs.2,800
Closing Stock Rs.9,000
Cost of goods sold will be ____.
(a) Rs.30,000
(b) Rs.32,000
(c) Rs.35,000
(d) Rs.40,000
Ans: (c)
Q13: Capital Expenditure and Revenue Expenditure
(a) are distinguished.
(b) are not distinguished.
(c) may or may not be distinguished.
(d) must not be distinguished.
Ans: (a)
Q14: Capital Receipts and Revenue Receipts
(a) are distinguished.
(b) are not distinguished.
(c) may or may not be distinguished.
(d) must not be distinguished.
Ans: (a)
Q15: Balance of Provision for Doubtful Debts (As on 1st April, 2019): Rs. 1,250; Bad Debts during the year were: Rs. 300. Provision for Doubtful Debts is required @ 5% on debtors of Rs. 10,000. Provision for Doubtful Debts credited to Profit and Loss Account will be
(a) Rs. 400.
(b) Rs. 500.
(c) Rs. 600.
(d) Rs. 450.
Ans: (d)
Q16: Calculation of Operating profit
(a) Gross profit –(Office & Administration exp. + Selling & Distribution Exp.)
(b) Gross profit – (Office & Administration exp. – Selling & Distribution EXp.)
(c) Gross profit – (Factory exp. + Office & Administration exp. + Selling & Distribution Exp)
(d) Gross profit –(Office & Administration exp.+ Selling & Distribution Exp+ Direct Exp.)
Ans: (a)
Q17: Loss of goods by fire should be credited to
(a) Sales Account
(b) Loss Account
(c) Profit & Loss Account
(d) Purchases Account
Ans: (d)
Q18: Any expenditure incurred in installation of Machinery
(a) Deferred Revenue Expenditure
(b) Promotional Exp.
(c) Revenue Exp.
(d) Capital Exp.
Ans: (d)
Q19: Wages paid for erection of Machinery are debited to
(a) Deferred wages account
(b) Machinery Account
(c) Profit & Loss Account
(d) Wages Account
Ans: (b)
Q20: Preliminary exp. fall in which category
(a) Revenue Receipt
(b) Deferred Revenue expenditure
(c) Intangible assets
(d) Deferred Capital receipts
Ans: (b)
Q21: If opening stock is Rs. 30000, closing stock is Rs. 40000, Purchases are Rs. 80000, Direct Expenses Rs. 30000. What will be the value of Cost of Goods sold
(a) 10000
(b) 120000
(c) 90000
(d) 80000
Ans: (a)
Q22: If insurance premium paid Rs. 2000 and prepaid insurance is Rs. 300. The amount of insurance premium shown in profit & Loss Account will be ____.
(a) Rs. 2300
(b) Rs. 2000
(c) 1700
(d) 300
Ans: (c)
Q23: The manager is entitled to a commission of 10% on Net Profit after charging such commission. If Net profit is Rs. 110000, then manager’s commission will be :
(a) Rs. 11000
(b) Rs. 20000
(c) 10000
(d) None of these
Ans: (c)
Q24: If the wages paid Rs. 4000 and outstanding wages Rs. 500. The amount of wages shown in Trading account will be:
(a) Rs. 4500
(b) Rs. 3500
(c) 500
(d) None of these
Ans: (a)
Q25: What is the treatment of Discount on purchase?
(a) Debited to Trading Account
(b) Credited to Profit & Loss Account
(c) Debited to Profit & Loss Account
(d) None of these
Ans: (b)
Q26: Goods given as samples is debited to
(a) General Expenses
(b) Sales promotion exp.
(c) Staff welfare expenses
(d) None of these
Ans: (b)
Q27: Bad debts mentioned in Trial balance will be shown in
(a) Trading Account
(b) Assets
(c) Profit & Loss Account
(d) None of these
Ans: (c)
Q28: Wages and Salaries account is shown in
(a) Profit & loss Account
(b) Assets
(c) Trading Account
(d) None of these
Ans: (c)
Q29: Give true or false. Goodwill is a tangible asset
Ans: False
Q30: A balance sheet is arranged in a particular date and not for a particular accounting period.
Ans: True
Q31: Balance of petty cash is 1. Expenses 2. Income 3. Liability 4. Asset
Ans: Asset
Very Short Answer Type Question
Q1: Which are the statement that is included in the financial statement?
Ans: The statement that is included in the financial statement are.
- Balance Sheet
- Trading and Profit and Loss A/c
Q2: Which is gross profit?
Ans: Gross profit is the surplus of a selling price of a product over the cost of goods sold.
Q3: State the formula to calculate the cost of goods sold.
Ans: Cost of goods sold = Sales – Gross Profit Or Opening Stock + Purchases + Direct Expenses – Closing Stock
Q4: Give two characteristics of the balance sheet.
Ans: The two characteristics of the balance sheet are.
- Determine the financial position of the enterprise on a specific date
- The balance sheet has two sides Assets and Liabilities
|
61 videos|154 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet Solutions: Financial Statements - I - Accountancy Class 11 - Commerce
| 1. What are financial statements? |  |
| 2. What are the main types of financial statements? |  |
| 3. Why are financial statements important for businesses? |  |
| 4. How are financial statements prepared? |  |
| 5. What is the purpose of analyzing financial statements? |  |




















