Worksheet: Nature and Purpose of Business - 1 | Business Studies (BST) Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
MCQ Questions
Q1: One of the functions of financial intermediaries includes liability-asset transformation under which they accept deposits as liability and convert them into assets, such as loan.
(a) True
(b) False
(c) Can’t say
(d) Partially true
Q2: ____ includes activities which are connected with production, purchase and sale of goods with the aim of earning profit.
(a) Business
(b) Profession
(c) Employment
(d) Job
Q3: Go Earth Ltd. manufactures jute bags and its factory has been set-up in a residential area. The company has employed unskilled and semi-skilled workers and it pays them lower wages on the pretext of at least providing jobs as the employment opportunities in the area is quite limited. During the production process, lots of residu is left. In order to decrease cost and increase profitability, the company dumps this residu in the residential area which is sold after a substantial time gap.
This practice causes lot of inconvenience to the residents of that area. Identify and explain the objective of management which is ignored by the company.
(a) Organisational
(b) Social
(c) Personal
(d) All of the above
Q4: Name the two broad categories of business activities.
(a) Trade and Commerce
(b) Trade and Industry
(c) Industry and Commerce
(d) None of the above
Q5: The maritime route linked the east and the west by Sea and were used for the trade of spices is known as ____ .
(a) Sea route
(b) Spice route
(c) Railway route
(d) None of these
Q6: Mr. Naresh Batra a businessman, incurred some financial loss due to the dishonesty of his workers. This loss is caused due to ____ .
(a) natural
(b) financial
(c) human
(d) economic
Q7: Patliputra was popularly known as commercial centre for ____ .
(a) export of stones
(b) import of horses
(c) centre of learning
(d) centre of textiles
Q8: Match the various types of manufacturing industry given in column I with their respective example given in column II.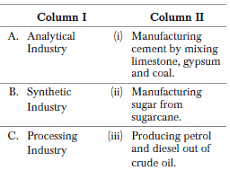
Codes A B C
(a) (i) (ii) (iii)
(b) (iii) (ii) (i)
(c) (iii) (i) (ii)
(d) (ii) (i) (iii)
Q9: Economic activities may be classified into business, ____ and employment.
(a) profession
(b) occupation
(c) vocation
(d) work
Q10: ____ is used for carrying out transactions in which money is passed from hand to hand in ancient times.
(a) Cheques
(b) Bill of exchange
(c) Hundi
(d) Demand draft
Q11: Identify the activity which is not an auxiliary to trade?
(a) Banking
(b) Warehousing
(c) Insurance
(d) Mining
Q12: Changes in market conditions, changes in price or changes in fashion and tastes of customers refer to which type of risk?
(a) Pure risk
(b) High risk
(c) Low risk
(d) Speculative risk
Q13: Industries like sugar mill or oil refinery are put under which category?
(a) Primary
(b) Secondary
(c) Tertiary
(d) None of these
Q14: Which of the following is not a true statement?
(a) The scope of commerce is narrower than business.
(b) Commerce includes trade and auxiliaries to trade.
(c) Foreign trade is purchase and sale by the traders of the same country.
(d) Traders serve as a link between producers and consumers.
Q15: Match the following.
Codes
A B C D
(a) (i) (ii) (iii) (iv)
(b) (iv) (iii) (i) (ii)
(c) (i) (iii) (iv) (ii)
(d) (iv) (i) (ii) (iii)
Q16: No business can survive without enough amount of funds. Banks are providing financial assistance to the businesses to overcome one of the following hindrance of trade.
(a) Hindrance of place
(b) Hindrance of time
(c) Hindrance of finance
(d) Hindrance of information
Q17: Which of the following is not a business activity?
(a) Production of goods
(b) Work in a factory for wages
(c) Exchange of goods
(d) Transportation
Q18: Name the occupation in which people work for others in return for wages or salaries?
(a) Employment
(b) Business
(c) Profession
(d) None of these
Q19: Which of the following is not a cause of business risk?
(a) Break down of machinery
(b) Efficient management
(c) Riot
(d) Changing government policy
Q20: Due to which characteristic of business, there is always a possibility of losses being incurred, despite the best efforts put into the business.
(a) Uncertainty of returns
(b) Production or procurement of goods and services
(c) Economic activity
(d) Profit earning
Q21: Which type of duty was used to be charged on imported articles by king in ancient times?
(a) Import Duty
(b) Sales Tax
(c) Export Duty
(d) Octroi
Q22: Earning of profit is considered to be the subsidiary objective of the business. The given statement is
(a) True
(b) False
(c) Can’t say
(d) Partially true
Q23: Unorganised sector is not directly controlled by the RBI. This sector includes money lenders, indigenous bankers, pawn brokers, traders and landlords.
(a) True
(b) False
(c) Can’t say
(d) Partially true
Q24: Which of the following is not an economic activity?
(a) Production
(b) Trading in goods
(c) Professional
(d) Social service
Q25: Why should a business earn profit?
(a) To provide return to investors.
(b) To provide funds for future growth
(c) To increase the reputation of business
(d) All of the above
Q26: Mr X started business of buying and selling of refrigerators. The business of Mr X will be considered as ____ .
(a) commerce
(b) trade
(c) selling
(d) transaction
Q27: Vijay Plastic Pvt. Ltd. are makers of plastic toys for children; earning a huge profit. A research conducted by The Indian Council of Child Welfare on the toys shows that colours used in manufacturing toys are harmful for the children. The test was conducted on toys manufactured by the company and case was filed against Vijay Plastic Pvt. Ltd. for using sub-standard colours.
However, managing director assured that the company will use standard colours only after certification from the research laboratory and the company will expand its production capacity by employing labour from unprivileged sections of the society. On the basis of the given information about Vijay Plastic Pvt. Ltd., specify the type of business activity performed by Vijay Plastic Pvt. Ltd.
(a) Trade
(b) Commerce
(c) Industry
(d) None of these
Q28: The possibilities of inadequate profits or even losses due to uncertainties are known as _____ .
(a) Business contingencies
(b) Business risks
(c) Business ventures
(d) None of the above
Q29: Arnav is working as sales executive in XYZ Limited Company. He is getting ` 40,000 per month. His job is to enhance the sale of the company. Identify which type of economic activity is highlighted in the case?
(a) Profession
(b) Employment
(c) Business
(d) None of these
Q30: GMR Industries entered the airports space in early 2000 and is today counted amongst the top 5 private airport developer and operators globally.
GMR Industries presently owns and operates Delhi International Airport and Hyderabad International Airport. Apart from being the largest private airport company in India, GMR Industries is the only Indian airport developer to have developed and operated airports outside India. Identify the type of industry being discussed in above case.
(a) Primary
(b) Secondary
(c) Tertiary
(d) None of the above
Q31: Which of the following is not a characteristic of business?
(a) Production
(b) Exchange or sale
(c) Wages or salaries
(d) Risk element
Q32: Which place was prominent for skilled artisans to work and convert raw material into finished goods which were high in demand?
(a) Village
(b) Karkhana
(c) Jhopari
(d) Chopal
Q33: Support services to industrial\business activities are clubbed under
(a) commercial industries
(b) secondary industries
(c) primary industries
(d) tertiary industries
Q34: There is a time gap between production and consumption of goods, therefore warehousing is required, which overcomes the problem of ____ .
(a) funds
(b) storage
(c) time
(d) place
Q35: Commerce includes activities relating to trade and ____ to trade.
(a) supporting
(b) subsidiaries
(c) auxiliaries
(d) None of these
Q36: Apoorvi, from a young age had a deep connection with traditional Indian textiles and craftsmanship. She fulfilled her life long dream of making a career in fashion by leaving her professional life behind and pursued a design programme at the Los Angeles School of Design and Merchandising.
Thus, Apoorvi got real world fashion exposure. With her love for Indian fabrics and her arsenal of fashion knowledge, she now intends to glorify these national treasures with her readymade store ‘Armaniya’.
‘Armaniya’ is an initiative to incorporate a perfect mix of latest trends, luxury fabrics, Indian traditional weaves and culture, all under one roof.
She manages the business along with two employees i.e., salesman and a cashier. She usually takes advice from her father in case of any managerial issue. Now-a-days, Apoorvi is facing a lot of problem as trends in the field are continuously changing, this ever-changing market along with strong competition has added to the trouble of declining sales.
Furthermore, One day Apoorvi found her cashier doing some embezzlement of funds. Which type of risk is she facing in the above said case?
(a) Pure risk
(b) Speculative risk
(c) Partial risk
(d) None of these
Q37: Advertising makes it possible for producers and trades to promote the goods and services available in the market, thus removing the hindrance of risk.
(a) True
(b) False
(c) Can’t say
(d) Partially false
Q38: “Greater the risk involved in a business, higher is the chance of profit”. This statement is true or false.
(a) True
(b) False
(c) Can’t say
(d) Partially false
Q39: Business risk generated out of carelessness or negligence of employees would emerge due to which of the following cause?
(a) Natural cause
(b) Human cause
(c) Economic cause
(d) Other cause
Q40: Mariah had done a diploma in fashion designing. She is very creative. She saw a picture of a party gown in an international fashion magazine, having a price tag of ₹ 50,000. She decided to make that gown herself with some customisation. She calculated that for making of gown, she has spent ₹ 4,000. Her friend liked the gown very much, so Mariah sold that gown to her friend for ₹ 8,500 and made a profit of ₹ 4,500.
Due to this transaction, Mariah decided to open a boutique of making gowns and selling them in the market with nominal profit. On the basis of the given information, identify the relevant feature of business highlighted here.
(a) Production of goods and services
(b) Profit earning
(c) Dealing in goods and services on regular basis
(d) Uncertainty of return
Q41: Neha cooks food at home for her family but Asha cooks food and sells it to others in a restaurant. Who is engaged in business activity?
(a) Neha
(b) Asha
(c) Both Neha and Asha
(d) None of these
Q42: Katherine wants to start a retail business of fashion items but changes in taste and preferences of customers may result in loss in such type of business.
She is hesitating as she is aware of risks which are inherent in every business. She approaches her friend Kristina who is the owner of a retail shop. Kristina advises her to go ahead with her idea as she will get profit as return for undertaking risk. She also told her that some risks in business can be insured by taking insurance policy.
On the basis of the given information about Katherine, identify the main features of business risk discussed in the above case.
(a) Uncertainties
(b) Degree of risk depends upon nature of business
(c) Size of business
(d) None of the above
Q43: Monica Khanna is a jewellery designer. She started her career from the scratch and took advanced designing course at jewellry product development center. On the completion of the course, she got a job at Gitanjali Gems. Being an experienced jewellery designer, Monica Khanna focuses on maintaining the originality and creativity of the ornaments that are custom designed and developed by her.
On the basis of the given information about Monica Khanna, identify the type of economic activity that Monica Khanna is engaged in.
(a) Profession
(b) Business
(c) Employment
(d) All of these
Q44: Which one is considered with production or processing of goods and materials?
(a) Trade
(b) Industry
(c) Commerce
(d) None of these
Q45: The process of exchanging ideas, information by speaking, writing etc. is termed as
(a) Sender
(b) Medium
(c) Communication
(d) None of the above
Q46: Mr. Y told Mr. T that for business, we need physical resources. Identify the physical resources given below.
(a) Bank
(b) Warehouse
(c) Plant and machinery
(d) None of these
Q47: Which auxiliary to trade bridges the time gap between production and consumption?
(a) Advertising
(b) Banking
(c) Insurance
(d) Warehousing
Q48: Match the various types of Industries given in column I with their respective example given in column II.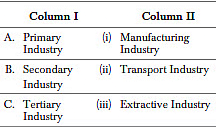
Codes A B C
(a) (iii) (i) (ii)
(b) (ii) (i) (iii)
(c) (i) (ii) (iii)
(d) (iii) (ii) (i)
Q49: Occupation in which people work for others and get salary or wages in return is termed as business.
(a) True
(b) False
(c) Can’t say
(d) Partially true
Q50: The type of industry which is engaged in breeding plants and animals for their use in further reproduction is ____ .
(a) extractive industry
(b) manufacturing industry
(c) genetic industry
(d) construction industry
Q51: Following are the characteristics of business risks. Identify the incorrect one.
(a) Loss is the reward for risk bearing.
(b) Business risks are due to uncertainties.
(c) Risk is an essential component of every business.
(d) Degree of risk depends mainly upon the nature and size of business.
Q52: Start-ups are usually small and initially financed and operated by a handful of founders or one individual.
These companies offer a product or service that is not currently being offered elsewhere in the market, or that the founders believe that it is being offered in an inferior manner. What does it take to Start-ups? A brilliant idea? A great team? Money?
Yes. All of those things. But more than anything what it takes, is belief. A belief that there is significance to the problem being addressed, and that the solution is something which the consumer wants. It is really amazing how most large companies have such humble stories of starting up.
All of them started with nothing but just plain conviction. Even with such conviction, they fail because of an inherent factor present in business. On the basis of the given information about Start-ups, Identify this inherent factor which leads to failure of business enterprise.
(a) Industry
(b) More of import trade
(c) Business risk
(d) None of the above
Q53: Match the various causes of business risk in column I with their respective statement in column II.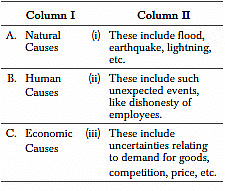
Codes A B C
(a) (i) (ii) (iii)
(b) (ii) (i) (iii)
(c) (iii) (ii) (i)
(d) (ii) (iii) (i)
Q54: The best example of analytical industry is
(a) cement
(b) computer
(c) sugar mill
(d) oil refinery
Q55: Human activities are of ……… types.
(a) one
(b) two
(c) three
(d) four
Q56: Mechanical failures, political disturbances and other unforeseen events are
(a) natural causes
(b) economic causes
(c) human causes
(d) other causes
Q57: Rohit and Gurvinder are partners selling electronic products across India. They import the components from their friend Atul who operates his business from China and assembles them in their factory established in a rural area of Jharkhand. Most of the workers in the factory are children and women.
They are paid very less salaries thus owners save on labour cost. They store their stocks in a warehouse but do not take proper safety measures against fire, burglary etc. There was a short circuit in the factory and as a result most of the stock was damaged.
On the basis of the given information about Rohit and Gurvinder, specify the type of business activity being performed by Atul.
(a) Import trade
(b) Entrepot trade
(c) Industry
(d) Export trade
Q58: Transfer of interest exists in the case of
(a) profession
(b) employment
(c) business
(d) None of these
Q59: Match the concepts in column I with their respective statement in column II.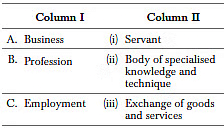
Codes A B C
(a) (i) (ii) (iii)
(b) (ii) (i) (iii)
(c) (iii) (i) (ii)
(d) (iii) (ii) (i)
Q60: In which form of economic activity, code of conduct is prescribed?
(a) Business
(b) Employment
(c) Profession
(d) None of these
Q61: Chettis community is specialised in trading and moving from one place to another place, sometimes with thousands of oxen, heavily loaded with food grains, salt and other daily use stuff.
(a) True
(b) False
(c) Can’t say
(d) Partially false
Q62: Which of the following cannot be classified as an objective of business?
(a) Investment
(b) Productivity
(c) Discovery
(d) Profit earning
Q63: The lack of knowledge about what is going to happen in the future is
(a) risk
(b) uncertainty
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Q64: The industry concerned with using the material which have already been extracted at the primary stage is
(a) primary industry
(b) tertiary industry
(c) secondary industry
(d) None of these
Q65: Match the concepts in column I with their respective statement in column II.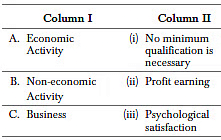
Codes A B C
(a) (i) (ii) (iii)
(b) (ii) (iii) (i)
(c) (ii) (i) (iii)
(d) (i) (iii) (ii)
Q66: Which of the following comes under economic causes of risk?
(a) Flood, famine
(b) Negligence of workers, stoppage of work
(c) Demand for goods, competition
(d) None of the above
Q67: Recognise the assembling industry out of these.
(a) Poultry, cattlefarms
(b) Cement, brick
(c) Sugar, cotton
(d) Television, computer
Q68: The position of an enterprise in relation to its competitors is termed as
(a) Market survival
(b) Growth
(c) Market standing
(d) None of the above
Q69: Profit can be re-invested in business. It is a good source of finance for expansion and growth of business.
(a) True
(b) False
(c) Can’t say
(d) Partially true
Q70: The amount of loss or damage and compensation for injury can be recovered by using which auxiliary to trade?
(a) Advertising
(b) Premium
(c) Insurance
(d) Policy
Q71: The banking system in India dated back to 1750 BC. In ancient India, there is evidence of loans from the Vedic period. From the writing of many foreign travellers during Mughal period we came to know about the use of various instruments in the then great commercial centres. In the Mughal period, historians found the evidence of loan deeds which were called dastawez. There were two types of dastawez – one was payable on demand and other was payable after a stipulated time. The most important class of credit instruments of exchange evolved in India at that time. Their use was most widespread in the twelfth century, and has continued till today.
On the basis of the given information about the banking system in India, identify the instrument of exchange prominent in the great ancient commercial centres of India.
(a) Bills of exchange
(b) Hundi
(c) Promissory note
(d) None of these
Q72: Activities which are meant for assisting trade are known as
(a) Trade
(b) Trade assistance
(c) Auxiliaries to trade
(d) None of these
Q73: The obligation of business firms to contribute for society and work for it refers to
(a) social responsibility
(b) human responsibility
(c) company responsibility
(d) None of the above
Q74: Sunstar Steel Ltd., a leading manufacturer of iron and steel decided to setup a new factory in a remote area in Rajasthan, so that unemployed youth from the rural areas could get same opportunities as those available in the urban areas.
This initiative has raised the standard of living of people in rural areas. All children in these families are getting good education and these families are also actively contributing to nation building process through their dedicated work. On the basis of the given information, identify the objective of business being followed by the company.
(a) Organisational
(b) Social
(c) Personal
(d) All of the above
Q75: Sunstar Steel Ltd., a leading manufacturer of iron and steel decided to setup a new factory in a remote area in Rajasthan, so that unemployed youth from the rural areas could get same opportunities as those available in the urban areas. This initiative has raised the standard of living of people in rural areas. All children in these families are getting good education and these families are also actively contributing to nation building process through their dedicated work. Identify the activity discussed in the given case.
(a) Economic
(b) Non-economic
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Q76: The production of goods takes place in particular locations but they are used at different places. So, the obstacle of place is removed by
(a) banking
(b) advertising
(c) insurance
(d) transport
Q77: Which one of the following may not be a factor behind starting a business?
(a) Routine workload
(b) Size of the firm
(c) Finance
(d) Location of the business
Q78: It was in the early 1970s, when Sh. M.P. Sharma started the journey towards a brighter future. Then the small sweet shop has now flourished into a family owned enterprise which consists of many outlets in Delhi. These outlets serve sweets and cuisines spanning Indian, Continental, Chinese, South Indian and Regional foods. Mehar Sweets follows the casual dining concept and provides a warm and hospitable ambience in the outlets.
Today, Mehar Sweets is a food business group with special ventures focused on Bengali Sweets and Multicuisine. During Diwali season this year, the shop owner employed women and children to meeting urgent orders and paid there marginal and limited salary. He prepared more Bengali Sweets then what he had sold last year. This way, Mehar Sweets generated more than the expected profit. On the basis of the given information about Mehar Sweets, which objective of business is not being fulfilled?
(a) Organisational
(b) Social
(c) Personal
(d) All of these
Q79: The merchant community derived power and prestige from guilds. Even kings were supposed to accept and respect the rules of these guilds. The guild chief dealt directly with the king or tax collectors and settled the market toll on behalf of its fellow merchants at a fixed sum of money.
The guild merchants also acted as custodians of religious interests. They undertook the task of building temples and made donations by levying a corporate tax on their members. The commercial activity enabled big merchants to gain power in the society. Identify the guild being specified in the above case.
(a) Intermediaries
(b) Zamindars
(c) Merchant corporations
(d) None of the above
Q80: Which of the following is not an example of non-economic activity?
(a) Patriotism
(b) Teaching
(c) Sentiment
(d) Sympathy
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Name the economic activity which involves specialised knowledge and in which entry is restricted.
Q2: Name any two professions and professionals.
Q3: Differentiate between business, profession and employment on the basis of reward/return.
Q4: Name the risk which involves both the possibility of loss as well as the possibility of profit.
Q5: Devesh is planning to set up a factory for manufacturing ready-made garments. List any two risks that he might face.
Q6: Name the industry which is concerned with extraction of natural resources and reproduction of living organisms.
Q7: Mention two types of primary industries.
Q8: Name the industries which is concerned with using the materials extracted at the primary stage to manufacture goods either for final consumption or for further processing by other industrial companies.
Q9: Name the industries which provide various support services to primary and secondary industries.
Q10: Name two broad categories into which various business activities can be classified.
Q11: Give any two examples of extractive industries
Q12: Give two example of manufacturing industries.
Q13: Name the type of manufacturing industry in which one material is separated into several useful products.
Q14: Name the type of industry which combines various ingredients to form a new product.
Q15: Name the type of manufacturing industry in which a raw material is processed through various stages of production for obtaining finished products.
Q16: Name the type of manufacturing industry in which manufactured parts are brought together to produce a new product?
Q17: Internal or inland trade may be classified into two categories. Name the category which involves buying and selling of goods in bulk quantities.
Q18: Name the auxiliary to trade which removes the hindrance of place.
You can access the solutions to this worksheet here.
|
38 videos|269 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet: Nature and Purpose of Business - 1 - Business Studies (BST) Class 11 - Commerce
| 1. What is the primary purpose of a business? |  |
| 2. How does the nature of business differ between goods and services? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of businesses based on ownership? |  |
| 4. Why is understanding the nature of business important for entrepreneurs? |  |
| 5. What role does competition play in the business environment? |  |

















