Worksheet Solutions: Accounting for Not-for-Profit Organizations | Accountancy Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
Q1: Differentiate between ‘Receipts and Payments Account’ and ‘Income and Expenditure Account’ on the basis of ‘Period’.
Ans: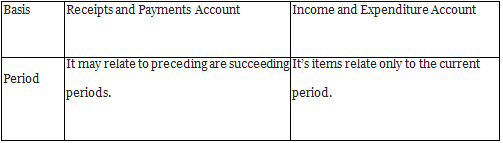
Q2: What is meant by ‘Life membership fees’?
Ans: Life membership fee is the lumpsum amount paid by members instead of paying periodic subscription.
Q3: State the main aim of a not-for-profit organisation.
Ans: Such organisations are formed to provide services such as education, health care, recreation, etc free of cost or at nominal cost.
Q4: How is life membership fee treated while preparing the financial statements of a not-for-profit organisation?
Ans: It will be added to capital fund on the liabilities side of balance sheet.
Q5: How are specific donations treated while preparing final accounts of a ‘Not-for-Profit Organisation’?
Ans: Specific donations are recorded on receipt side of receipts and payments account and liabilities side in the balance sheet.
Q6: State the basis of accounting of preparing ‘Income and Expenditure Account’ of a ‘Not-for-Profit Organisation’.
Ans: It is prepared following accrual basis of accounting.
Q7: Not-for-profit organisations have some distinguishing features from that of profit organisations. State any one of them.
Ans: Such organisations are formed not to earn profits but to provide service such as education, healthcare, recreation, sports, etc either free of cost, or at nominal cost.
Q8: Give two main sources of income of not-for-profit organisations.
Ans: Two main sources of their income are
- Subscriptions from their members
- Membership fees/entrance fees
Q9: Name any two financial statements required to be prepared by not-for-profit organisations at the end of the year.
Ans:
- Income and expenditure account
- Balance sheet
Q10: Unrestricted funds raised by non-profit organisations through various sources are credited to which account?
Ans: Fund raised by non-profit organisations through various sources are credited to ‘Capital Fund’ or ‘General Fund’.
Q11: What is the capital of a non-profit organisation generally known as?
Ans: Accumulated fund or Capital fund.
Q12: From the following information, calculate the amount of subscriptions received by Happy Sports Club during the year ended 31st March, 2018.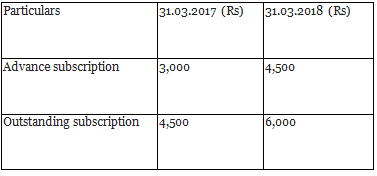
The Club has 2,000 members each paying an annual subscription of Rs 500.
Ans:
Q13: Calculate the amount of stationery to be debited to ‘Income and Expenditure Account’ of New Friends Club for the year ended 31st March, 2018. Also present the relevant information in the Balance Sheet of the Club as at 31st March, 2018.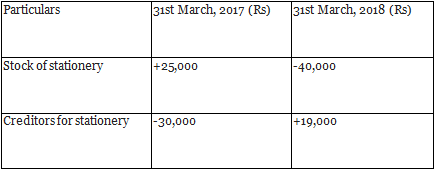
During the year Rs 46,000 were paid to the creditors for stationery and stationery of Rs 6,000 was purchased in cash.
Ans: 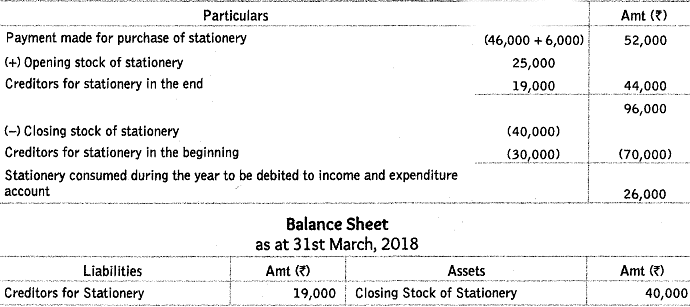
Q14: From the following information, calculate the amount of ‘Sports Material’ to be debited to Income and Expenditure Account of Young Football Club for the year ended 31st March, 2018.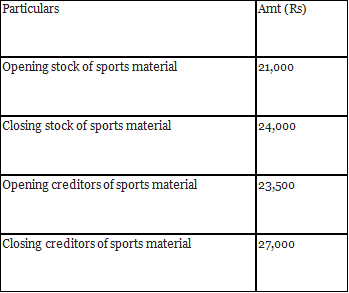
During the year, the creditors for sports material were paid ₹ 1,10,000.
Ans: Calculation of Sports Material to be Debited to Income and Expenditure Account.
Q15: From the following information, calculate the amount of sports material consumed by Durga Sports Club for the year ended 31st March, 2018.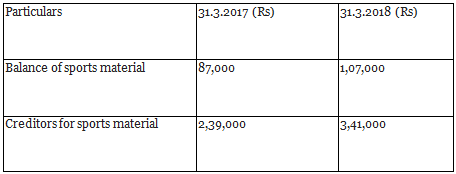
During the year, sports material purchased was ₹ 4,94,000.
Ans:
Q16: From the following information, calculate the amount of stationery consumed by Shree Club for the year ended 31st March, 2018.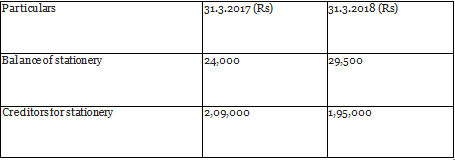
During the year, creditors were paid ₹ 3,00,000. (All India 2019)
Ans:
Q17: From the following information, calculate the amount of medicines to be debited to ‘Income and Expenditure Account’ of a Charitable Hospital for the year ended 31st March, 2018. Also present the relevant information in the Balance Sheet of the hospital; as at 31st March, 2018.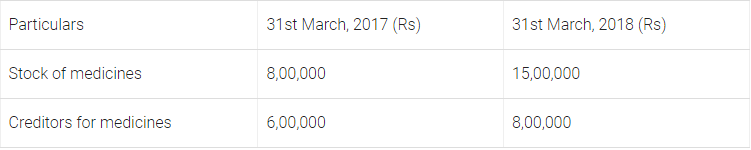
Cash paid to the creditors of medicines during the year was ₹ 25,00,000.
Ans: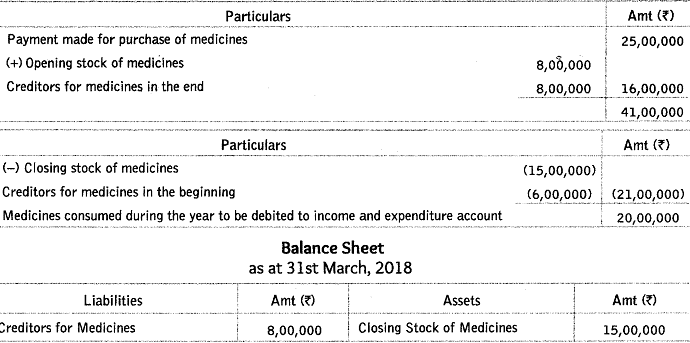
Q18: Janta Kalayan Club has 1,250 members each paying an annual subscription of? 150. During the year ended 31st March, 2018 the club did not receive subscription from 45 members and received subscriptions in advance from 46 members for the year ending 31st March, 2019. On 31st March, 2017 the outstanding subscriptions were ₹ 15,000 and subscriptions received in advance were ₹ 3,000.
Calculate the amount of subscription that will be debited to the Receipts and Payments Account for the year ended 31st March, 2018.
Ans: Calculation of amount of subscription received for the year ended 31st March, 2018
Q19: How the following items for the year ended 31st March, 2018 will be presented in the financial statements of Aisko Club.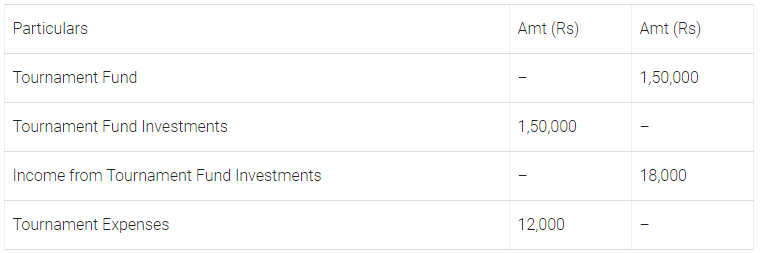
Additional Information:
Interest accrued on tournament fund investments Rs 6,000. Delhi 2019
Ans: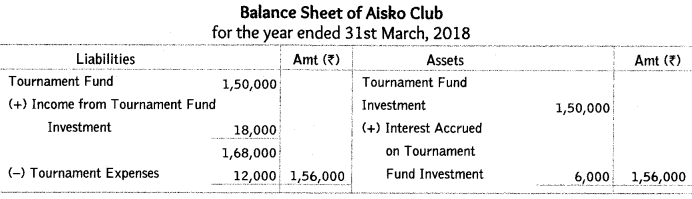
Q20: Present the following information for the year ended 31st March, 2018 in the financial statements of a not-for-profit organisation.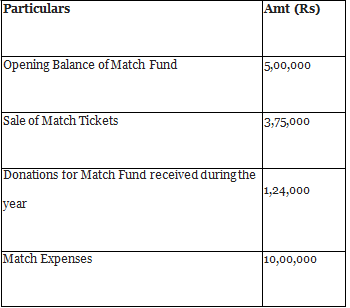
Ans: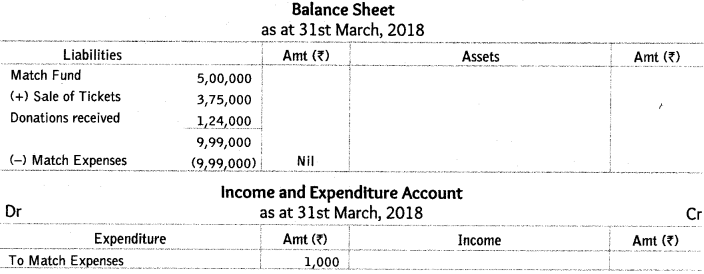
NOTE As match expenses are greater than match fund.
Excess amount of expenses will be charged from income and expenditure account.
Q21: From the following information, calculate the amount of subscriptions outstanding as at 31st March, 2009.
A club has 250 members each paying an annual subscription of ₹ 1,000. The receipts and payments account for the year showed a sum of ₹ 2,65,000 received as subscriptions. The following additional information is provided
Subscriptions outstanding on 31st March, 2008 – 40000
Subscriptions received in advance on 31st March, 2009 – 30000
Subscriptions received in advance on 31st March, 2008 – 12000
Ans: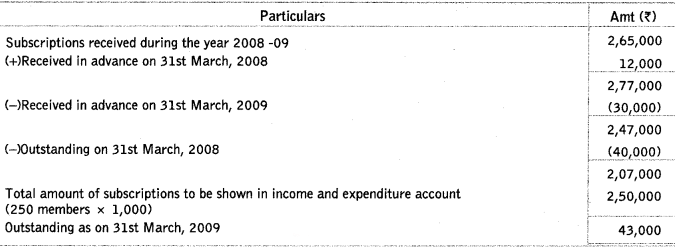
Q22: State the meaning of non-profit organisation.
Ans: Not-for-profit organisations are those organisations whose objective is not to earn profit but to provide services to its members and to the society. These organisations are set up for the welfare of the society as a whole, rather than for the benefit of any one individual and are set up for the purpose of promoting culture, art, religion, education, etc. e.g. Clubs, hospitals, libraries, schools, societies for promotion of sports, arts and culture, etc.
Q23: What is the capital fund? How is it calculated?
Ans: In case of not-for-profit organisation, capital fund can be considered as excess of its assets over its liabilities. Any surplus or deficit ascertained from income and expenditure account is added to (deducted from) the capital fund. This is also termed as accumulated fund.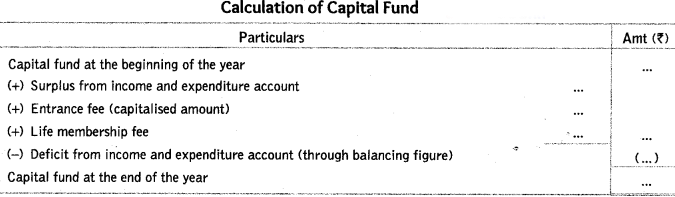
Q24: What is subscription? How is it calculated?
Ans: It is the membership fee paid by the members on annual basis. It is the main source of income of non-profit organisations.
Q25: Show the treatment of the following items by a not-for-profit organisation.
(i) Annual subscription
(ii) Specific donation
(iii) Sale of fixed assets
(iv) Sale of old periodicals
(v) Sale of sports material
(vi) Life membership fees
Ans: (i) Annual subscription is shown on the credit side of income and expenditure account.
(ii) It is to be capitalised and shown on the liabilities side of balance sheet.
(iii) Amount received from sale of old assets is debited to receipts and payments account. Any profit on sale of asset is credited and any loss on sale of asset is debited to income and expenditure account.
(iv) Amount realised from the sale of periodicals should be shown on the credit, i.e. income side of income and expenditure account.
(v) It is shown as an income in the income and expenditure account of a sports club.
(vi) It is treated as a capital receipt and added to the capital fund/general fund on the liabilities side of balance sheet, or is shown as a separate head in the liabilities side.
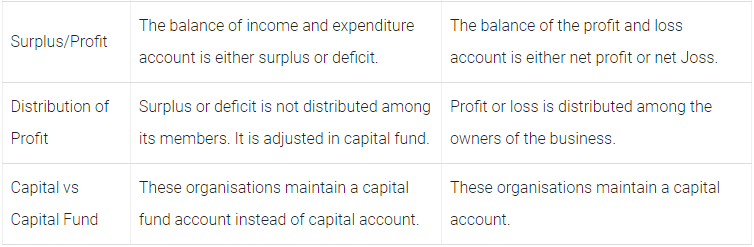
Q26: Distinguish between not-for-profit organisations and profit earning organisations.
Ans: The differences between not-for-profit organisations and profit earning organisations are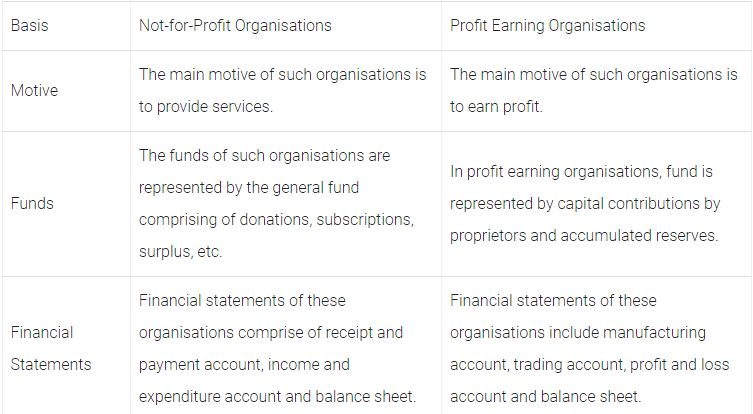
Q27: Is entrance/admission fees a revenue receipt?
Ans: Yes, it is a revenue receipt.
Q28: State the nature of receipts and payments account.
Ans: It is a real account.
Q29: Name the account which shows the classified summary of transactions of a cash book in a not-for-profit organisation.
Ans: Receipts and payments account.
Q30: Why adjustments for outstanding expenses, prepaid expenses or depreciation are not made in the receipts and payments account?
Ans: Adjustments for outstanding expenses, prepaid expenses or depreciation are not made in the receipts and payments account because receipts and payment account is prepared on cash basis of accounting.
Q31: State the basis of accounting, on which a receipts and payments account is prepared in case of not-for-profit organisation.
Ans: It is prepared on cash basis of accounting.
Q32: Can the balance in receipts and payments account be treated as income of the period?
Ans: No, as the balance in receipts and payments account is closing cash and bank balance.
Q33: Every receipt and payment, whether capital or revenue and irrespective of the period is recorded in receipts and payments account. Why? Give reason.
Ans: It is so because receipts and payments account is prepared on cash basis of accounting.
Q34: Explain the statement, ‘receipts and payments account is a summarised version of cash book’.
Ans: Receipts and payments account is a summary of the cash book. This account is generally prepared by non-profit organisations. All cash receipts are recorded on the receipts side (i.e. debit side) and all cash payments are recorded on the payments side (i.e. credit side) of receipts and payments account. It begins with the opening balance of cash and bank and ends with the closing balances of cash and bank (balancing figure) at the end of the accounting period. It records all the cash and bank transactions, both of capital and revenue nature, which may relate not only to the current period but also to the previous or next accounting period. This account helps an NPO in ascertaining closing cash balance. It is referred to assummarised version of cash book.
Q35: What are the features of receipts and payments account?
Ans: The features of receipts and payments account are
- Nature Receipts and payments account is a real account in nature.
- Period In this account, all receipts and payments, irrespective of the period to which they pertain, are shown.
- Capital and Revenue All cash receipts and cash payments whether of capital nature or of revenue nature are included.
- Banking Transactions Receipts/payments made through bank are also recorded.
- Non-cash Items Non-cash items such as depreciation, outstanding expenses, accrued income, etc., are not shown in this account.
- Opening and Closing Balance It begins with opening balance of cash in hand and cash at bank or bank overdraft and closes with the year end balance of cash in hand and cash at bank or bank overdraft.
Q36: From the following particulars relating to Royals Club, New Delhi, prepare a receipts and payments account for the year ending 31st March, 2016.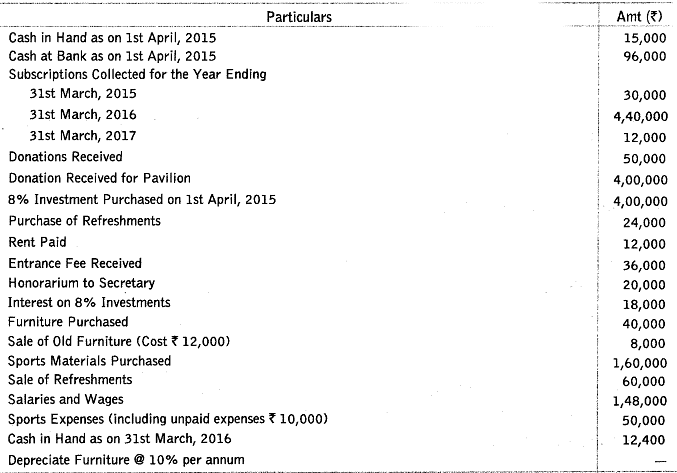
Ans: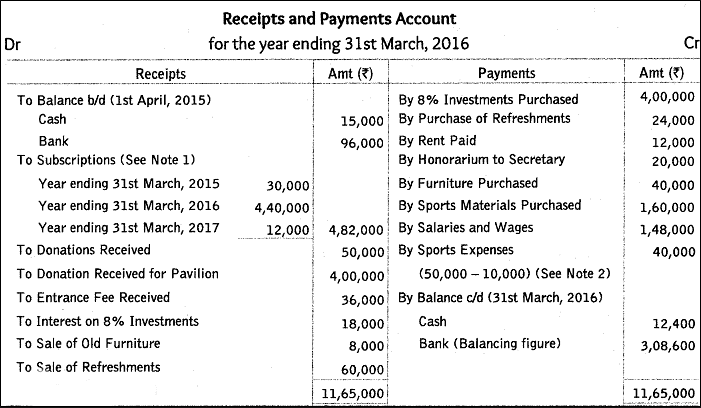
Q37: Where is general donation received shown in the final accounts of a non-profit organisation?
Ans: It is shown on the credit side of the income and expenditure account.
Q38: Where will you record the life membership fees while preparing the final accounts of non-profit organisation?
Ans: It will be added to capital fund on the liabilities side of balance sheet.
Q39: Income and expenditure account is prepared following which basis of accounting?
Ans: It is prepared following accrual basis of accounting.
Q40: State the nature of income and expenditure account.
Ans: It is a nominal account.
Q41: Write one difference between ‘receipts and payments account’ and ‘income and expenditure account’.
Ans: Receipts and payments account is prepared on cash basis and the income and expenditure account is prepared on accrual basis of accounting.
Q42: Receipts and payments account and income and expenditure account have a similarity between them. State the similarity.
Ans: Both are prepared by non-profit organisations.
Q43: How is capital fund of a non-profit organisation calculated if it is not given in the question?
Ans: Capital fund is calculated by preparing an opening balance sheet.
Q44: What is the amount or property received by a non-profit organisation as stated by the will of a deceased person commonly known as?
Ans: Legacy
Q45: Name the account which is similar to profit and loss account in case of a not-for-profit organisation.
Ans: Income and expenditure account.
Q46: All the revenue items relating to the current accounting period are shown in income and expenditure account. Why?
Ans: It is so because it is prepared on accrual basis of accounting.
Q47: Name the term used for denoting ‘excess of income over expenditure’ in case of non-profit organisations.
Ans: Surplus
Q48: What is the term given to excess of expenditure over income in case of non-profit organisations?
Ans: Deficit
Q49: Honorarium is a kind of remuneration paid to a person who is not the employee of a non-profit organisation. What kind of expenditure is it?
Ans: It is a revenue expenditure.
Q50: ‘Income and expenditure account of a not-for-profit organisation is akin to profit and loss account of a business concern.” Explain the statement,
Ans: Income and expenditure account is prepared by a non-profit organisation and is a summary of income and expenditure of the accounting year. Income and expenditure account is akin to profit and loss account because of the following similarities which are observed amongst these accounts
- Both are nominal accounts.
- Both are prepared on accrual basis.
- Both record revenue items related to current accounting year only.
- In both the accounts, expenses and losses are recorded on the debit side and incomes and gains are recorded on the credit side.
Q51: Explain the basic features of income and expenditure account,
Ans: The basic features of income and expenditure account are
- Nature It is a nominal account.
- Capital Items No capital items are recorded in this account.
- Debit and Credit Sides Its debit side includes all the expenses pertaining to the particular period and credit side includes all the income pertaining to the same period.
- Opening and Closing Balances No opening and closing balances are recorded in it.
- Only Current Period Items No item, either revenue or expenditure, pertaining to the past period or the future period is entered in this account.
- Similar to Profit and Loss Account This account is prepared in the same manner in which a profit and loss account is prepared.
- Surplus/Deficit Credit balance is called surplus, i.e. ‘excess of income over expenditure’ and debit balance is called deficit, i.e. ‘excess of expenditure over income’, i.e. deficit.
Q52: Show the treatment of items of income and expenditure account when there is a specific fund for those items.
Ans: Certain special funds are created for certain purposes/activities, e.g. Prize funds, match fund, sports fund, etc. The income earned from such funds (e.g. interest on investment for which investment fund is maintained) is added to the respective fund (i.e. investment fund) and not credited to income and expenditure account and also the expenses incurred on such specific purposes (e.g. tournament expenses for which tournament fund is maintained) are also deducted from the special fund (i.e. tournament).
Q53: Distinguish between income and expenditure account and profit and loss account.
Ans: The differences between income and expenditure account and profit and loss account are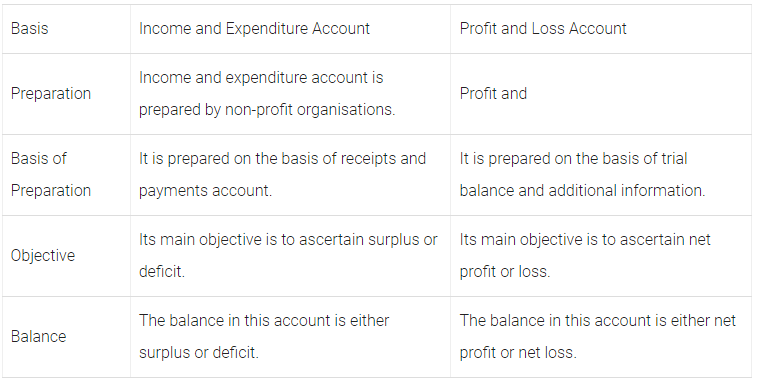
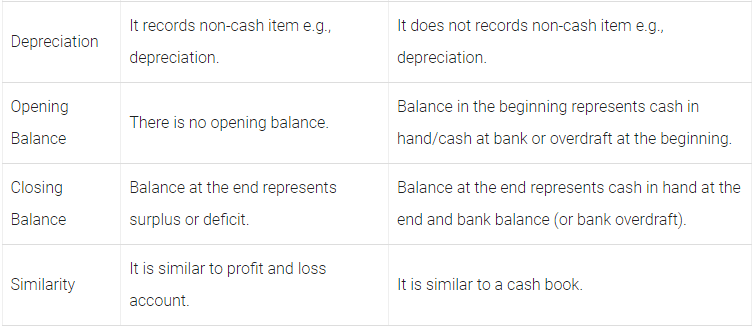
Q54: Distinguish between income and expenditure account and receipts and payment account.
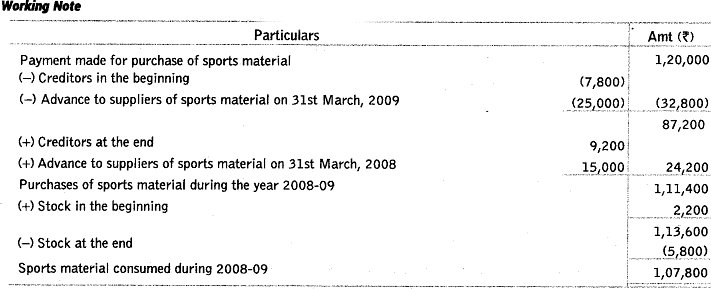
Ans: The differences between income and expenditure account and receipts and payments account are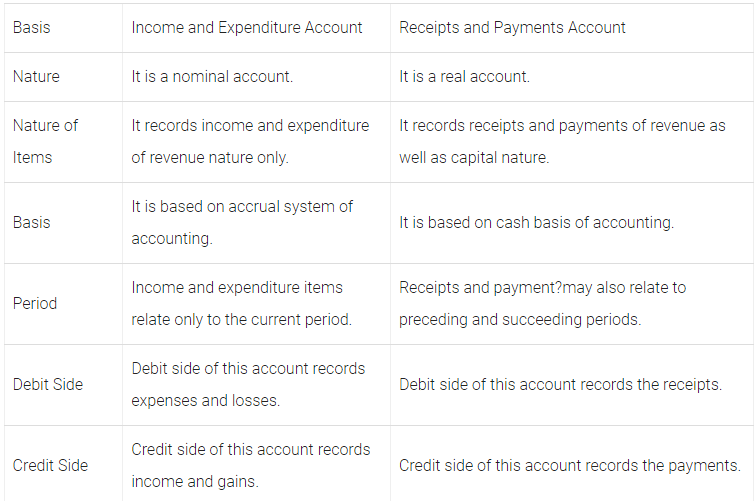
Q55: From the following information of a not-for-profit organisation, show the ‘sports material’ items in the ‘income and expenditure account’ for the year ending 31st March, 2009 and the balance sheets as at 31st March, 2008 and 31st March, 2009.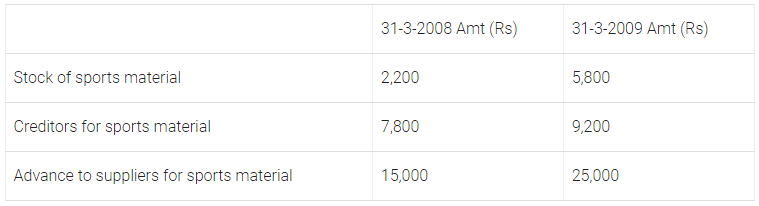
Payment to suppliers for the sports material during the year was ₹ 1,20,000, there were no cash purchases made.
Ans: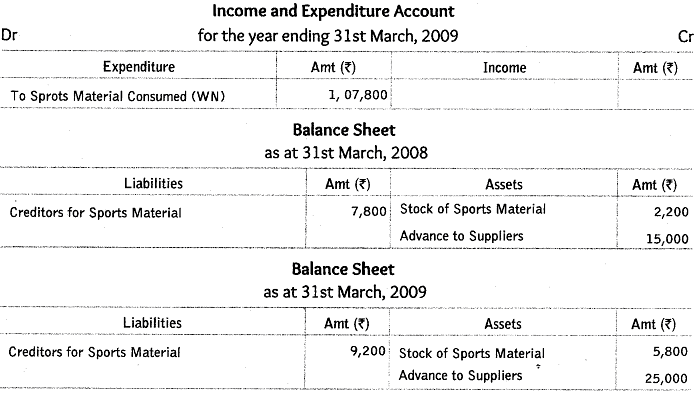
Q56: Prom the following information of Gems Club, prepare income and expenditure account for the year ended 31st March, 2018.
Receipts and Payments Account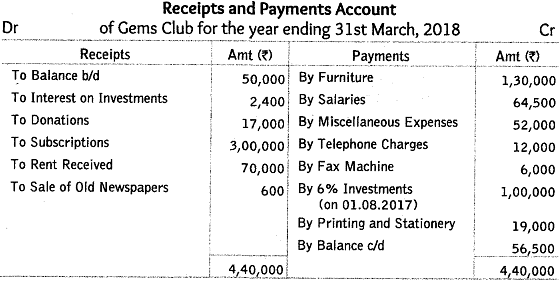
Additional Information:
Subscriptions received included ₹ 15,000 for 2018-19. The amount of subscriptions outstanding on 31st March, 2018 were ₹ 20,000. Salaries unpaid on 31st March, 2018 were ₹ 8,000 and rent receivable was ₹ 2,000. Opening stock of printing and stationery was ₹ 12,000, whereas closing stock was ₹ 15,000.
Ans: In the books of Gems Club Income and Expenditure Account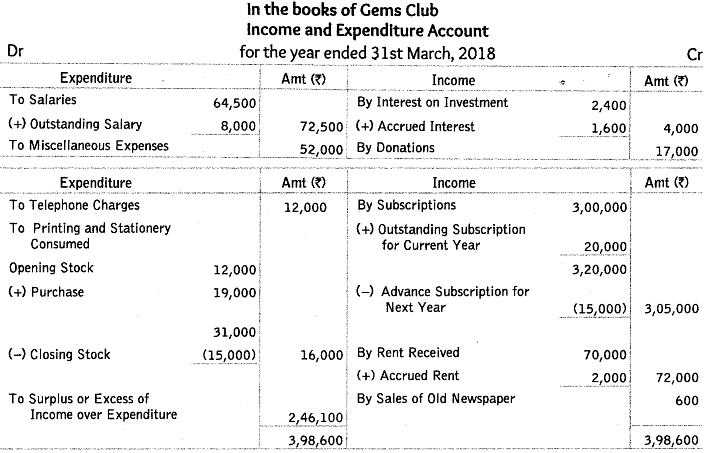
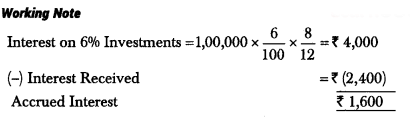
Q57: From the following receipts and payments account and additional information of swachh Bharat Club, New Delhi for the year ended 31st March, 2018, prepare income and expenditure account and balance aheet.
Receipts and Payments Account of Swachh Bharat Club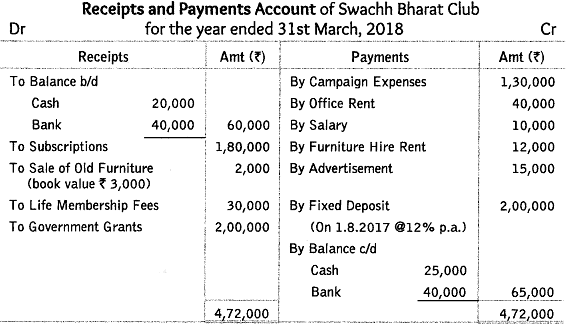
Additional Information:
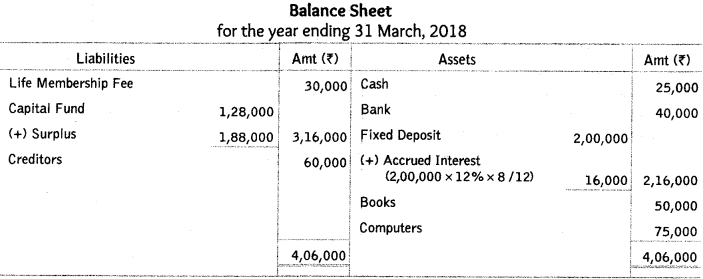
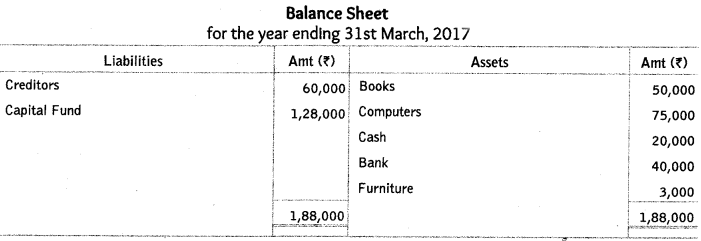
Assets on 1.4.2017 were Books ₹ 50,000; Computers ₹ 75,000. liabilities and Capital fund on 1.4.2017 were Creditors ₹ 60,000; Capital fund ₹ 1,28,000.
Ans:
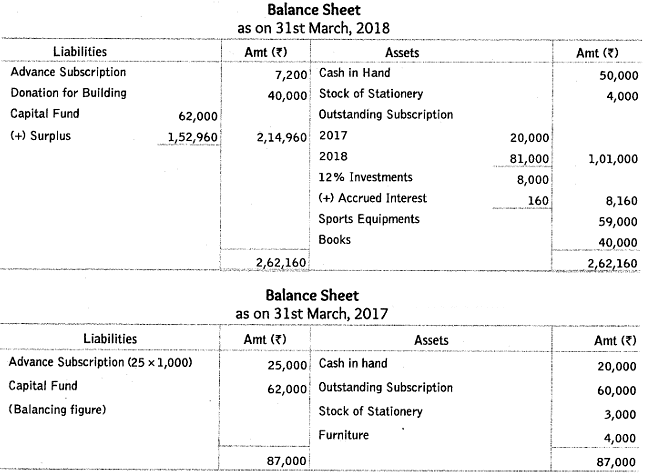
Q58: From the following receipts and payments account and additional information, prepare income and expenditure account and balance sheet of Sears Club, Noida as on 31st March, 2018.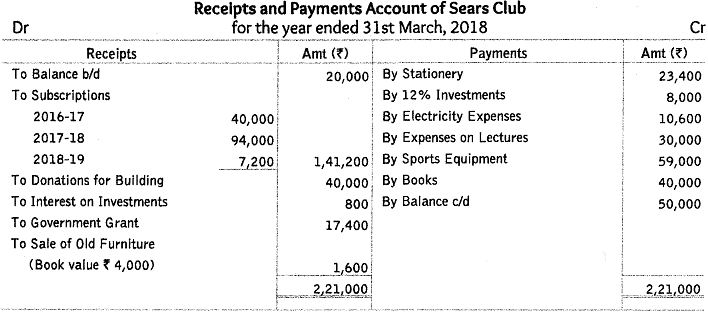
Additional Information:
(i) The club has 200 members each paying an annual subscription of ₹ 1,000. ₹ 60,000 were in arrears for last year and 25 members paid in advance in the last year for the current year.
(ii) Stock of stationery on 1-4-2017 was ₹ 3,000 and 31-3-2018 was ₹ 4,000.
Ans: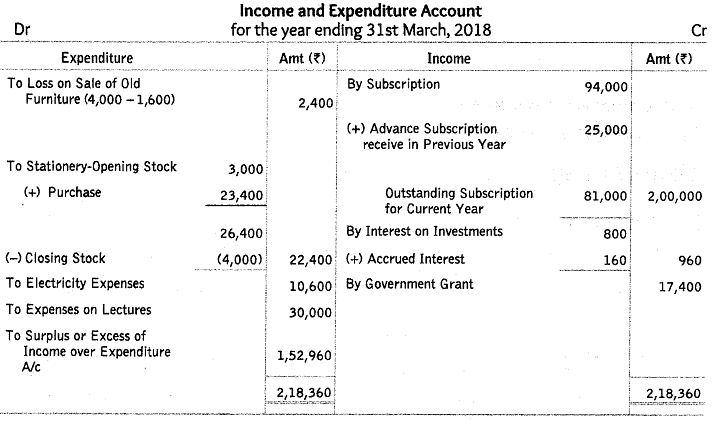
Q59: Which of the following is/are account(s) in NPO where outstanding expenses, prepaid expenses, etc are not recorded?
(a) Receipt and payment account
(b) Income and expenditure account
(c) Balance sheet
(d) All of these
Ans: (a) Receipt and payment account
Q60: What is the source of income for a non-profit organisation?
(a) Subscriptions from members
(b) Donations
(c) Legacies
(d) All of these
Ans: (d)
Q61: Non-profit organisation provide it’s services in the field of
(a) education
(b) healthcare
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) manufacturing of goods
Ans: (c) Both (a) and (b)
Q62: Receipt and payment account is
(a) personal account
(b) real account
(c) capital account
(d) final account
Ans: (b) real account
Q63: Which of the following cannot be recorded in receipt and payment account?
(a) Subscription received in advance
(b) Last year subscription received
(c) Current year outstanding subscription
(d) All of the above
Ans: (c) Current year outstanding subscription
Q64: On 1st January, 2017 outstanding subscription ₹ 160. For 2017, amount received from subscription ₹ 4,200. On 31st December, 2017 outstanding subscription ₹ 240. Which of the following will be recorded in receipt and payment account as subscription received?
(a) ₹ 4,200
(b) ₹ 4,280
(c) ₹ 4,120
(d) ₹ 4,600
Ans: (a) ₹ 4,200
Q65: Specific donations appearing on the receipts side of the receipt and payment account are to be carried to
(a) debit side of income and expenditure account
(b) assets side of balance sheet
(c) liabilities side of the balance sheet
(d) credit side of income and expenditure account
Ans: (c) liabilities side of the balance sheet
Q66: Income and expenditure account is
(a) personal account
(b) real account
(c) nominal account
(d) None of these
Ans: (c) nominal account
Q67: Income and expenditure account records transactions of
(a) capital nature
(b) revenue nature
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Ans: (b) revenue nature
Q68: Subscription
2014 – 2015 – ₹ 1,200
2015 – 2016 – ₹ 26,500
2016 – 2017 – ₹ 500
Subscription outstanding as on 31st March, 2015 was ₹ 2,000 and on 31st March, 2016 ₹ 2,500. Amount to be shown in income and expenditure account will be
(a) ₹ 25,800
(b) ₹ 24,800
(c) ₹ 28,200
(d) ₹ 27,500
Ans: (c) ₹ 28,200
Q69: The balance of income and expenditure account before adjustment is ₹ 400 deficit. Accrued interest-? 600 Outstanding wages ₹ 300 Prepaid insurance ₹ 200 Amount after adjustment will be
(a) ₹ 200 deficit
(b) ₹ 100 deficit
(c) ₹ 100 saving/surplus
(d) ₹ 300 surplus
Ans: (c) ₹ 100 saving/surplus
Q70: Any excess of assets over liabilities in non-profit organisation is called
(a) cash
(b) working capital
(c) loan
(d) capital fund
Ans: (d) capital fund
Q71: Balance of income and expenditure account is transferred to
(a) assets side of balance sheet
(b) liabilities side of balance sheet
(c) capital fund
(d) adjusted in assets
Ans: (c) capital fund
Q72: Consider the following information.
Tournament fund ₹ 20,000;
Tournament expenses ₹ 6,000;
Receipt from tournament ₹ 9,000.
Amount to be transferred to liabilities side of balance sheet will be
(a) ₹ 22,000
(b) ? 23,000
(c) ₹ 18,000
(d) ₹ 230
Ans: (b) ₹ 23,000
Q73: Find insurance premium to be debited to income and expenditure account?
If prepaid premium (opening) is ₹ 2,000, Prepaid premium closing ₹ 2,800,
Premium paid during the year ₹ 7,200.
(a) ₹ 6,400
(b) ₹ 8,000
(c) ₹ 12,000
(d) None of these
Ans: (a) ₹ 6,400
|
42 videos|199 docs|43 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet Solutions: Accounting for Not-for-Profit Organizations - Accountancy Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What is the purpose of accounting for not-for-profit organizations? |  |
| 2. How do not-for-profit organizations differ from for-profit organizations in terms of accounting? |  |
| 3. What are the key financial statements prepared by not-for-profit organizations? |  |
| 4. How are contributions and donations recorded in the accounting records of not-for-profit organizations? |  |
| 5. What are the potential challenges in accounting for not-for-profit organizations? |  |
















