Textbook Solutions: Soil Erosion and Conservation | Eureka Plus Class 5: Book Solutions, Notes & Worksheets PDF Download
I. Give one word to represent each of the following:
1. the part of the soil formed from the remains of plants and animals ___________
Ans: Humus
2. the layer of soil which is essential for the growth of plants ___________
Ans: Topsoil
3. an open space of land which does not have plants growing on it ___________
Ans: Barren land
4. sand and pebbles are formed from it ___________
Ans: Rocks
5. to develop a new forest-like area ___________
Ans: Afforestation
II. Tick (✔) the true sentences and correct the false ones.
1. A long time ago, there was no soil on the Earth.
Ans: True
2. The roots of plants hold soil particles together and prevent soil erosion.
Ans: True
3. Deforestation and strong winds are the two natural causes of soil erosion.
Ans: False
Deforestation and flowing water
4. Planting more trees leads to soil conservation.
Ans: True
5. Wind and flowing water make the soil fertile.
Ans: False
Humus in the topsoil makes the soil fertile
6. Cover crops, bunds and shelter belts protect the soil of farmlands.
Ans: True
III. The steps involved in soil formation are given below. Number the boxes (1-6) in the correct sequence. Now, write the sentences in your notebook in order to complete a short note on the formation of soil.

1. In the beginning, the entire Earth was covered only with rocks.
Ans: This step indicates the initial state of the Earth’s surface, without any soil.
2. Heat from the sun followed by rain continuously heated and cooled the rocks. This formed cracks in the rocks.
Ans: Temperature fluctuations cause rocks to expand and contract, leading to the formation of cracks.
3. Flowing rainwater and the sun’s heat widened the cracks.
Ans: Weathering processes, including the mechanical action of water and thermal expansion, further break down the rocks.
4. With time, the rocks broke into pieces.
Ans: As these processes continue, the rocks fragment into smaller pieces.
5. Fast flowing water and strong winds broke the rocks into small pieces, forming sand, silt and clay.
Ans: Erosion by water and wind reduces the rock fragments to even smaller particles that will become components of soil.
6. Gradually, plants grew on the Earth. When the plants died, their remains mixed with the soil and, thus, fertile soil began to form.
Ans: The development of plant life contributes organic matter to the mix, which decomposes to form humus, enriching the soil and making it fertile.
IV. Define the following terms.
1. soil erosion
Ans: The process that damages or removes the topsoil from a region.
2. soil conservation
Ans: Prevention of soil erosion; taking measures to protect and manage the soil to ensure its fertility.
3. deforestation
Ans: The felling of trees in large numbers from a region.
4. afforestation
Ans: The process of planting trees and other plants on barren lands to develop new forest-like areas.
V. Answer the following questions.
1. Why is terrace farming practised in hilly regions?
Ans: Terrace farming is practiced in hilly regions to prevent soil erosion. If the slope of a hill is cleared for farming, rainwater would flow downwards with force and wash away the fertile topsoil. Terrace farming, with steps on the slopes, reduces the flow of water and prevents soil erosion.
2. How does afforestation help to prevent soil erosion?
Ans: Afforestation helps prevent soil erosion by planting trees and other plants on barren lands. The roots of these plants bind the soil, reducing the impact of wind and flowing water. This, in turn, prevents the soil from being washed away.
3. How are farmlands near river banks protected from being washed away?
Ans: Farmlands near river banks are protected by building bunds of stones along the riverbanks. These bunds act as barriers, preventing the river water from flowing with force into adjacent lands and washing away the fertile soil.
4. What is the importance of cover crops in farming?
Ans: Cover crops are grown on farmland during periods when the land is barren, typically after each crop is harvested. These crops prevent soil erosion by covering the land and protecting it from the heat of the sun. Some types of grasses and pulses are often grown as cover crops, and they also serve as cattle feed.
5. What are shelter belts? Why do farmers grow them?
Ans: Shelter belts are rows of trees and shrubs grown along the boundaries of farmland. Farmers grow them to reduce the force of strong winds, thereby preventing soil erosion. These belts act as barriers that protect the farmland from the impact of wind and flowing rainwater.
Think and answer
I. Study the illustrations. Explain why wind and flowing rainwater affect the same piece of land differently in the situations (A and B) given below.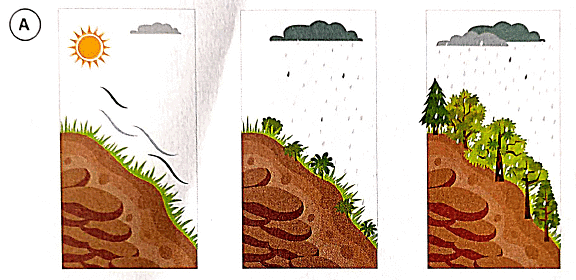
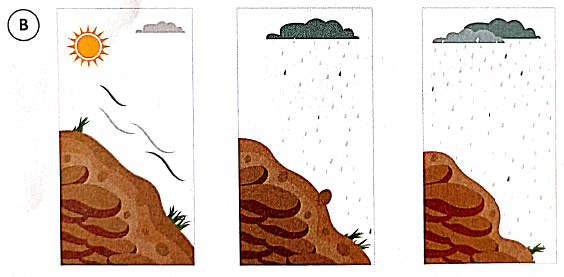
1. In which situation does the topsoil get completely removed?
(a) (A)
(b) (B)
Ans: (a)
The topsoil gets completely removed in situation (A), where there are no plants to protect the soil, and thus it is vulnerable to the forces of wind and rain.
2. List the environmental factors that cause soil erosion.
Ans: The environmental factors that cause soil erosion include wind, flowing rainwater, and the absence of vegetation.
3. What has protected the soil in one of the above situations?
Ans: In situation B, the presence of plants with their roots system has protected the soil. The plants and their roots help to bind the soil together, preventing it from being washed or blown away.
4. Is growing plants an effective measure to prevent soil erosion?
Ans: Yes, growing plants is an effective measure to prevent soil erosion. The roots of plants help to hold the soil particles together, reducing the impact of wind and water flow, which can remove topsoil.
II. Two different options of growing a crop on a slope are shown below. Study the pictures and explain which is a better method to prevent soil erosion.

Ans: The images depict two different agricultural practices for growing crops on a slope:
(A) Shows a slope with crops grown directly on the hillside without any apparent structural modifications. This method is more susceptible to soil erosion because rainwater can flow down the slope unimpeded, potentially washing away the topsoil.
(B) Displays what is known as terrace farming. In this method, the hillside has been modified into a series of flat, stepped levels. This is a more effective method to prevent soil erosion for several reasons:
- Reduced Runoff: The terraces reduce the speed of water runoff by breaking the length of the slope, which lessens the erosion potential.
- Water Conservation: Terraces can help to conserve water by allowing it to soak into the soil, benefiting the crops.
- Soil Retention: The terraced steps prevent the soil from being washed away downhill because the flat areas act as barriers.
Therefore, option B, terrace farming, is the better method to prevent soil erosion on slopes. It is a sustainable agricultural practice that protects the soil, conserves water, and can lead to improved crop yields due to more effective water use and reduced soil loss.




















