UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 27th November 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Ozone Hole Detected over Antarctica |

|
| Social Audits in MGNREGS |

|
| Nidirana noadihing |

|
| Wasp-107b |

|
| Amplifi 2.0 Portal |

|
| Amaterasu |

|
| Investor Risk Reduction Access Platform |

|
GS-I
Ozone Hole Detected over Antarctica
Subject: Geography
Why in News?
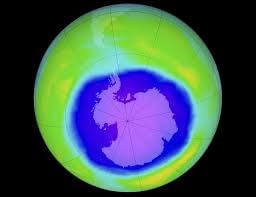
In the past four years, a recent study published in Nature Communications has reported a substantial increase in the size of the Antarctic Ozone Hole.
What is Ozone Layer and what are Ozone Holes?
- Ozone layer, also called ozonosphere, is a region of the upper atmosphere, between roughly 15 and 35 km (9 and 22 miles) above Earth’s surface which contains relatively high concentrations of ozone molecules (O3).
- Approximately 90 percent of the atmosphere’s ozone occurs in the stratosphere, the region extending from 10–18 km (6–11 miles) to approximately 50 km (about 30 miles) above Earth’s surface.
- The ozone layer effectively blocks almost all solar radiation of wavelengths less than 290 nanometres from reaching Earth’s surface, including certain types of ultraviolet (UV) and other forms of radiation that could injure or kill most living things.
- The term 'ozone hole' doesn't indicate an actual gap but rather a region in the stratosphere with significantly low ozone concentrations during specific months.
- The most commonly discussed ozone holes occur over Antarctica, emerging annually in September, October, and November.
- These holes result from unique meteorological and chemical conditions at the South Pole and can reach sizes ranging from 20 to 25 million square kilometers.
- Similar ozone holes are observed over the North Pole, but due to warmer temperatures compared to the South Pole, they are considerably smaller in size.
Ozone creation and destruction
- The production of ozone in the stratosphere results primarily from the breaking of the chemical bonds within oxygen molecules (O2) by high-energy solar photons. This process, called photodissociation, results in the release of single oxygen atoms, which later join with intact oxygen molecules to form ozone.
- The amount of ozone in the stratosphere varies naturally throughout the year as a result of chemical processes that create and destroy ozone molecules and as a result of winds and other transport processes that move ozone molecules around the planet.
- Over the course of several decades, however, human activities substantially altered the ozone layer.
- Ozone depletion, the global decrease in stratospheric ozone observed since the 1970s, is most pronounced in polar regions, and it is well correlated with the increase of chlorine and bromine in the stratosphere.
- Those chemicals, once freed by UV radiation from the chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and other halocarbons (carbon-halogen compounds) that contain them, destroy ozone by stripping away single oxygen atoms from ozone molecules.
- As the amount of stratospheric ozone declines, more UV radiation reaches Earth’s surface, and scientists worry that such increases could have significant effects on ecosystems and human health.
Ozone Holes Grow and Shrink Every Year
- The size of the ozone hole over Antarctica changes annually, typically opening in August and closing in November or December.
- It’s caused by special winds over Antarctica due to the Earth’s rotation, creating a shield over the continent that prevents mixing with surrounding air. When the winds calm down, the hole closes.
Causes of the Giant Ozone Hole in 2023
- The large ozone hole this year may be linked to volcanic eruptions at Hunga Tonga in Tonga during December 2022 and January 2023.
- Normally, gas from volcanic eruptions stays below the stratosphere, but this one released a lot of water vapor into the stratosphere.
- The water vapor, through chemical reactions, impacted the ozone layer and altered its heating rate. It also contained elements like bromine and iodine that can deplete ozone.
- There isn’t strong evidence to attribute this ozone hole to human activities.
Is Climate Change Reopening Ozone Holes?
- Ozone depletion isn’t a primary driver of global climate change, but rising temperatures could have an influence on ozone holes.
- Mitigation efforts for ozone holes were effective since the 1980s, but the 2020 and 2021 ozone holes were unusually deep and long-lasting, with wildfires in southeastern Australia contributing to the 2020 hole.
- The impact of ozone holes on Earth’s climate is not entirely clear; some data suggests they might have cooling effects by reducing the greenhouse gas effect.
Source: Down To Earth
GS-II
Social Audits in MGNREGS
Subject: Governance

Why in News?
Recent data from the Management Information System (MIS) on Social Audit, maintained by the Ministry of Rural Development (MoRD), sheds light on the progress and challenges of the social audit in the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS).
What is the Progress of Social Audits in MGNREGS?
- In terms of the progress of social audits in the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS), data from the Management Information System (MIS) reveals that only six out of the 34 States and Union Territories have completed social audits for over 50% of the works conducted in gram panchayats.
- Kerala stands out as a leader, achieving 100% coverage of gram panchayats in social audits, indicating a comprehensive and inclusive approach.
- Apart from Kerala, five other states have exceeded the 50% mark in social audit coverage. These states are Bihar (64.4%), Gujarat (58.8%), Jammu and Kashmir (64.1%), Odisha (60.42%), and Uttar Pradesh (54.97%).
- Only three states have covered 40% or more villages, namely Telangana (40.5%), Himachal Pradesh (45.32%), and Andhra Pradesh (49.7%).
- Among the states heading into elections, the social audit coverage is notably low. Specifically, Madhya Pradesh has a coverage of 1.73%, Mizoram at 17.5%, Chhattisgarh at 25.06%, and Rajasthan at 34.74%.
What is a Social Audit?
- About:
- Social audit is a process of reviewing official records and determining whether state reported expenditures reflect the actual money spent on the ground.
- Social audit is the inbuilt anti-corruption mechanism in the MGNREGA Act, 2005.
- It involves quality checks of infrastructure created under the MGNREGA, financial misappropriation in wages, and checking for any procedural deviations.
- Objectives:
- Aimed at empowering local communities, social audits enable citizens to scrutinize and assess the efficiency and effectiveness of government initiatives.
- Legal Framework:
- In the context of MGNREGS, Section 17 of the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) mandates the gram sabha to monitor the execution of works, providing a legal basis for social audits.
- The Audit of Scheme Rules, 2011, also known as the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Audit of Schemes Rules, 2011, were developed by the Ministry of Rural Development in collaboration with the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) of India.
- These rules outline the procedures for social audits and the duties of various entities, including the Social Audit Unit (SAU), state government, and field workers of MGNREGA, to be followed nationwide.
- Social audit units operate independently of the implementing authorities, ensuring an unbiased evaluation of the programs.
- To ensure the autonomy of Social Audit Units, they are entitled to funds equivalent to 0.5% of the MGNREGA expenditure incurred by the state in the previous year.
- In cases where states fail to conduct regular social audits, the Centre has the authority to withhold funds allocated under MGNREGS.
- Challenges in Implementation:
- Limited awareness of the legal framework for social audits, especially among local communities, can impede their active involvement in the process.
- Limited financial resources for Social Audit Units can compromise their ability to carry out thorough and effective audits, restricting the scope of their activities.
- The intrusion of political influence can hinder the impartiality of social audits, impacting the authenticity and objectivity of the evaluation process.
- Lack of cooperation and coordination of the implementing authorities and the social audit units.
- Lack of follow-up and action on the findings and recommendations of the social audit reports.
- Lack of protection and support for the social auditors and the whistle-blowers who face threats and harassment from the vested interests.
Source: The Hindu
Nidirana noadihing
Subject: Environment and Ecology

Why in News?
Bitupan Boruah, V Deepak, and Abhijit Das documented their discoveries in an article that appeared in the November 15 issue of the Zootaxa journal.
About Nidirana noadihing
- The Noa-Dihing Music Frog boasts a ‘robust’ body.
- The males measure approximately 1.8 to 2.3 inches and females ranging from about 2.4 to 2.6 inches. ( New Species of frog in Andaman found)
- It received its name, Nidirana noadihing, as a homage to the Noa-Dihing River, the vicinity where these unique specimens were encountered and collected.
- They have ’rounded’ snouts and ‘smooth’ skin, adorned with bony protrusions on their backs.
- They showcase a striking colour palette, featuring a ‘pale cream’ line bordered with dark brown along the centre of their bodies.
- Light brown limbs, adorned with dark stripes, further enhance their visual distinctiveness.
- The speciality of this new species of frog, Nidirana noadihing, is that both the male and female are vocal.
- Noa-Dihing Music Frogs are distinguished not only by their size but also by their oval toe tips, the tubercles on their backs, and a distinctive call.
- The irregularly shaped and sized spots on their eyelids, along with dark stripes around their moderately large eyes, contribute to their unique visual features.
Significance of the Discovery
This discovery marks the first confirmation of the Nidirana genus’s presence in India, expanding its known habitat beyond regions in Japan, Taiwan, China, Vietnam, Laos, and Thailand.
Source: The Hindu
Wasp-107b
Subject: Science and Technology

Why in News?
NASA's James Webb Telescope has identified a recently discovered exoplanet that shares the dimensions of Jupiter.
About Wasp-107b
- WASP-107b is an exoplanet.
- It was discovered in 2017.
- It orbits the star WASP-107.
- It is 200 light years away from the Earth.
- It is located in the constellation Virg.
- Earlier, scientists believed that the planet was huge in size due to the huge gas envelope that surrounded the planet.
- Also, the scientists believed that such huge gas envelopes are possible only with massive and dense cores.
- However, a recent study says that the cores of WASP-107b are not as dense as thought earlier.
- It orbits the star WASP-107.
- It is 200 light years away from the Earth.
- It is located in the constellation Virg
Source: Times of India
Amplifi 2.0 Portal
Subject: Government policies and Interventions
Why in News?
Recently, the Union Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs launched the Amplifi 2.0 portal.
Amplifi 2.0 Portal: Enhancing Urban Data Accessibility
- Objective: Amplifi (Assessment and Monitoring Platform for Liveable, Inclusive, and Future-Ready Urban India) aims to centralize raw data from Indian cities onto a unified platform.
- Policymaking Support: The platform serves as a valuable resource for academics, researchers, and stakeholders, facilitating the formulation of policies based on data-driven insights.
- Coverage: Currently, the portal has integrated 258 urban local bodies (ULBs), providing data for 150 cities.
- Information Spectrum: The platform presents a diverse array of data for various cities, encompassing metrics such as total diesel consumption and the number of water quality samples tested.
Urban Outcomes Framework 2022: A Holistic Approach
- Developers: Crafted by the National Institute of Urban Affairs and PwC India for the Ministry.
- Shift in Focus: This framework moves away from indices, emphasizing comprehensive indicators and promoting data-centric analysis.
- Sectors Covered: Encompassing 14 sectors, including demography, economy, education, energy, environment, finance, governance, health, housing, mobility, planning, safety and security, solid waste management, and water and sanitation.
- Data Streamlining: Aims to streamline data across sectors, enhancing focus on collection, analysis, and the creation of new frameworks on open data.
Source: The Hindu
GS-III
Amaterasu
Subject: Science and Technology

Why in News?
Scientists recently detected the most powerful cosmic ray seen in more than three decades, which has been named ‘Amaterasu’.
Amaterasu: The Cosmic Phenomenon
- Overview: Named after the Japanese sun goddess, Amaterasu is among the highest-energy cosmic rays ever recorded.
- Energy Magnitude: Exceeds 240 exa-electron volts (EeV), a scale millions of times greater than particles generated in the Large Hadron Collider.
- Comparison: Second only to the Oh-My-God particle, another ultra-high-energy cosmic ray detected in 1991 at 320 EeV.
- Extraordinary Energy: Equivalent to the energy of a golf ball traveling at 95 mph, signifying its remarkable cosmic force.
- Emergence: Originates from the Local Void, an expansive, nearly empty region bordering the Milky Way galaxy.
Cosmic Rays: Celestial Messengers of Energy
- Origins: Cosmic rays originate from intense celestial occurrences that strip matter of its subatomic structures, causing it to be propelled through the universe at speeds close to that of light.
- Particle Diversity: Cosmic rays consist of charged particles, including positive protons, negative electrons, and entire atomic nuclei.
- Continuous Earth Impact: Persistently bombarding Earth, cosmic rays collide with its upper atmosphere, particularly with oxygen and nitrogen nuclei, resulting in the generation of numerous secondary particles.
- Atmospheric Impact: The secondary particles have a limited range within the atmosphere, initiating a cascade effect that leads to the creation of a shower containing billions of particles, dispersing across the Earth's surface.
Source: Indian Express
Investor Risk Reduction Access Platform

Why in News?
Recently, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) introduced the Investor Risk Reduction Access (IRRA) to establish a 'safety net' for investors when encountering technical glitches with a trading member or stock broker.
- A trading member or stock broker, authorized and licensed to engage in the buying and selling of securities on behalf of investors in financial markets, serves as an intermediary. This involves facilitating transactions within the stock market or other financial exchanges, acting as a link between buyers and sellers.
What is the IRRA Platform?
- About:
- The IRRA platform has been developed to reduce risks faced by investors in the eventuality of technical glitches at the trading member’s end at both the primary site and disaster recovery site.
- Its purpose is to provide investors with an opportunity to square off/close their open positions and cancel pending orders using the IRRA platform in case of technical glitches or unforeseen outages that render the trading member’s site inaccessible.
- It is not meant for taking fresh positions or orders, but only to cancel the pending orders.
- Developed By:
- IRRA has been jointly developed by all the stock exchanges – BSE (Bombay Stock Exchange), NSE (National Stock Exchange), NCDEX (National Commodity and Derivatives Exchange), MCX (Multi Commodity Exchange) and Metropolitan Stock Exchange of India (MSE)
- Mechanism of Working:
- IRRA can be invoked by trading members when they are faced with a technical glitch at their end impacting their ability to service clients across exchanges from both – the primary site and disaster recovery site, where relevant.
- Even stock exchanges can also monitor parameters like connectivity, order flow and social media posts, and suo moto initiate the enablement of the IRRA service, if needed, irrespective of any such request by the trading member.
- This service shall be enabled by the exchanges, suo moto, only in case of disruption of trading services of trading members across all the exchanges, where the trading member is a member.
- Need:
- With technology glitches increasingly disrupting trading services, investors face risks, especially in volatile markets, with no means to close positions.
- Despite business continuity plans, certain disruptions like delayed recovery sites or Cyber-Attacks persist.
- This initiative ensures contingency services by stock exchanges during such crises.
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|















