MCQ & Extra Questions: Fun with Magnets | Physical Science for High School - Grade 9 PDF Download
Extra Questions
Q1: In which direction does a suspended magnet come to rest?
Ans: Magnet comes to rest in the N-S (north-south) direction.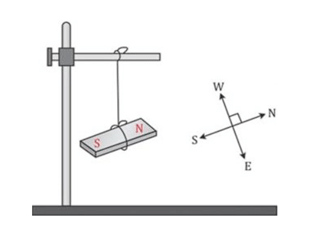
Q2: Name the compound of iron contained in lodestone.
Ans: The compound of iron is iron oxide or magnetite.
Q3: A tailor was stitching buttons on his shirt. The needle slipped from his hand onto the floor. Can you help the tailor to find the needle?
Ans: The needle can be found by using a magnet. Since the needle is magnetic, when a magnet is wavered over the floor, it will stick to the magnet.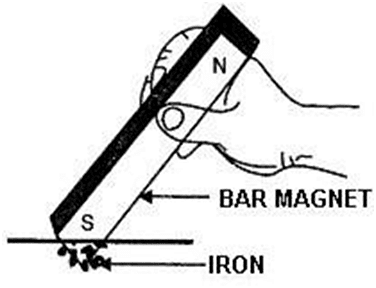
Q4: What is the difference between magnetic and non-magnetic materials? Give examples.
Ans: The materials that get attracted towards a magnet are magnetic. For example-iron, cobalt, etc.
Materials that are not attracted to a magnet are nonmagnetic. For example plastic, glass, etc.
Q5: What is demagnetisation?
Ans: Magnets lose their magnetic properties when hammered, heated, dropped from a height, or not stored properly. This loss in magnetic property is termed demagnetisation.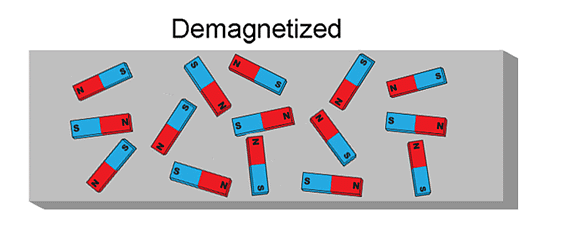
Q6: Write two cautions to keep a magnet.
Ans: Bar magnets should be kept in pairs with their unlike poles on the same side. They must be separated by a piece of wood. For horseshoe magnets, one should keep a piece of iron across the poles.
Q7: Write any three properties of a magnet.
Ans: (a) Magnet has two poles north and South Pole.
(b) The same poles of two magnets repel each other.
(c) Opposite poles of two magnets attract each other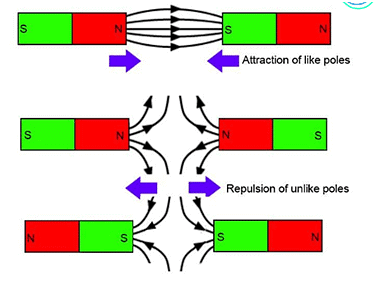
Q8: A toy car has a bar magnet laid hidden inside its body along its length. Using another magnet how will you find out which pole of the magnet is facing the front of the car?
Ans: If the front of the toy car gets attracted to the north pole of the given magnet then it is the south pole of the bar magnet hidden inside the car.
Q9: What is a magnetic compass?
Ans: A magnetic compass is a small box with a glass cover. It consists of a magnetised needle, which rotates freely and indicates a north-south direction when comes to rest.
Q10: Classify the following as magnetic and non-magnetic material: Iron, plastic, rubber, glass, mirror, cobalt
Ans: Magnetic material - iron, cobalt
Non-magnetic material - plastic, rubber, glass, mirror
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1: How can a rectangular iron bar be turned into a magnet?
(a) By heating it to a high temperature
(b) By rubbing a bar magnet over it
(c) By exposing it to sunlight for a long time
(d) By applying a strong electric current to it
Ans: (b)
A rectangular iron bar can be turned into a magnet by rubbing a bar magnet over it. This process, known as magnetization, involves aligning the magnetic domains within the iron bar to induce magnetism. The study notes provide a step-by-step procedure for this method.
Q2: Which property of magnets makes them useful in finding directions?
(a) Force of attraction
(b) Magnetic poles
(c) Magnetic property of lodestone
(d) Ability to align freely in the north-south direction
Ans: (d)
Magnets have the property of aligning themselves in the north-south direction. When a bar magnet is suspended freely by a thread, it aligns itself with the Earth's magnetic field, making it a valuable tool for navigation and finding directions.
Q3: What happens when a bar magnet is freely suspended by a thread?
(a) It points towards the south
(b) It aligns itself in the east-west direction
(c) It aligns itself in the north-south direction
(d) It exhibits no specific alignment
Ans: (c)
When a bar magnet is freely suspended by a thread, it aligns itself in the north-south direction. This property is essential for the use of magnets, such as in compasses, which rely on the alignment of the magnetic needle to indicate directions.
Q4: What is the role of lodestone in ancient naval warfare, according to historical beliefs?
(a) Used to sink enemy ships
(b) Used to pull nails from enemy ships
(c) Used to repel enemy ships
(d) Used as a directional guide for enemy ships
Ans: (b)
According to historical beliefs, "Archimedes," the ancient Greek scientist, is believed to have used lodestone (a natural magnet) to pull nails from enemy ships. The removal of nails made the ships sink, showcasing the magnetic properties of lodestone.
Q5: What is the primary purpose of a magnetic compass?
(a) Attracting magnetic materials
(b) Finding the magnetic poles
(c) Aligning with the Earth's magnetic field
(d) Indicating directions
Ans: (d)
A magnetic compass is an instrument used to find directions. It consists of a thin magnetic needle that aligns itself with the Earth's magnetic field, indicating the north-south direction. The compass is a valuable tool for navigation and orientation.
Q6: How can a rectangular iron bar be turned into a magnet?
(a) By rubbing a bar magnet over it
(b) By heating it to a high temperature
(c) By exposing it to sunlight for a long time
(d) By applying a strong electric current to it
Ans: (a)
To turn a rectangular iron bar into a magnet, one can rub a bar magnet over it. This process involves placing one pole of the bar magnet near one edge of the iron bar, moving it along the length of the bar, and repeating the process multiple times. This causes the iron bar to acquire magnetic properties.
Q7: What property of magnets prevents the separation of their poles?
(a) Magnetic alignment
(b) Magnetic force
(c) Magnetic induction
(d) Magnetic polarity
Ans: (d)
The poles of a magnet always exist in pairs, and they cannot be separated. This property is known as magnetic polarity. Each magnet has a north pole and a south pole, and they are inseparable, demonstrating the inherent characteristic of magnetic poles.
Q8: What precautions should be taken to protect magnets from losing their magnetic properties?
(a) Heating the magnets
(b) Hammering the magnets
(c) Dropping magnets from heights
(d) Keeping magnets away from magnetic materials
Ans: (d)
To protect magnets from losing their magnetic properties, the best approach is to avoid bringing them close to magnetic materials that might interfere with their magnetic field or cause demagnetization.
Q9: Which materials should be kept away from magnets to prevent damage?
(a) Plastic items
(b) Wooden items
(c) Magnetic materials
(d) Glass items
Ans: (c)
Certain items such as CDs, DVDs, debit cards, credit cards, audio and video cassettes, and mobile phones contain magnetic materials. To prevent damage, it is advisable to keep these magnetic materials away from magnets, as the magnetic field can interfere with or damage these items.
Q10: What is the significance of the red tip on the north pole of a magnetic compass needle?
(a) Indicates danger
(b) Aesthetic purpose
(c) Enhances visibility
(d) Represents the North Pole
Ans: (d)
The red tip on the north pole of a magnetic compass needle serves to distinguish the north pole from the south pole. It is a visual indicator that helps users easily identify the orientation of the compass. This convention aids in correctly interpreting the direction indicated by the magnetic compass.
|
87 videos|276 docs|72 tests
|
FAQs on MCQ & Extra Questions: Fun with Magnets - Physical Science for High School - Grade 9
| 1. What are the properties of magnets? |  |
| 2. How do magnets work? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of magnets? |  |
| 4. Can magnets lose their magnetism? |  |
| 5. What are some common uses of magnets? |  |

















