MCQ & Extra Question: Light, Shadows and Reflections | Class 6 All Subjects (Old NCERT) PDF Download
Extra Questions
Q1: Define opaque objects with example.
Ans: Those materials which do not allow light to pass through them, are called opaque objects. Examples wood, stone, etc.
Q2: Observe the picture given in figure. A sheet of some material is placed at position ‘P’, still the patch of light is obtained on the screen. What is the type of material of this sheet?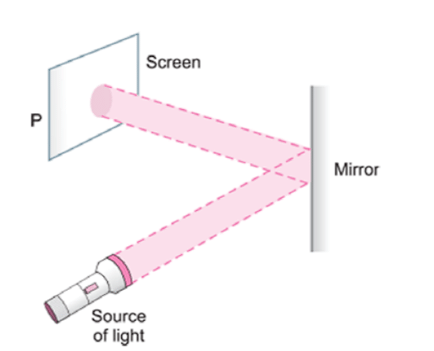 Ans: A sheet of transparent material is placed at ‘P’.
Ans: A sheet of transparent material is placed at ‘P’.
Q3: Moon is a non-luminous object. How does it shine at night?
Ans: Moon reflects the light of the sun at night.
Q4: What is the difference between transparent and translucent object?
Ans: If we are able to see clearly through an object, it is said to be transparent. Whereas there are some objects through which we can see but not clearly. Such objects are known as translucent objects. Transparent objects allow light to pass through them completely whereas translucent objects doesn’t allow light to pass through them completely.
Q5: How is shadow formed?
Ans: When an object is placed in path of light, a dark portion is formed on the opposite side of object. This dark portion is shadow.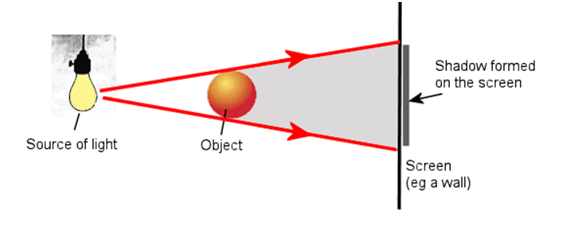
Q6: State difference between a luminous and a non-luminous body.
Ans: The bodies which emit light are called luminous bodies. Example: sun, stars, burning candle etc. The bodies which does not emit light are called non-luminous bodies. Example: moon, earth, blackboard.
Q7: Define reflection of light.
Ans: When light rays after striking the smooth and shiny surface return to same medium, this phenomenon is called reflection of light.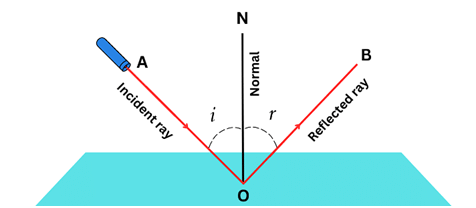
Q8: What is a pinhole camera? What type of images is formed by it?
Ans: A pinhole camera is a device which forms a photographic image of a bright object on a screen. The images formed by a pinhole camera are upside down (inverted images).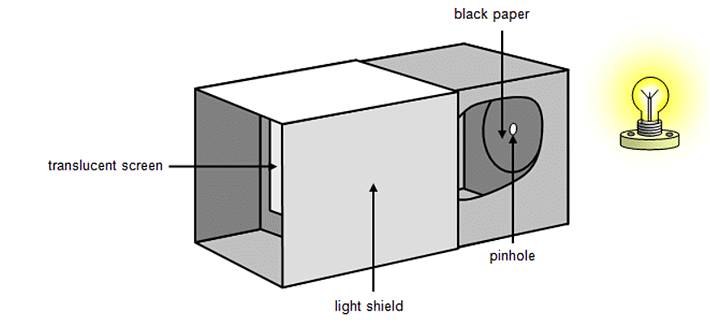
Q9: What do you mean by scattering of light?
Ans: When a beam of light falls on a rough surface it is turned back in different directions. It is called scattering of light.
Q10: What happens to the direction of a ray of light after it falls on a plane mirror?
Ans: When a ray of light falls on a plane mirror, it changes its direction because it gets reflected from the surface of the mirror at the same angle at which it falls on the surface.
Multiple Choice Question
Q1: Which one is a transparent object?
(a) Stone
(b) Reading glass
(c) Dense fog
(d) Wax paper
Ans: (b)
Sol: Option (a): Stone
- Stones are generally opaque, meaning they do not allow light to pass through them.
- Light is either absorbed or reflected by the stone, making it impossible to see through.
Option (b): Reading glass
- Reading glasses are made of transparent materials, such as glass or plastic.
- These materials allow light to pass through them, making it possible to see through the object.
- As a result, reading glasses are considered transparent objects.
Option (c): Dense fog
- Dense fog is a collection of tiny water droplets suspended in the air.
- While light can pass through the fog, it is scattered in different directions, making it difficult to see clearly through the fog.
- Therefore, dense fog is not considered a transparent object.
Option (d): Wax paper
- Wax paper is a type of paper coated with a layer of wax, making it water-resistant and somewhat translucent.
- Translucent materials allow some light to pass through but not enough to see objects clearly through them.
- As a result, wax paper is not considered a transparent object.
Q2: ____________ helps us to see the objects.
(a) Mirror
(b) Light
(c) Shadow
(d) Transparent objects
Ans: (b)
Sol: Light Helps Us See Objects
Role of light: Light is a form of energy that enables us to see the objects around us. When light falls on an object, it reflects off the surface and enters our eyes, making the object visible.
Reflection of light: Objects reflect light in different ways, depending on their surface properties. Smooth surfaces, like mirrors, reflect light uniformly, while rough surfaces scatter light in different directions.
Formation of images: When light enters our eyes, it passes through the cornea, lens, and vitreous humor, finally reaching the retina. The retina contains photoreceptor cells that convert light energy into electrical signals, which are then transmitted to the brain via the optic nerve. The brain processes these signals and forms the images we see.
Importance of light: Without light, we would not be able to see anything around us. Light is essential for vision, as well as for various biological processes, such as photosynthesis in plants and regulation of sleep-wake cycles in animals and humans.
Q3: Light is a form of
(a) Length
(b) Energy
(c) Mass
(d) Power
Ans: (b)
Sol: Light is a form of energy because it exhibits the following properties:
Electromagnetic Radiation:
- Light is a type of electromagnetic radiation, which is a form of energy that travels in waves.
- The electromagnetic spectrum includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays, all of which are forms of energy.
Ability to Cause Physical Changes:
- Light can cause physical changes in materials, such as heating, chemical reactions (like photosynthesis in plants), and even electrical energy generation (like in solar panels).
- These changes indicate that light carries energy and can transfer it to other objects or materials.
Wave-Particle Duality:
- Light exhibits both wave-like and particle-like properties, known as wave-particle duality.
- As a particle, light is composed of photons, which are packets of energy.
- The energy carried by a photon is directly proportional to its frequency, further demonstrating that light is a form of energy.
Speed of Light:
- Light travels at a constant speed of approximately 299,792 kilometers per second (186,282 miles per second) in a vacuum.
- This speed is a fundamental constant of the universe and is related to the energy carried by light.
In conclusion, light is a form of energy because it is a type of electromagnetic radiation, can cause physical changes, is composed of energy-carrying photons, and travels at a constant speed related to its energy content.Light is a form of energy.
Eg. Sunlight
Q4: To see a shadow we need
(a) A source of light and translucent object
(b) A source of light and transparent object
(c) A source of light and an opaque object
(d) Many source of light and opaque object
Ans: (c)
Sol: A source of light and an opaque object:
- Shadows are formed when an object blocks the path of light.
- An opaque object does not allow light to pass through it, thus creating a shadow.
- A translucent object allows some light to pass through, resulting in a partial or lighter shadow.
- A transparent object allows light to pass through completely, so it does not create a shadow.
- Therefore, the correct answer is C: A source of light and an opaque object is needed to see a shadow. A shadow is formed only when a source of light is obstructed by an opaque object.
Q5: Which of the following will not form a circular shadow
(a) Shoe box
(b) A ball
(c) A circular disk
(d) Ice-cream cone
Ans: (a)
Sol: Shoe box (a):
- Rectangular shape with sharp edges.
- Shadow will have angular and straight lines, similar to the shape of the box.
- Cannot form a circular shadow.
A ball (b):
- Spherical shape with no edges.
- Shadow will be circular, as the shape is uniform and round.
A circular disk (c):
- Flat, round shape with no edges.
- Shadow will also be circular, as the shape is round and flat
Ice-cream cone (d):
- Conical shape with a round base.
- Shadow can be circular when light is directed on the round base of the cone.
Based on the given shapes, a shoe box (A) is the one that will not form a circular shadow.Shoe box will not form a circular shadow as it is rectangular in shape.
Q6: Which of the following absorbs light the most?
(a) A mirror
(b) A piece of white paper
(c) A black wallet
(d) A green leaf
Ans: (c)
Sol:
- A mirror: Reflects most of the light, and thus, absorbs very little.
- A piece of white paper: Reflects most of the light, especially in the visible spectrum, and absorbs relatively less light.
- A black wallet: Absorbs most of the light that falls on it, making it the object that absorbs the most light among the given choices.
- A green leaf: Absorbs light in the red and blue parts of the spectrum, while reflecting green light.
- Although it absorbs more light than a mirror or white paper, it still absorbs less light than a black wallet.
Q7: In the morning, when the sun rises in the east, your shadow will be seen on the
(a) North
(b) West
(c) South
(d) East
Ans: (b)
Sol:
- When the sun rises in the east, it is positioned low in the sky.
- As a result, the sunlight comes from the eastward direction.
- Shadows are formed when an object blocks the path of light.
- Therefore, when the sun is in the east, your shadow will be cast in the opposite direction, which is towards the west.
Q8: Which of the following is not a luminous object
(a) Unlit candle
(b) Burning gas lantern
(c) Glow worm
(d) Sun
Ans: (a)
Sol: Luminous objects are those that emit their own light. Among the given options:
- Unlit candle (a):
- Does not emit light on its own
- Requires a source of ignition to produce light
- Burning gas lantern (b):
- Emits light when gas is ignited
- Produces its own light
- Glow worm (c):
- Emits light through bioluminescence
- Generates its own light
- Sun (d):
- Major source of light in our solar system
- Emits light through nuclear fusion reactions
Based on the descriptions, the Unlit candle (A) is not a luminous object because it does not emit its own light.
Q9: Which of the following objects does not emit light of its own?
(a) The sun
(b) A firefly
(c) The star
(d) The moon
Ans: (d)
Sol:
- The sun is a star itself and emits light through nuclear fusion in its core, converting hydrogen into helium and producing energy in the form of light and heat.
- A firefly is an insect that emits light through a process called bioluminescence, in which a chemical reaction within the firefly's body produces light.
- The star also emits light through nuclear fusion, similar to the sun. This process generates massive amounts of energy, which is released as light and heat, making stars visible from Earth.
- The moon does not emit light of its own. Instead, it reflects the light from the sun. The moon's surface is made up of materials that reflect sunlight, making it visible to us on Earth.
Therefore, the correct answer is d. The moon, as it does not emit light of its own and only reflects sunlight.
Q10: All planets are
(a) Luminous during day
(b) Non-luminous body
(c) Non-luminous during night
(d) Luminous body
Ans: (b)
Sol:
- Planet Characteristics: Planets don't have their own light source. They are classified as non-luminous bodies because they don't produce or emit their own light.
- Reflection of Light: Planets are visible from Earth because they reflect sunlight. The light we see from planets comes from the Sun, which is a luminous body that emits light and heat.
- Visibility: The visibility of planets during day and night depends on their position relative to the Earth and the Sun. However, this doesn't change the fact that they are non-luminous bodies.
- Examples: Earth, Mars, Jupiter, and all other planets in our solar system are non-luminous bodies. They are visible in the sky because they reflect sunlight, not because they emit their own light.
|
297 videos|1066 docs|204 tests
|
FAQs on MCQ & Extra Question: Light, Shadows and Reflections - Class 6 All Subjects (Old NCERT)
| 1. What is light? |  |
| 2. What is a shadow? |  |
| 3. How are shadows formed? |  |
| 4. What is reflection of light? |  |
| 5. What is refraction of light? |  |

















