UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 11th December 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Kadalekayi Parishe
Subject: Art and Culture

Why in News?
Kadalekayi Parishe started recently.
Background:-
- Efforts are being made to keep the festival plastic-free.
About Kadalekayi Parishe:-
- Kadalekai parishe is ground nut fair held at heart of Bengaluru near basavana gudi.
- It is offering of first crop to dodda basava or nandi whose temple is atop the bugle rock.
- Farmers from various districts of Karnataka comes down to the festival to offer the first ground nut crop followed by fair which is spread across close to a kilometer.
- Kadalekayi Parishe welcomes the first yield of the groundnut crop
- It is popularly known as the groundnut festival.
- It is held on the last Monday of Karthika Masa each year.
- As the festival follows the Hindu calendar, its exact date as per the English calendar doesn’t stay fixed.
- Kadale kai parishe in Basavanagudi of Bengaluru is between 9th December 2023 to 11th December 2023.
- The prime event is held on 11th December 2023.
- Karnataka’s farmers congregate at the Bull Temple each year to seek blessings for a good harvest.
- During Kadalekai Parishe, visitors buy groundnuts in bulk directly from farmers at prices cheaper than market rates.
- During Kadalekai Parishe special pooja and prayers are held at the bull temple.
- Decorated streets will have lots of shopping options, food outlets, games and toys for kids. Locals look forward to the festival and indulge in celebrations as well as shopping.
Source: Hindustan Times
GS-II
Zonal Councils
Subject: Polity
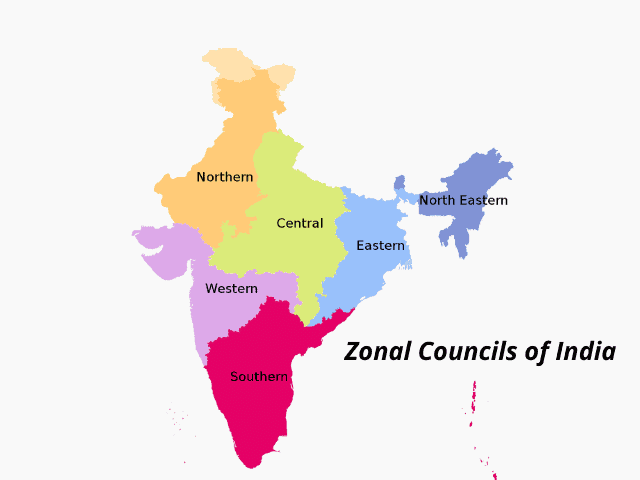
Why in News?
Recently, Union Home Minister Amit Shah chaired the 26th Eastern Zonal Council Meeting in Patna.
Background:-
- Addressing the representatives of Bihar, Jharkhand, West Bengal and Odisha Mr. Shah appealed to all members to work with the spirit of cooperative federalism for all-round development.
About Zonal Council:-
- Zonal Councils are the statutory (and not the constitutional) bodies.
- They are established by an Act of Parliament, that is, the States Reorganization Act of 1956.
Historical Background:-
- The idea of the creation of Zonal Councils was mooted by the first Prime Minister of India, Pandit Jawahar Lal Nehru in 1956.
- Five Zonal Councils were set up vide Part-III of the States Re-organisation Act, 1956 – north, south, east, west and central.
- The North Eastern Statese. (i) Assam (ii) Arunachal Pradesh (iii) Manipur (iv) Tripura (v) Mizoram (vi) Meghalaya and (vii) Nagaland are not included in the Zonal Councils
- Their special problems are looked after by the North Eastern Council, set up under the North Eastern Council Act, of 1972.
- The State of Sikkim has also been included in the North Eastern Council vide the North Eastern Council (Amendment) Act, 2002.
Objectives:-
- Zonal Councils aim to promote collaboration and coordination among states, UTs, and the Union.
- They discuss and give recommendations on several topics.
- They are only consultative and deliberative bodies.
- The States Reorganization Act of 1956 established these statutory entities. The country was divided into 5 zones by the Act:-
- Northern Zonal Council: It comprises the States of Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Punjab, Rajasthan, the National Capital Territory of Delhi, Union Territory of Chandigarh and Ladakh.
- Headquarter: New Delhi
- Central Zonal Council: It comprises the States of Chhattisgarh, Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh.
- Headquarter: Allahabad
- Eastern Zonal Council: It comprises the States of Bihar, Jharkhand, Orissa, Sikkim and West Bengal.
- Headquarter: Kolkata
- Western Zonal Council: It comprises the States of Goa, Gujarat, and Maharashtra and the Union Territories of Daman & Diu and Dadra & Nagar Haveli.
- Headquarter: Mumbai
- Southern Zonal Council: It comprises the States of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu and the Union Territory of Puducherry.
- Headquarter: Chennai
Structure:-
- Chairman – The Union Home Minister is the Chairman of each of these Councils.
- Vice Chairman – The Chief Ministers of the States included in each zone act as Vice-Chairman of the Zonal Council for that zone by rotation, each holding office for a period of one year at a time.
- Members- Chief Minister and two other Ministers as nominated by the Governor from each of the States and two members from Union Territories included in the zone.
Functions:-
- Each Zonal Council is an advisory body and may discuss any matter in which States have a common interest and advise the Government.
- In particular, a Zonal Council may discuss, and make recommendations with regard to:
- any matter of common interest in the field of economic and social planning;
- any matter concerning border disputes, linguistic minorities or inter-State transport;
- any matter connected with or arising out of, the re-organization of the States under the State’s Reorganization Act.
Source: AIR
PM-JANMAN Scheme for PVTGs
Subject: Government Schemes

Why in News?
The Union Tribal Ministry informed the Rajya Sabha that the population of Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) is not declining, contrary to earlier data.
- The Pradhan Mantri-Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan (PM-JANMAN) aims to provide basic facilities to PVTGs, with a significant budget allocation.
Who are the PVTGs?
- Definition and Characteristics: PVTGs, formerly known as Primitive Tribal Groups, are identified by criteria like declining population, pre-agrarian technology, economic backwardness, and low literacy.
- Distribution: Spread across 18 States and Union Territories, India has 75 PVTGs, with the highest numbers in Odisha and Andhra Pradesh.
- Historical Context: These groups inhabit remote areas and have historically been among the most vulnerable sections of Scheduled Tribes.
PM-JANMAN: Objectives and Funding
- Mission Goals: The mission, announced earlier in the year, focuses on improving infrastructure and basic amenities in PVTG areas.
- Budget Allocation: The Cabinet approved a ₹24,000 crore package, with contributions from both the central and state governments.
- Implementation Strategy: The program involves nine ministries and aims to enhance housing, connectivity, healthcare, education, and economic opportunities in PVTG villages.
Challenges in Implementation
- Data Gaps: A key challenge is the lack of current and accurate data on PVTG populations and socio-economic conditions.
- Baseline Surveys: While surveys are being conducted, their results are not yet public, and there has been no separate Census for PVTGs since 1951.
- Recommendations: The National Advisory Council suggested conducting a specific Census for PVTGs to better understand their needs in education, health, and housing.
Conclusion
- Critical Need for Accurate Data: Effective implementation of development projects for PVTGs hinges on having reliable data.
- Holistic Approach: The government’s initiative reflects a comprehensive approach to improving the living standards of PVTGs, addressing various aspects of their well-being.
- Continued Monitoring and Evaluation: Ongoing assessment and adaptation of strategies will be crucial to ensure the success of these development efforts for PVTGs.
Source: The Hindu
Conference on Disarmament (CD)
Subject: International Relations

Why in News?
Recently, Foreign Secretary Vinay Kwatra and, the UN Under-Secretary-General discussed India’s presidency of the Conference on Disarmament.
Background:-
- Their talks centred around global advancements in arms control and disarmament, with a focus on key initiatives discussed at the recent 78th UNGA First Committee.
About Conference on Disarmament (CD):-
- Established: 1979.
- HQ: Palais des Nations in Geneva.
- It is a multilateral disarmament forum established by the international community.
- Objective: to negotiate arms control and disarmament agreements.
- The Conference meets annually in three separate sessions in Geneva.
- Members: The Conference is comprised of 65 member States, including the five NPT nuclear-weapon States and 60 other States of key military significance.
- The CD has three sessions each year.
- The CD conducts its work by consensus.
- The Director-General of the United Nations Office at Geneva, is the Secretary-General of the Conference on Disarmament.
- The CD and its predecessors have negotiated major multilateral arms limitation and disarmament agreements such as:-
- the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT),
- the Convention on the Prohibition of the Development, Production and Stockpiling of Bacteriological (Biological) and
- Toxin Weapons and on Their Destruction (BWC),
- the Convention on the Prohibition of the Development, Production, Stockpiling and Use of Chemical Weapons and on Their Destruction (CWC)
- Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT).
Historical Background:-
- The Conference on Disarmament (CD), was recognized by the Tenth Special Session on Disarmament of the United Nations General Assembly (SSOD-I) (1978) as a single multilateral disarmament negotiating forum of the international community.
- It succeeded other Geneva-based negotiating fora, which include the Ten-Nation Committee on Disarmament (1960), the Eighteen-Nation Committee on Disarmament (1962-68), and the Conference of the Committee on Disarmament (1969-78).
- It was renamed the Conference on Disarmament in 1984.
Functions:-
- Cessation of the nuclear arms race and nuclear disarmament.
- Prevention of nuclear war, including all related matters.
- Prevention of an arms race in outer space.
- Effective international arrangements to assure non-nuclear-weapon States against the use or threat of use of nuclear weapons.
- New types of weapons of mass destruction and new systems of such weapons; radiological weapons.
- Comprehensive programme of disarmament.
- Transparency in armaments.
Source: The Hindu
Who is a J&K Resident?
Subject: Polity and Governance

Why in News?
The rights and interests of the people of Jammu and Kashmir have been a central theme in discussions across Parliament, the Supreme Court, and among citizens.
- Union Home Minister spoke about The J&K Reservation (Amendment) Bill, 2023, and The J&K Reorganisation (Amendment) Bill, 2023, emphasizing their benefits for migrant Kashmiris, women, and others deprived of rights for 70 years.
- Origins: The concept of “state subjects” and “permanent residents” in J&K originated during the rule of the Dogra dynasty.
- Government Order No. I-L/84: Issued on April 20, 1927, by Maharaja Hari Singh, this order divided inhabitants into four classes.
- Class I: Included those residing in J&K before Maharaja Gulab Singh’s reign (1846) and those settled before 1885.
- Class II: Covered individuals who settled and acquired immovable property in J&K before 1911.
- Class III: Comprised permanent residents with property acquired under specific concessions.
- Class IV: Included certain companies registered within the state, with government interest or economic benefit to the state.
- Privileges and Rights: The order prioritized Class I over others in scholarships, land grants, and state service recruitment.
- Order No. 13L/1989: Issued on June 27, 1932, by Hari Singh, it addressed the status of J&K state subjects living abroad and foreign nationals in J&K.
- Provisions for Emigrants: J&K emigrants and their descendants up to two generations were considered state subjects but with specific conditions for internal rights.
- Foreign Nationals: They could acquire state nationality after age 18, property purchase, and 10 years of continuous residence.
- Constitution Adoption: On November 17, 1956, the Constituent Assembly of J&K adopted a separate constitution, redefining state subjects as “permanent residents.”
- Permanent Residency Criteria: Included Indian citizenship as of May 14, 1954, and specific residency or property criteria. Provisions for Class I/II subjects who migrated to Pakistan and returned were also included.
- Legislation by Sheikh Abdullah’s Government: The J&K Resettlement Bill, passed in 1982, allowed certain migrants to return as permanent residents.
- Supreme Court Intervention: Implementation was halted due to a stay order by the Supreme Court, obtained by Prof Bhim Singh.
- High Court Decision: In 2003, it was ruled that women do not lose permanent resident status upon marrying non-permanent residents.
- Legislative Response: The PDP-Congress government passed a bill in 2004 to disqualify such women, which was initially supported by the NC but later opposed by the Congress in the Legislative Council and did not pass.
- Article 370 Amendment and J&K Bifurcation: The central government redefined “permanent residents” as “domiciles” following the amendment of Article 370 and bifurcation into two Union Territories.
- New Domicile Definition: Includes individuals with 15 years of residency, seven years of education and Class 10/12 exams in J&K, registered migrants and their children, and children of central government officials with 10 years of service in J&K.
Source: Indian Express
75th anniversary of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights
Subject: International Relations
Why in News?
December 10, 2023 marked the 75th anniversary of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR).
- UDHR is the landmark document enshrining human rights and fundamental freedoms for all individuals.
Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR)
- Background
- On 10 December 1948, the UN General Assembly approved the Universal Declaration of Human Rights at a meeting in Paris.
- It laid one of the foundation stones of the international order that emerged following the horrors of World War II.
- It was a response to the atrocities of World War II and an effort to establish a common understanding of the basic rights and freedoms to which all people are entitled.
- About
- A relatively compact document, the declaration consists of a preamble and 30 articles setting out fundamental rights and freedoms.
- These 30 articles articulate a broad range of civil, political, economic, social, and cultural rights.
- These rights are considered universal, meaning they apply to all people regardless of nationality, ethnicity, gender, religion, or any other status.
- It is not a legally binding treaty, but it has served as a source of inspiration for the development of international human rights law.
- Features
- Preamble
- The preamble sets out the reasons for the adoption of the declaration, emphasizing the inherent dignity and equal and inalienable rights of all members of the human family.
- Articles
- The UDHR consists of 30 articles that articulate a broad range of civil, political, economic, social, and cultural rights.
- Some examples of rights outlined in the UDHR include:
- the right to life, liberty, and security of person;
- the right to freedom of religion; of expression and assembly;
- the right to work and education; and
- the right to an adequate standard of living.
- The declaration says that “all are equal before the law” and that everyone is entitled to “a fair and public hearing by an independent and impartial tribunal.”
- And it says that “everyone has the right to seek and to enjoy in other countries asylum from persecution.”
- Preamble
Achievements of UNDHR
- It is recognized as having inspired and paved the way for more than 70 human rights treaties at global and regional levels, according to the U.N.
- It inspired the decolonization movement, the anti-apartheid movement.
- It also inspired freedom fighters all around the world, be it on gender issues, be it on LGBTIQ+ issues, be it against racism.
What is the situation now?
- The 75th anniversary comes as human rights are challenged in the war between Israel and Hamas, Russia’s war in Ukraine, internal conflicts in Myanmar and Sudan and in a host of other places and situations.
- UN. Secretary-General Antonio Guterres said the universal declaration has been too often misused and abused.
- It is exploited for political gain and it is ignored, often, by the very same people.
- However, Amnesty International says the declaration is living proof that a global vision for human rights is possible & can be realized.
- Despite the many times the declaration has been ignored or exploited, it is still relevant, and the world should honour its successes and learn from its failures.
Source: Indian Express
GS-III
Foreign portfolio investors (FPIs)
Subject: Economy
Why in News?
Recently, Foreign portfolio investors (FPIs) injected ₹26,505 crore into the Indian equity markets in the first six trading sessions of December
Background:-
- Kislay Upadhyay, the founder of FidelFolio Investments, attributed the FPI inflows to the outcome of major State elections that signalled political stability going forward.
About Foreign Portfolio Investors (FPIs):-
- Foreign portfolio investors are those who invest funds in markets outside of their homes.
- Their investments typically include equities, bonds and mutual funds.
- It does not provide the investor with direct ownership of financial assets.
- It is relatively liquid depending on the volatility of the market.
- Examples of FPIs include stocks, bonds, mutual funds, exchange-traded funds, American Depositary Receipts (ADRs), and Global Depositary Receipts (GDRs).
- FPI is part of a country’s capital account and is shown on its Balance of Payments (BOP).
Advantages:-
- Investors can gain substantially from exchange rate differences.
- Helps companies raise significant capital without incurring massive expense.
- FPIs help investors diversify their portfolios, which, in turn, boosts their confidence.
- FPIs inevitably move towards larger markets with lower competition. This combination is rather attractive to any investor.
Disadvantages:-
- Economic turmoil and political instability may have a negative impact on any investment via the FPI route.
- Despite the fluid nature of FPIs, losses may pile up if funds are not withdrawn hastily.
FPIs vs FDIs:-
- An FDI, by default, establishes a tangible and direct business interest in the target country. An FPI does not entail any such hands-on business It is a passive form of investing.
- Unlike FDIs, an FPI does not require any transfer of IP, technology, or know-how. There is no need to enter a joint venture with a partner company.
- FDI comprise significantly larger sums and any tie-ups or operations tend to last longer than portfolio investors.
- FDIs are usually the domain of major players in the industry, venture capital ecosystems, and investment branches of globally recognized financial institutions. Most FPIs include smaller players who invest in a foreign country’s assets and securities for short-term profit.
Source: The Hindu
India Plans to Boost Renewable Energy Capacity
Subject: Environment and Ecology

Why in News?
- The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) has proposed an exemption for green hydrogen developers from adhering to its list of authorised manufacturers to enable them to import solar PV modules and wind turbine models from China.
- Additionally, MNRE also proposed an exemption on duties and taxes up till 2035 on equipment imports for setting up export-oriented green hydrogen projects.
What is the MNRE’s Proposal?
- The MNRE has proposed examining the possibility of exempting green hydrogen developers from its list of authorised manufacturers.
- This will allow them to import solar PV modules and wind turbine models from China in order to make exports of green hydrogen competitive.
- Currently, MNRE’s Approved List of Models and Manufacturers (ALMM) and Revised List of Models and Manufacturers (RLLM) do not include Chinese manufacturers.
- Background of the MNRE’s Proposal:
- Following the Galwan Valley skirmishes in 2020, the Indian government issued orders to clamp down on participation of Chinese vendors in public procurement.
- Recently, the Indian procurement portal GeM announced the removal of hundreds of Chinese vendors over the past three years.
- The government’s sidelining of Chinese manufacturers comes at a time when energy companies are doubling down on mass producing green hydrogen, for which renewable energy equipment and electrolysers are key.
- This is part of the MNRE’s policy to boost domestic manufacturing of renewable energy equipment.
- While central PSUs may not be able to import electrolysis machinery from China, it has not stopped others from doing so.
- In FY23, India imported machines and apparatus for electro-plating, electrolysis/electrophoresis worth $45.61 million, a 40% jump from the previous fiscal year.
- Following the Galwan Valley skirmishes in 2020, the Indian government issued orders to clamp down on participation of Chinese vendors in public procurement.
- Significance of the MNRE’s Proposal:
- Importing solar PV modules from China will help with supply and in making Indian exports of green hydrogen competitive at the global level.
- This will enable central PSUs like Indian Oil Corporation Ltd and NTPC Ltd, which have announced green hydrogen projects, to procure equipment manufactured in China.
- This will make India competitive in producing green hydrogen and achieve the targets set out in the National Green Hydrogen Mission.
- Importance of China for India:
- Besides, to meet its green hydrogen targets by 2030, India needs to add an additional renewable energy capacity of 125 gigawatt, nearly 3/4th of its current total capacity of 179 gigawatt.
- India has earmarked a total of Rs 4,400 crore for the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme for boosting domestic manufacturing of electrolysers under MNRE’s flagship Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen (SIGHT) programme.
- However, it could take years before India reaches some degree of self-sufficiency in electrolyser manufacturing capacity.
- While India plans to install 60 gigawatt of electrolysis capacity to meet its 2030 target of producing 5 million metric tonnes of green hydrogen, the domestic industry is still in nascent stages.
- China is a global hub for manufacturing electrolysers, with a 40% of global manufacturing capacity for electrolysers.
- Even as imports of Chinese solar PV modules to India fell by 76% during the first half of 2023 compared to the first half of 2022, they continue to be cheaper than those made in India.
Source: The Hindu
|
38 videos|5167 docs|1089 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 11th December 2023 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is Kadalekayi Parishe? |  |
| 2. What are Zonal Councils? |  |
| 3. What is the PM-JANMAN Scheme for PVTGs? |  |
| 4. What is the Conference on Disarmament (CD)? |  |
| 5. Who is considered a J&K Resident? |  |
















