12 Minute Test: Tables | Logical Reasoning (LR) and Data Interpretation (DI) - CAT PDF Download
The CAT exam tests not just accuracy but also your ability to interpret data quickly and make decisions under pressure. This focused test helps you sharpen your skills in reading, analysing, and comparing data from tables—one of the most common formats in the Data Interpretation section. With practice, you’ll develop both speed and precision, giving you an edge in the actual exam.
Benchmarking Performance
This test contains 2 sets of 4 questions each (8 questions in total). Aim to complete each set within 6 minutes, or about 1.5 minutes per question.
If you finish each set within 6 minutes:
You’re operating at a strong performance level. Try to improve further by reducing your average time per question to about 1 minute, while maintaining accuracy.If you exceed 6 minutes per set:
Review where you’re losing time—perhaps in reading the table too slowly, doing lengthy calculations, or missing key relationships. Revisit those questions, simplify your approach, and only then check the solutions to understand faster, smarter methods.
Stay focused, trust your preparation, and make every minute count. Good luck!
Set 1
An agency entrusted to accredit colleges looks at four parameters: faculty quality (F), reputation (R), placement quality (P), and infrastructure (I). The four parameters are used to arrive at an overall score, which the agency uses to give an accreditation to the colleges. In each parameter, there are five possible letter grades given, each carrying certain points: A (50 points), B (40 points), C (30 points), D (20 points), and F (0 points). The overall score for a college is the weighted sum of the points scored in the four parameters. The weights of the parameters are 0.1, 0.2, 0.3 and 0.4 in some order, but the order is not disclosed. Accreditation is awarded based on the following scheme: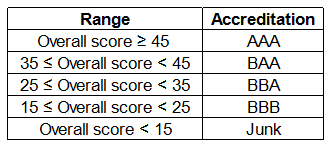
Eight colleges apply for accreditation, and receive the following grades in the four parameters (F, R, P, and I):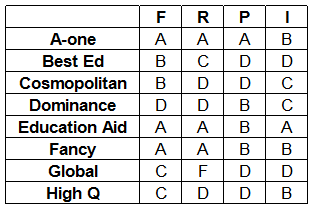
It is further known that in terms of overall scores:
1. High Q is better than Best Ed;
2. Best Ed is better than Cosmopolitan; and
3. Education Aid is better than A-one.
Q1: What is the weight of the faculty quality parameter?
(a) 0.2
(b) 0.3
(c) 0.4
(d) 0.1
Q2: How many colleges receive the accreditation of AAA?
Q3: What is the highest overall score among the eight colleges?
Q4: How many colleges have overall scores between 31 and 40, both inclusive?
(a) 0
(b) 2
(c) 1
(d) 3
Sol:It is given that: High Q > Best Ed > Cosmopolitan and Education Aid > A-one
We can say that High Q > Cosmopolitan
We can see that both High Q and Cosmopolitan got same points in reputation (R) and placement quality (P). High Q received more points in infrastructure (I) than Cosmopolitan whereas Cosmopolitan received more points in faculty Quality (F) than High Q.
Hence, we can say that Infrastructure’s weight should be greater than Faculty quality. i.e. I > F
Similarly, We can see that both Best Ed and Cosmopolitan got same points in faculty Quality (F) and placement quality (P). Best Ed received more points in reputation (R) than Cosmopolitan whereas Cosmopolitan received more points in infrastructure (I) than Best Ed.
Hence, we can say that reputation’s weight should be greater than infrastructure. i.e. R > I
Similarly, We can see that both Education Aid and A-one got same points in faculty Quality (F) and reputation (R). Education Aid received more points in infrastructure (I) than A-one whereas A-one received more points in placement quality (P) than Education Aid.
Hence, we can say that reputation’s weight should be greater than infrastructure. i.e. I > P
So basically there are two possible cases: R > I > P > F or R > I > F > P
Case 1: Order of weights assigned = R > I > P > F
R = 0.4, I = 0.3. P = 0.2, F = 0.1
In this case overall score received by Best Ed = 0.1*40+0.4*30+0.2*20+0.3*20 = 26
In this case overall score received by High Q = 0.1*30+0.4*20+0.2*20+0.3*40 = 27
We can see that High Q’s overall score is higher than Best Ed. Hence, this is a possible case.
Case 2: Order of weights assigned = R > I > F > P
R = 0.4, I = 0.3. P = 0.1, F = 0.2
In this case overall score received by Best Ed = 0.2*40+0.4*30+0.1*20+0.3*20 = 28
In this case overall score received by High Q = 0.2*30+0.4*20+0.1*20+0.3*40 = 28
We can see that High Q’s overall score is not greater than the overall score received Best Ed. Hence, this case is not possible.
Now that we know the weight of each parameter, we can calculate the overall score and accreditation received by each college.
Ans 1: We can see that the weight of the faculty quality parameter = 0.1. Hence,option D is the correct answer.
Ans 2: Three colleges received AAA rating.
Ans 3: The highest overall score among the eight colleges is 48.
Ans 4: From the table we can see that none of the mentioned college received an overall scores between 31 and 40, both inclusive. Hence, option A is the correct answer.
Set 2
DIRECTIONS: Read the table given below and answer the questions accordingly.
Shares traded on Bangalore, Madras, Bombay Stock Exchanges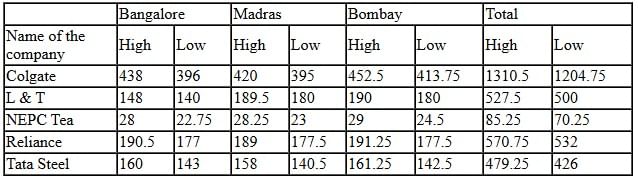
Q1: The average of the high rates of share in all the three Stock Exchanges for NEPC Tea is
A: Rs.28.42
B:Rs.27.42
C: Rs.29.1
D: Rs.28.93
Ans: A
Sol: The last column is the total of all three stock exchanges (high rates and low rates, resp.) for every company. So, the average for NEPC high rates = 85.25/3= Rs. 28.42. Hence, the answer is 1st option.
Q2: For Reliance, the low rate of share is less than the average of the low rates of shares of the same company, in the Stock Exchange at
A: Madras
B: Bombay
C: Bangalore
D: None of these
Ans: C
Sol: On: Average of low rates of shares of Reliance = (177.5+177.5+177)/3> 177, which is the low rate of share of Reliance at Bangalore stock exchange. So, the correct option is 3.
Alternatively,
We know that, the city having the smallest value will be lesser than the average and the city having the largest value will be definitely more than the average. Using this logic, the answer can be marked as Bangalore.
Q3: For Tata Steel, the ratio of the high rate of share to the low rate is maximum in the Stock Exchange at
A: Bangalore
B: Madras
C: Bombay
D: None of these
Ans: C
Sol: At Bangalore Stock Exchange, ratio of high rate to low rate = (160/143) = 1.11;At Madras Stock Exchange, ratio of high rate to low rate = (158/140.5) = 1.12;
At Bombay Stock Exchange, ratio of high rate to low rate = (161.25/142.5) = 1.13.
As the maximum ratio is in Bombay, it will be the answer. Hence, the answer option is 3.
Q4: The low rate of share in L & T at Madras Stock Exchange bears a ratio, to the total low rate of share of the same company, of
A: 8/19
B: 9/20
C: 11/25
D:9/25
Ans: D
Sol: Low rate of share of L & T at Madras Stock Exchange = Rs. 180.
Total of low rate of share of L & T in all three Stock Exchanges = Rs. 500.
Ratio of (i)/(ii)= 180/500 = 9/25. Hence, the answer is 4th option.
|
77 videos|180 docs|96 tests
|
FAQs on 12 Minute Test: Tables - Logical Reasoning (LR) and Data Interpretation (DI) - CAT
| 1. What is the purpose of the 12 Minute Test? |  |
| 2. How can I prepare for the 12 Minute Test? |  |
| 3. What types of questions are included in the 12 Minute Test? |  |
| 4. Is the 12 Minute Test difficult? |  |
| 5. How is the 12 Minute Test scored? |  |
















