Law: Meaning and Sources | Business Laws for CA Foundation PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Law? |

|
| What are Sources of Law? |

|
| Customs |

|
| Precedent |

|
| Legislation |

|
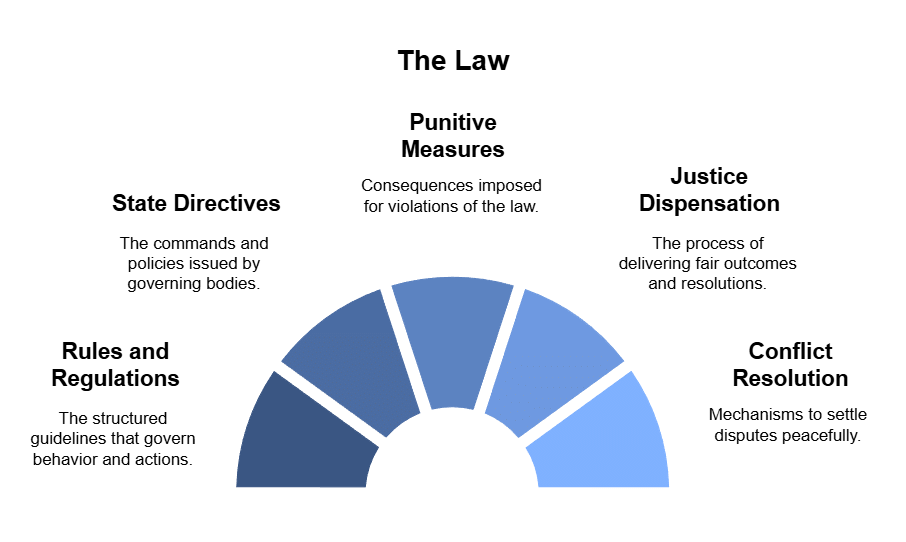
What is Law?
- The law encompasses rules and regulations endowed with legal authority, serving as a universal guide applicable to all individuals.
- It constitutes the directives of the state or the will of a sovereign, playing a pivotal role in governing behaviour and fostering compliance.
- The violation of these legal precepts results in punitive measures.
- In a civil society, the significance of law cannot be overstated, as it is indispensable for the smooth functioning of society.
- Thomas Hobbes vividly depicts a state of nature in his work "Leviathan," wherein the absence of a sovereign leads to a war against all.
- The primary objective of law is to ensure the dispensation of justice and facilitate conflict resolution.
Law derives from various sources, including customs, legislation, religion, judicial decisions, and precedent.
What are Sources of Law?
- Having established the existence of various law sources, this paper will specifically address three primary ones: customs, precedent, and legislation.
- Customs, recognized as the oldest legal source, have been shaped by traditions, norms, and values.
- The influence of religion and morality is evident in the formation of laws.
- The prominence of legislation as a significant source of law began to emerge after the 13th century.
- In the modern era, judicial decisions have also become a crucial source of legal principles.
- Additionally, Justice, Equity, and Good Conscience serve as other noteworthy sources of law.
Customs
Meaning
Customs are essentially unwritten rules or practices observed by a wide population, carrying a sense of obligation. In ancient times, people were primarily governed by customs, and over time, these practices became incorporated into major social institutions. The transition to a more rigid form occurred when these customs were adopted by legal or political entities, marking a significant historical evolution into law. An illustrative example is evident in Hindu marriage ceremonies, where the couple traditionally takes seven rounds around a holy fire. This well-established custom found its codification in section 7 of the Hindu Marriage Act, of 1955.
Essentials
Not every custom qualifies as a law; certain prerequisites must be met for a custom to attain legal recognition. The forthcoming paragraph delves into these essential criteria.
- A custom must have a longstanding practice, demonstrating antiquity.
- It should be openly known and not clandestinely observed.
- Furthermore, the custom must be reasonable in its nature, aligning with societal morality and established norms and values.
- Additionally, the custom should not contradict existing legislation, as there are instances where laws have nullified certain customs, such as child marriage and dowry.
Types
Customs can be broadly categorized into two groups: customs without sanctions and customs with sanctions. Customs without sanctions lack legal backing and are followed based on tradition and practice alone. On the other hand, customs with sanctions are obligatory in nature. This category is further divided into two types: legal customs and conventional customs. Conventional customs are binding on the parties involved in an agreement.
Precedent
Meaning
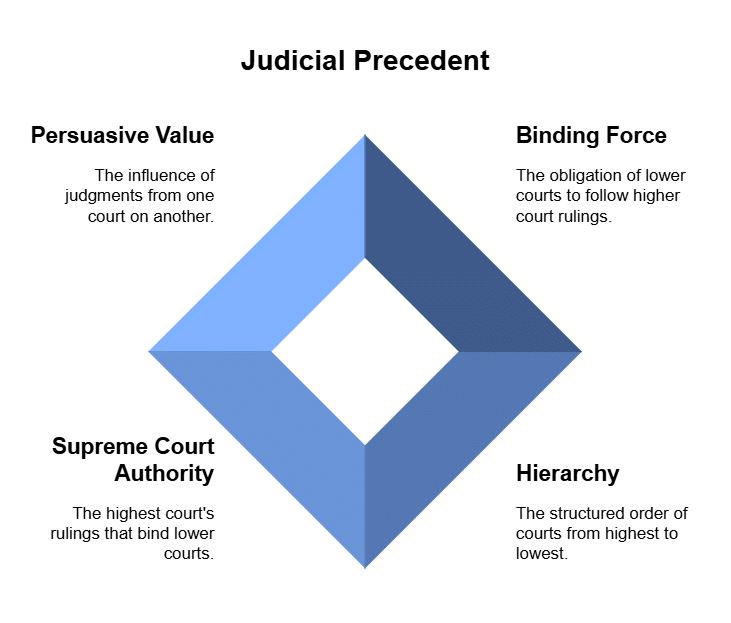
- The role of precedent, or judicial precedent, is highly significant in the legal systems of any nation.
- Positioned between the antiquity of customs and the modernity of legislation, judicial precedent involves the reliance on previous judgments.
- It carries the binding force on lower courts.
- The concept of hierarchy holds a crucial role in determining the authority to be adhered to in decision-making.
- The Supreme Court's judgments are binding on lower courts, establishing a strict hierarchy.
- Among other High Courts, they are considered subordinate to each other, and the judgments they render hold persuasive value.
- This hierarchical structure is delineated in the Indian constitution, and the courts play a pivotal role in interpreting and imparting broader perspectives to the law.
Essentials
Judicial precedent is characterized by its binding nature and hierarchical structure, where the authority is crucial in determining which judgments must be followed. This form of law is often referred to as judge-made law, highlighting the significant role judges play in expanding and shaping legal principles.
 |
Download the notes
Law: Meaning and Sources
|
Download as PDF |
Types
- A precedent consists of two components: Ratio Decidendi and Obiter Dicta.
- Only the Ratio Decidendi holds a binding nature, providing the rationale employed by the judge in reaching a decision.
- Lower courts are obligated to follow it when confronted with the same legal question.
- Conversely, the Obiter Dicta lacks binding authority; it represents a general observation of the judge and possesses only persuasive value over lower courts.
Legislation
Meaning
- The term legislation originates from the Latin language, translating to "making the law."
- This term holds significance as one of the crucial sources of law, backed by legal authority and widely acknowledged by various institutions.
- It encompasses two meanings: firstly, referring to the process of making laws, and secondly, denoting the laws themselves.
Essentials
From its meaning itself, essentials can be derived. Following are some of the main essentials:
- Legal backing
- It is a law-making process
- Recognition etc.
Types
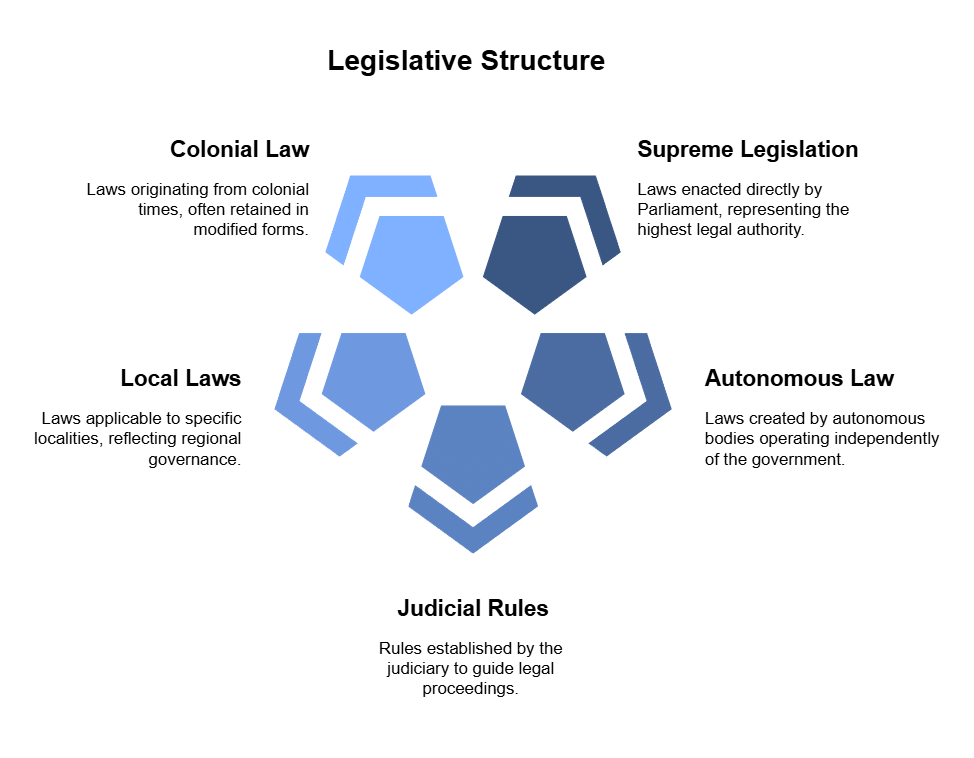
Legislation can be categorized into two segments: supreme legislation and subordinate legislation. Supreme legislation pertains to laws enacted by the Parliament. On the other hand, subordinate legislation is crafted by entities that are subordinate to the supreme authority or have been delegated authority by the sovereign. The following entities are included in the subordinate authority:
a. Autonomous Law
b. Judicial Rules
c. Local laws
d. Colonial Law
e. Laws made by the Executive
|
51 videos|110 docs|57 tests
|
FAQs on Law: Meaning and Sources - Business Laws for CA Foundation
| 1. What is the definition of law? |  |
| 2. What are the main sources of law? |  |
| 3. How do customs function as a source of law? |  |
| 4. What is the role of precedent in law? |  |
| 5. How does legislation impact the legal system? |  |