Unit 1: Introduction to Business Economics Chapter Notes | Business Economics for CA Foundation PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Overview |

|
| What is Business all about? |

|
| Definitions of Business Economics |

|
| Nature of Business Economics |

|
| Scope of Business Economics |

|
| Difference Between Economics and Business Economics |

|
Overview
What is Business all about?
A business is an activity related to the economy. There are many different types of businesses such as:- Manufacturing
- Mining
- Construction
- Agriculture
- Poultry farming
- Food processing
- Banking
- Insurance
- Health services
- Education
- Transportation
- Communication
Each type of business involves changing a set of inputs into outputs, which is the main idea of economic activity. This process results in the creation of net value added, which is the primary goal of all these activities.
The inputs in a business can be categorized as:
- Labor (people)
- Materials
- Machines
- Management
Economists also group inputs into four main categories: land, labour, capital, and entrepreneurship. The outputs refer to various kinds of goods and services. Within goods, there are different types such as:
- Consumer goods
- Producer goods
- Capital goods
- Private goods
- Public goods
- Merit goods (like essential items)
- Non-merit goods (like cigarettes)
Some goods are non-durable or meant for single use, while others are durable and can be used multiple times.
The main goal of any economic activity—like production, consumption, distribution, exchange, and inventory building—is to generate surplus or profit.
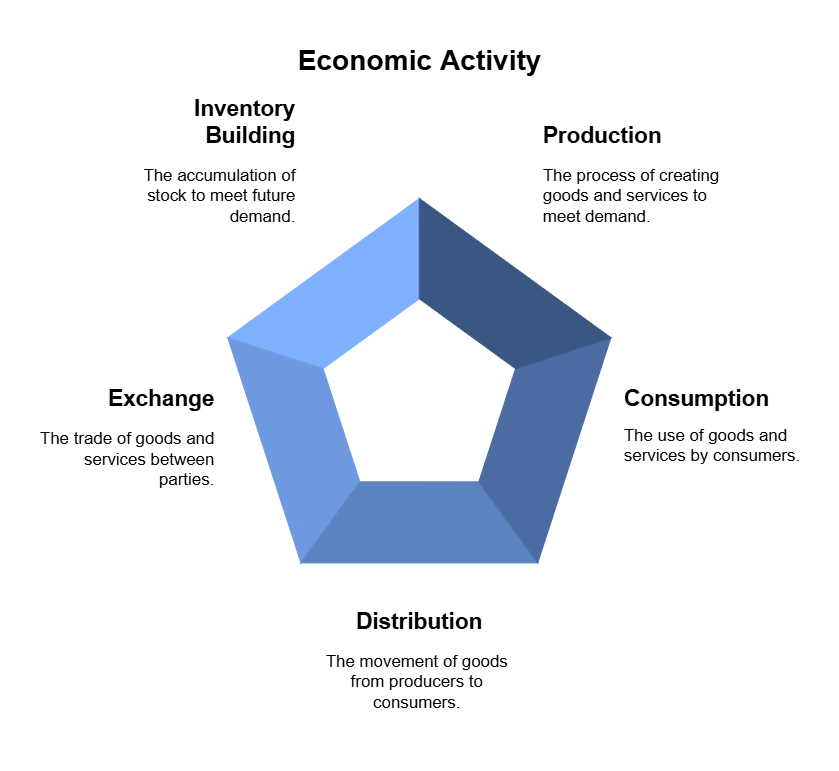 Some Non-Profit Organizations (NPOs) may not focus on making private profits but instead aim for social benefits.
Some Non-Profit Organizations (NPOs) may not focus on making private profits but instead aim for social benefits.
In the context of all economic enterprises, various decisions must be made. For example:
A production unit needs to decide:
- What to produce?
- When to produce?
- For whom to produce?
- Why to produce?
A finance enterprise dealing with funds must determine:
- When to raise funds?
- Where to use these funds?
- What should be the terms and maturity of these funds?
Each decision-making situation presents a choice, and economics is a field that helps in understanding the reasoning and best choices in these situations.
What is Economics about?
- The word ‘Economics’ comes from the Greek term ‘Oikonomia’, which means ‘household’.
- Up until the 19th century, Economics was referred to as ‘Political Economy’.
- Adam Smith's book, ‘An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations’ (1776), often called ‘The Wealth of Nations’, is seen as the first modern Economics work.
- To understand Business Economics, we first need to grasp what Economics means.
Example Scenario:
Imagine it’s your birthday, and your mother gives you ₹1000 as a gift.
You have multiple ways to spend this money, such as:
- Option 1: Throw a party for your friends and spend it all.
- Option 2: Buy a dress for ₹1000.
- Option 3: Go to a movie and dine at your favourite restaurant.
- Option 4: Purchase a book and save the remaining money.
- Notice that you have various options, but you can’t do everything at once.
- You’ll need to choose one option or combine a few, as you can’t have it all with just ₹1000.
- Choosing the best option gives you the most satisfaction.
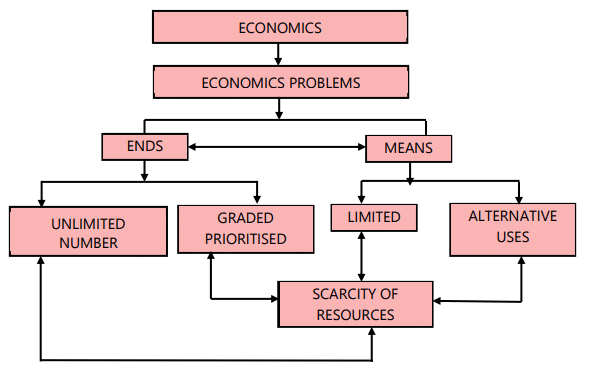
The Basics of Economics:
Two fundamental points about Economics are:
- Human beings have unlimited wants.
- Resources to satisfy these wants are limited.
- Economics studies how society allocates limited resources to meet competing wants.
- Efficient use of resources occurs when they are directed to their most valued purposes.
- In essence, Economics examines how people work together to transform limited resources into goods and services to meet their many wants.
Broader Aspects of Economics:
Modern Economics focuses on using scarce resources to meet human needs, but this view is not complete.
Today, economies have seen a huge increase in productive capacity:
- Population and workforce size have grown.
- New raw materials have been discovered.
- Improvements in technology and equipment have been made in various sectors.
- Better education and skills have enhanced workforce productivity.
- New energy sources, like shale gas and renewable energy, have emerged.
- However, growth in production and income can be uneven, with some periods seeing declines, such as during the Global Financial Crisis in 2007 or the COVID-19 pandemic in 2019.
- During downturns, many resources may go unused due to low demand.
Economic Issues:
Everyday economic issues include:
- Fluctuations in the prices of various goods and the overall price level.
- Disparities in economic prosperity and living standards between different countries.
- Some businesses earn large profits while others fail.
- Studying Economics helps us develop analytical skills to understand and address various economic issues.
- Economic tools assist in making informed decisions among different alternatives.
- It’s important to remember that economic problems are often complex and influenced by many factors, including political and social elements.
- While Economics can’t solve every problem, it provides a framework for examining issues and finding effective solutions.
Meaning of Business Economics
- Mr. G. Ramamurthy, the CEO of Worldwide Food Limited, asked his Board of Directors if they should enter the soft drink industry.
- Swaminathan expressed the need for more time, stating that this decision would significantly affect the company's future.
- Ramamurthy pointed out that the soft drinks market is expanding quickly and aligns with their main business of food.
- Another board member highlighted the tough competition from White Soft Drinks Ltd. and Black Nectar Ltd., which have been in the market for years.
- Ramamurthy acknowledged the competition but noted that there is still potential for growth in the soft drink market, especially as the food segment is nearing maturity.
- Ashok Aggrawal reminded everyone of Swati Foods, which failed in the soft drink sector, and questioned the reliability of their data and market trends.
- Ramamurthy assured the board that extensive analysis indicated a strong chance for higher returns in the soft drink industry than in their current food business.
- He emphasized the importance of acting quickly to seize the opportunity before it passes.
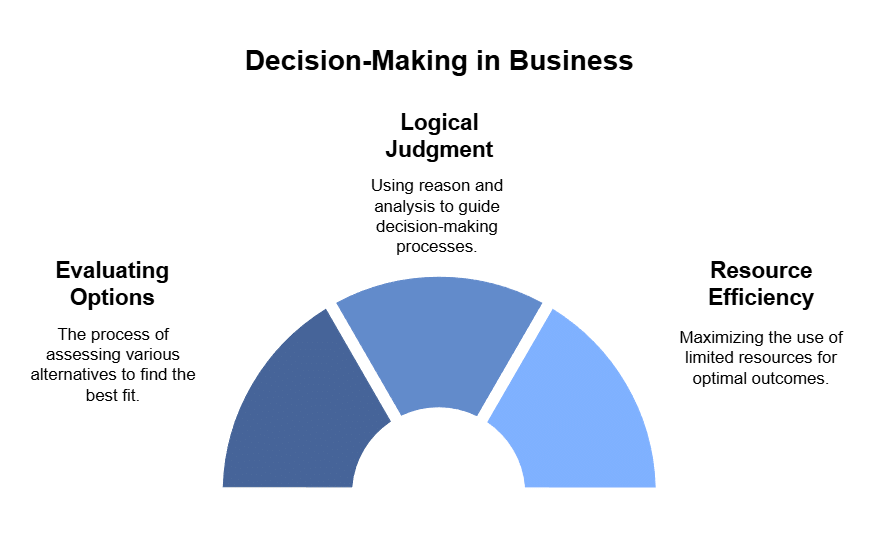
Decision-Making in Business:
- The situation shows that the company's management is faced with a decision-making challenge.
- The success of any business relies on making sensible decisions.
- Decision making involves choosing the best option from several alternatives to achieve a specific goal.
- It requires evaluating different options, using logical judgment based on information, and selecting the most suitable choice.
- Since resources like land, labour, capital, and management are limited, businesses must choose the most efficient options and dismiss the less effective ones.
Types of Decisions in Business:
Companies must make strategic, tactical, and operational decisions.
Key decision-making issues may include:
- Should our company enter this business?
- Should we launch a product in a competitive market?
- If we launch a product, which production technique should we use?
- Where should we source necessary inputs, and at what cost?
- Should we produce components ourselves or purchase them from others?
- What should be the optimal output and selling price?
- How will we market the product and which customer segments should we target?
- How can we manage risks and uncertainties?
- Making these decisions is complex due to the dynamic economic environment.
- Decisions are often made with imperfect knowledge and uncertainty.
- Therefore, management needs the right methods and analytical tools for effective decision-making.
Role of Business Economics:
- Business Economics helps management by providing a wealth of theories and techniques.
- It combines economic theory with real-world business practices, often referred to as Managerial Economics.
- Economic theories offer tools to understand concepts like demand, supply, costs, price, and competition.
- Business Economics applies these theories to business decision-making processes.
- It includes knowledge, logic, theories, and analytical tools that aid in making rational business decisions.
- Business Economics connects with Micro and Macro Economics, Operations Research, Statistics, Mathematics, and Decision-Making Theory.
- A skilled business economist combines concepts from these fields to analyze real managerial problems.
- Business Economics is valuable not only for profit-driven businesses but also for non-profit organizations such as NGOs and voluntary groups.
Definitions of Business Economics
Business Economics, often referred to as Managerial Economics, involves applying economic analysis to make informed business decisions regarding the optimal use of an organization's limited resources. Joel Dean described Business Economics as the utilization of economic analysis in shaping business policies. Essentially, Business Economics is a branch of Applied Economics, incorporating various quantitative techniques such as:- Linear Programming
- Regression Analysis
- Capital Budgeting
- Break-Even Analysis
- Cost Analysis
This text emphasizes the core of Business Economics, which is the Microeconomic Theory concerning the behavior of consumers and firms in both competitive and non-competitive markets. This theory equips managers with a fundamental framework for making crucial decisions about the allocation of their firm's scarce resources.
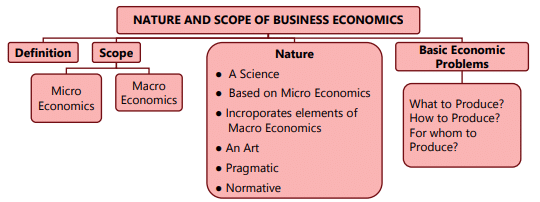
Nature of Business Economics
- Economics is mainly divided into two important categories: Micro Economics and Macro Economics.
- To understand business economics, it is essential to recognize the differences between these two areas first.
- Microeconomics focuses on individual units, such as households and businesses, and how they make decisions regarding resource allocation.
- Macroeconomics, on the other hand, looks at the economy as a whole, examining large-scale factors like national income, overall employment, and inflation.
- Understanding these distinctions helps clarify the role and nature of Business Economics.
Micro and Macro Economics
Micro Economics:
- Micro Economics focuses on the behaviour of individuals and organizations within an economic system. It looks at how individual units, such as consumers or companies, decide to use their limited resources effectively. This area concentrates on a small number of units rather than the whole economy, so it does not provide insights into larger economic trends.
Key areas studied in Micro Economics include:
- Product pricing
- Consumer behavior
- Factor pricing
- The economic conditions of specific groups
- Firm behaviour
- Industry location
Macro Economics:
- In contrast, Macro Economics looks at the economy as a whole rather than its individual parts. This field studies large economic aggregates, such as total output, employment levels, overall consumption, savings, investments, exports, imports, and foreign investments.
- It examines how these aggregates change over time and the overall economic environment that affects firms, governments, and households.
Important topics in Macro Economics include:
- National Income and National Output
- The general price level and interest rates
- Balance of trade and balance of payments
- The external value of the currency
- The overall level of savings and investment
- The level of employment and rate of economic growth
Business Economics mainly deals with Micro Economics, but Macro Economics also plays a crucial role. It helps analyze the broader economic conditions that can significantly affect a firm's performance and decision-making. Businesses need to understand the macroeconomic environment in which they operate. For instance, knowledge about inflation and interest rates is valuable for business economists when developing appropriate policies. Additionally, the long-term trends in business are influenced by the prevailing macroeconomic factors.
Having understood the meaning of Micro and Macro Economics, we shall examine the nature of Business Economics:
Nature of Business Economics
- Science: Business Economics is considered a science because it involves the systematic study of cause-and-effect relationships. It uses tools from decision sciences like Mathematics, Statistics, and Econometrics, along with Economic Theory, to formulate strategies for businesses. The approach is scientific, and the results are empirically tested for validity.
- Microeconomic Foundation: Business Economics is primarily based on Microeconomics. It focuses on the decision-making problems of individual businesses aiming to achieve specific objectives for long-term survival and profitability. Microeconomic techniques are heavily relied upon in this field.
- Macroeconomic Elements: While grounded in Microeconomics, Business Economics also considers Macroeconomic factors. Businesses do not operate in isolation; they are influenced by the broader economic environment, including factors like general price levels, income and employment levels, and government policies. Business managers need to be aware of these macroeconomic variables that can impact their operations.
- Art of Application: Business Economics is also an art because it involves the practical application of rules and principles to achieve set objectives. It requires judgment and creativity in applying economic theories to real-world situations.
- Market and Private Enterprise Theory: Business Economics utilizes the theory of markets and private enterprises. It focuses on the theory of the firm and resource allocation within the context of a private enterprise economy.
- Pragmatic Approach: Unlike Microeconomics, which can be abstract and theoretical, Business Economics takes a pragmatic approach. It addresses practical problems faced by firms in the real world, making it more applicable to everyday business situations.
- Interdisciplinary Nature: Business Economics is interdisciplinary, drawing on concepts and tools from various fields such as Mathematics, Operations Research, Management Theory, Accounting, Marketing, Finance, Statistics, and Econometrics. This broadens its analytical framework and enhances its applicability.
- Normative Perspective: Business Economics is generally normative in nature. It involves value judgments and prescribes what should be done in specific circumstances. While it incorporates positive economic theory to understand the environment, the emphasis is on providing guidelines for policy formulation, decision-making, and future planning.
Scope of Business Economics
The field of Business Economics is quite broad and addresses many practical challenges faced by managers and businesses. These challenges can be categorized into two main types:
- Internal issues or operational issues, which can be addressed using Microeconomics.
- External issues or environmental issues, which can be solved using Macroeconomics.
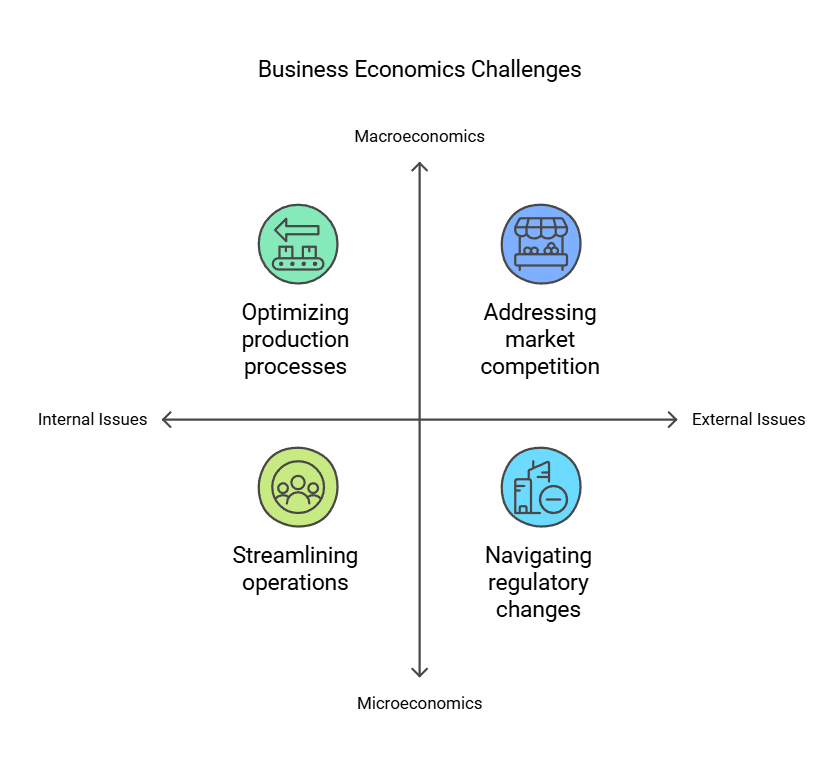
1. Microeconomics and Internal Issues
Internal or operational issues arise within an organization and are within the control of management. Examples include:- Choosing the type and size of the business.
- Decisions related to products.
- Technology and combinations of resources.
- Pricing strategies and promotional sales.
- Financing and managing investments and inventory.
Several microeconomic theories help tackle these issues:
Demand Analysis and Forecasting:
This area studies how consumers behave in the market. It looks at:
- Consumer preferences.
- Effects of changes in demand factors such as prices, income, and consumer tastes.
Demand forecasting involves predicting future demand based on past behaviors. Accurate forecasting helps businesses produce the right amount of goods at the right time.
Production and Cost Analysis:
This theory explains the link between inputs and outputs. A business economist must determine:
- The optimal output size is based on the firm's goals.
- Ways to avoid unnecessary costs.
Production analysis helps choose the right technology and cost-effective methods for production. Cost analysis helps understand how costs change with varying outputs.
Inventory Management:
Theories in inventory management guide firms to reduce costs related to:
- Work-in-process.
- Raw materials.
- Finished goods.
Methods like ABC analysis and mathematical models assist in maintaining optimal inventory levels.
Market Structure and Pricing Policies:
Analyzing the market structure reveals:
- The level of competition firms face.
- Market power and pricing abilities.
This analysis helps develop effective pricing strategies under different market conditions.
Resource Allocation:
- Business Economics uses tools like linear programming to identify the best strategies for efficiently using resources.
Theory of Capital and Investment Decisions:
To maximize profits, firms must carefully assess their investment choices and allocate capital wisely. Theories of capital provide guidelines for:
- Choosing investment projects.
- Evaluating the efficiency of capital use.
Profit Analysis:
Profit levels often fluctuate due to changing market conditions. Profit theory assists firms in:
- Measuring and managing profits.
- Planning for future profits.
Risk and Uncertainty Analysis:
- Businesses typically operate under risk and uncertainty. Analyzing these factors helps firms make informed decisions and create plans based on available data.
2. Macroeconomics and External Issues
External factors greatly impact how businesses operate. Key macroeconomic factors include:- The type of economic system.
- The stage of the business cycle.
- Trends in national income, employment, prices, savings, and investments.
- Government economic policies, including industrial, competition, fiscal, and trade policies.
- The role of central banks and the financial sector.
- Socio-economic organizations like trade unions and cooperatives.
- The social and political environment.
Business decisions must take these present and future environmental factors into account. Management cannot control these factors but should adapt its policies to lessen their negative impacts.
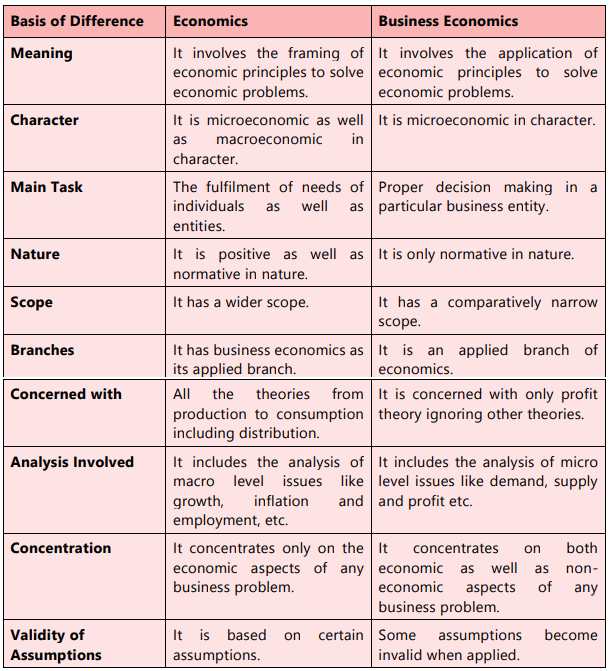
Difference Between Economics and Business Economics
|
86 videos|200 docs|58 tests
|
FAQs on Unit 1: Introduction to Business Economics Chapter Notes - Business Economics for CA Foundation
| 1. What is the definition of Business Economics? |  |
| 2. What is the nature of Business Economics? |  |
| 3. What is the scope of Business Economics? |  |
| 4. How does Business Economics differ from traditional Economics? |  |
| 5. Why is Business Economics important for firms? |  |
















