Acute Kidney Injury | Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| AKI-etiology |

|
| AKI-Clinical features |

|
| AKI-Complications |

|
| AKI-Diagnosis |

|
| AKI-Management |

|
Introduction
- Acute kidney injury (AKI), formerly known as acute renal failure, is characterized by the gradual impairment of kidney filtration and excretory function over a period of days to weeks.
- AKI is not a singular disease but rather a term encompassing a diverse range of conditions that exhibit common diagnostic features, primarily marked by an elevation in serum creatinine (SCr) concentration and frequently accompanied by reduced urine volume.
- The retention of nitrogenous and other waste products, typically eliminated by the kidneys, is a key consequence of AKI.
- The risk of developing or exacerbating chronic kidney disease (CKD) is heightened in individuals experiencing AKI.

AKI-etiology
AKI may be community-acquired or hospital-acquired.
Prerenal (60% of cases)
Any condition leading to decreased renal perfusion:
- Hypovolemia (e.g., burns, pancreatitis, diuretics)
- Hypotension (e.g., sepsis, dehydration)
- Renal vasoconstriction or stenosis (e.g., hepatorenal syndrome)
- NSAIDs/ACE inhibitors/Cyclosporine
Intrinsic (~35% of cases)
Any disease causing severe direct kidney damage:
- Acute tubular necrosis (causes approximately 85% of intrinsic AKIs)
- Glomerulonephritis
- Vascular
- HUS, TTP
- Malignant hypertension
- Tubulointerstitial nephritis
- Drug-induced
- Infectious
- Immunological
Postrenal (~5% of cases)
Any condition causing obstruction to urinary flow:
- Congenital malformations
- Acquired obstructions (e.g., iatrogenic/catheter-associated, tumors, stones, bleeding)
AKI-Clinical features

AKI-Complications
- Uremia: Mental status changes and bleeding complications.
- Hypervolemia: Weight gain, dependent edema, raised JVP, and pulmonary edema.
- Hyponatremia: Neurological abnormalities and seizures.
- Hyperkalemia: Fatal arrhythmias.
- Acidosis: Increased anion gap metabolic acidosis.
- Hyperphosphatemia and Hypocalcemia: Perioral paresthesias, muscle cramps, seizures, carpopedal spasms, and prolongation of the QT interval on electrocardiography.
- Bleeding: AKI-related uremia causes decreased erythropoiesis and platelet dysfunction.
- Cardiac Complications: Arrhythmias, pericarditis, and pericardial effusion.
- Malnutrition: AKI is a hypercatabolic state.
AKI-Diagnosis
- Blood Test Findings:
- Acute increase in serum creatinine and decrease in urine output.
- Metabolic acidosis.
- Hyperkalemia, hypocalcemia, and hyperphosphatemia.
- Urine Microscopy:
- Hyaline casts: A non-specific finding that may be observed in prerenal AKI (e.g., due to hypovolemia resulting in concentrated urine).
- Ultrasound:
- May reveal urinary tract obstruction and increased kidney size in postrenal AKI.
- Biopsy:
- In suspected rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis.
Types of AKI - Comparison
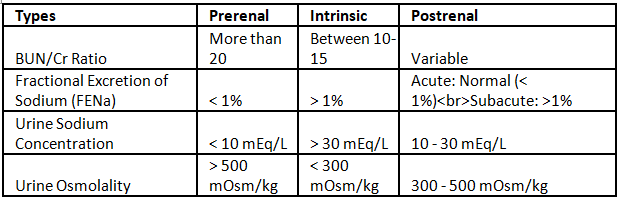
General Issues
- Enhancement of overall and renal hemodynamics through careful administration of fluids and appropriate use of vasopressors.
- Removal of nephrotoxic substances (e.g., ACE inhibitors, ARBs, NSAIDs, aminoglycosides) if feasible.
- Commencement of renal replacement therapy when deemed necessary.
The initiation of dialysis should not be delayed until a life-threatening complication of renal failure arises. * Some nephrologists commence dialysis for AKI empirically when the BUN surpasses a certain threshold (e.g., 100 mg/dL) in patients showing no clinical signs of kidney function recovery.
The available methods for renal replacement therapy in AKI necessitate access to either the peritoneal cavity (for peritoneal dialysis) or the major blood vessels (for hemodialysis, hemofiltration, and other hybrid procedures).
AKI-Management

Acute Renal failure
Q: Enumerate common etiological conditions for acute renal failure (ARF) in India. Discuss, in brief the management of ARF. (2011)
|
7 videos|219 docs
|
FAQs on Acute Kidney Injury - Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is the most common cause of acute kidney injury (AKI)? |  |
| 2. What are the clinical features of AKI? |  |
| 3. What are some complications of AKI? |  |
| 4. How is AKI diagnosed? |  |
| 5. How is AKI managed? |  |

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
















