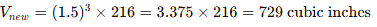Overview: Cubes and Cube Roots | Quantitative for GMAT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is a Cube? |

|
| What is a Cube Root? |

|
| The Cube Root Symbol |

|
| You Can Also Cube Negative Numbers |

|
| Perfect Cubes |

|
| Examples |

|
Cubes and cube roots often appear in various real-world contexts, from calculating the volume of objects to understanding growth patterns and exponential increases. For example, determining the volume of a box or calculating a growth rate over time relies on these principles.  In GMAT, mastering cubes and cube roots can provide you with quick shortcuts and insights to solve problems involving large numbers, measurements, and mathematical operations.
In GMAT, mastering cubes and cube roots can provide you with quick shortcuts and insights to solve problems involving large numbers, measurements, and mathematical operations.
What is a Cube?
- The cube of a number is the result of multiplying that number by itself three times.
- In other words, for any number y, the cube of y is given by y x y x y = y3
- Cube of 3 = 3 x 3 x 3 = 27
Example: What is 3 Cubed?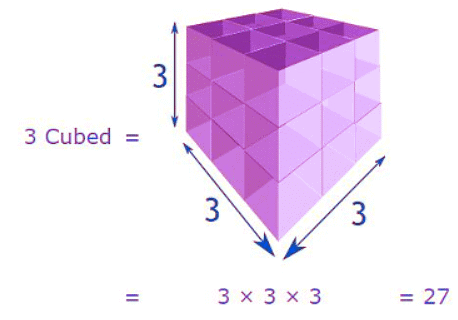 Note: we write "3 Cubed" as 33
Note: we write "3 Cubed" as 33
(The 3 in superscript means the number appears three times in multiplying)
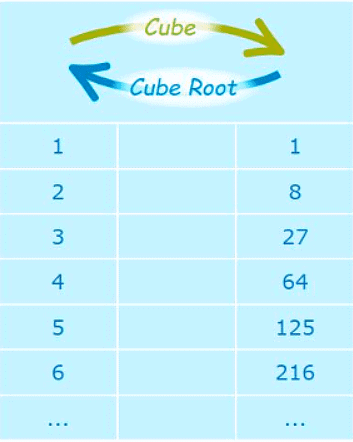
Cubes From 03 to 63
- 0 3 = 0 × 0 × 0 = 0
- 13 = 1 × 1 × 1 = 1
- 23 = 2 × 2 × 2 = 8
- 33 = 3 × 3 × 3 = 27
- 43 = 4 × 4 × 4 = 64
- 53 = 5 × 5 × 5 = 125
- 63 = 6 × 6 × 6 = 216
What is a Cube Root?
- The cube root of a number is a value that, when multiplied thrice, gives back the original number. If we have a number 27, the cube root of 27 is a number 3 such that: 3 x 3 x 3 = 27
- A cube root goes the other direction: 3 cubed is 27, so the cube root of 27 is 3.

- Some of the cubes and cube roots are given below
- Example: Find the cube root of 343?
Sol: 343 = 7 x7 x 7
Therefore , cuberoot of 343 = 7
The Cube Root Symbol
- The symbol of cube root is given below

- This is the special symbol that means "cube root", it is the "radical" symbol (used for square roots) with a little three to mean cube root.
- You can use it like this
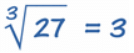
You Can Also Cube Negative Numbers
Have a look at this:
When we cube +5 we get +125: +5 × +5 × +5 = +125
When we cube −5 we get −125: −5 × −5 × −5 = −125
So the cube root of −125 is −5
 |
Download the notes
Overview: Cubes and Cube Roots
|
Download as PDF |
Perfect Cubes
The Perfect Cubes are the cubes of the whole numbers It is easy to work out the cube root of a perfect cube, but it is really hard to work out other cube roots.
It is easy to work out the cube root of a perfect cube, but it is really hard to work out other cube roots.
Examples
Example 1: If and are positive integers such that and , find the values of and
Sol: We are given Start by checking possible integer values of and :
For and would give .
So, +0=1000, which works.
Therefore, the solution is x=10 and y=0.Answer: Option 1
Example 2: A rectangular solid has a volume of 216 cubic inches. If the length of each edge is increased by 50%, what will be the new volume of the solid?
a. 324 cubic inches
b. 486 cubic inches
c. 512 cubic inches
d. 648 cubic inches
Sol: The volume of a rectangular solid is the product of its length, width, and height. If the edge length is increased by 50%, the new edge length is 1.5 times the original.
If the original volume is V=216 cubic inches, the new volume will be
|
115 videos|106 docs|113 tests
|
FAQs on Overview: Cubes and Cube Roots - Quantitative for GMAT
| 1. What is a cube in mathematics? |  |
| 2. How do you calculate the cube root of a number? |  |
| 3. Can you cube negative numbers, and what is the result? |  |
| 4. What are perfect cubes, and can you provide examples? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of the cube root symbol, and how is it used? |  |