UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC > Hip Joint
Hip Joint | Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Articular Surfaces |

|
| Ligaments |

|
| Neurovascular Supply |

|
| Relations |

|
Articular Surfaces
- Head of femur
- Acetabulum
- Ball and Socket type joint
Ligaments

(a) Frontal section through the right hip joint

(b) Anterior view of right hip joint, capsule in place

(c) Posterior view of right hip joint, capsule in place

Question for Hip JointTry yourself: Which type of joint is formed between the head of the femur and the acetabulum?View Solution
Neurovascular Supply

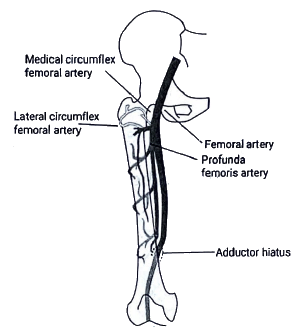
Relations
Anterior
- Pectineus lateral fibers
- Iliopsoas tendon
- Rectus femoris, straight head
- Femoral vein
- Femoral artery
- Femoral nerve
Posterior
- Obturator externus tendon, concealed by Quadratus femoris
- Obturator internus and gemelli
- Piriformis
- Sciatic nerve
- Gluteus maximus

Superior
- Rectus femoris, reflected head, concealed by minimus, medius, and partially by maximus
Inferior
- Pectineus lateral fibers and obturator externus
- Gracilis
- Adductors longus, brevis, magnus, and hamstring muscles

Congenital Hip Dislocation:
- More prevalent in the hip than in any other joint
- Arises from a developmental deficiency in the upper margin of the acetabulum, causing the femur head to move upward onto the gluteal surface of the ilium
Traumatic Dislocations:
- Three types: posterior (more frequent), anterior, or central
- Posterior hip dislocation can lead to sciatic nerve injury
Fractures:
- Fractures of the femoral neck are common in older individuals due to minor injuries. Damage to retinacular arteries results in avascular necrosis of the femoral head.
- Trochanteric fractures commonly occur in robust, adult individuals and are typically the outcome of severe and violent injuries.
Question for Hip JointTry yourself: Which hip muscle is concealed by the quadratus femoris tendon?View Solution
Hip diseases show an interesting age patter

Hip joint-Repeats
- Describe the hip joint under the following headings: ligaments, relations, movements, applied anatomy (1997) Describe the hip joint under the following headings: (2016)
i. Classification
ii. Movements
iii. Blood supply
iv. Ligaments - Describe HIP joint under the following headings: (2018)
i. Articular surface and Types
ii. Ligaments
iii. Relations
iv. Blood supply and Nerve supply
v. Movement
The document Hip Joint | Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
7 videos|219 docs
|
FAQs on Hip Joint - Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What are the articular surfaces of the hip joint? |  |
Ans. The articular surfaces of the hip joint are the acetabulum of the pelvis and the head of the femur. The acetabulum is a concave socket located on the lateral side of the pelvis, while the head of the femur is a spherical ball-like structure that fits into the acetabulum.
| 2. What ligaments support the hip joint? |  |
Ans. The hip joint is supported by several ligaments. The ligaments of the hip joint include the iliofemoral ligament, pubofemoral ligament, and ischiofemoral ligament. These ligaments help to stabilize the hip joint and prevent excessive movement.
| 3. What is the neurovascular supply of the hip joint? |  |
Ans. The neurovascular supply of the hip joint is primarily provided by the branches of the medial and lateral circumflex femoral arteries. These arteries supply blood to the hip joint, while the nerves such as the femoral nerve and obturator nerve provide the innervation.
| 4. What are the relationships of the hip joint? |  |
Ans. The hip joint is located in close proximity to various structures. Anteriorly, it is related to the inguinal ligament and the femoral nerve. Posteriorly, it is related to the gluteus maximus muscle and the sciatic nerve. Laterally, it is related to the tensor fasciae latae muscle and the iliotibial tract. Medially, it is related to the adductor muscles and the obturator nerve.
| 5. What are some common hip joint disorders? |  |
Ans. Some common hip joint disorders include osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, hip bursitis, hip labral tears, and hip impingement. These conditions can cause pain, stiffness, and limited range of motion in the hip joint. Treatment options vary depending on the specific disorder but may include medication, physical therapy, and in severe cases, surgical intervention.

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches
















