OP Poisoning | Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Organophosphorus Compounds-Classification |

|
| Clinical Manifestations |

|
| Management |

|
| Intermediate Syndrome |

|
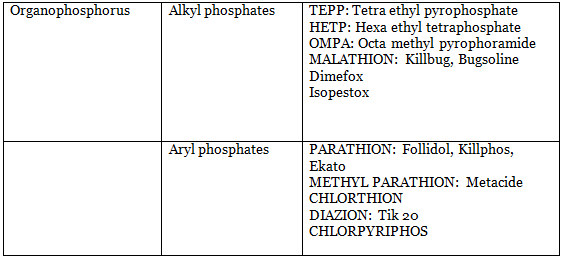
Organophosphorus Compounds-Classification
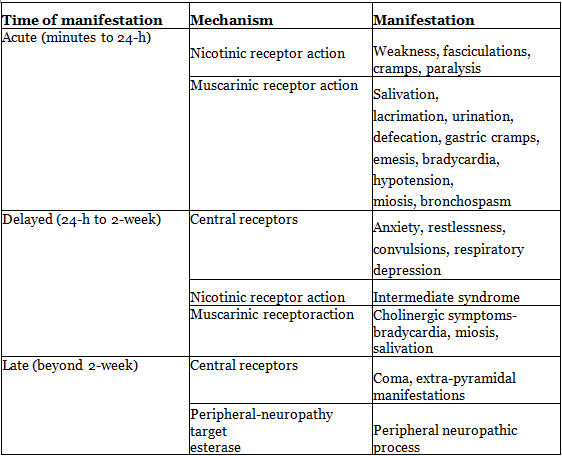
Clinical Manifestations
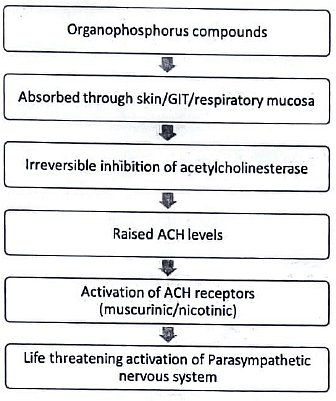
Pathophysiology
Memory aid for the clinical characteristics of organophosphate poisoning
Dumbbelss
- Diarrhea
- Urination
- Miosis
- Bronchospasm
- Bradycardia
- Neuromuscular Excitation
- Lacrimation
- Sweating
- Salivation
Management
Prioritize personal safety by wearing neoprene gloves, a gown, and a charcoal cartridge mask. Remove contaminated clothing and cleanse the affected skin. Perform patient decontamination, including clothing removal and skin cleansing. Ensure airway security, and measure erythrocyte cholinesterase activity, specifically 4-acetylcholinesterase activity with EC6.
Medication
Atropine: Administer 2 mg intravenously, repeat every 10 minutes until signs of atropinization, such as dryness of the mouth, manifest (up to 200 mg in a day). Sustained therapy with maintenance doses may be necessary for 1-2 weeks.
Oximes: Pralidoxime (2-PAM), obidoxime, should be administered only after atropine to mitigate the risk of transient worsening of acetylcholinesterase inhibition. Administer intravenously slowly at a dose of 1-2 g (20-40 mg/kg for children). Initiate treatment as early as possible, within a few hours, before the phosphorylated enzyme undergoes 'aging' and becomes resistant to hydrolysis.
Intermediate Syndrome
- Incidence
- Timing
- Presentation
- Management
Chronic organophosphorus poisoning
Cause:
- The etiology of this toxicity remains unknown, ruling out ChE inhibition as the contributing factor.
Presentation:
- Polyneuritis and demyelination develop after repeated exposure to specific fluorine-containing and triaryl organophosphates, with a latent period ranging from days to weeks.
Treatment:
- Recovery may extend over several years, and currently, there is no specific treatment available.
OP Poisoning-Repeats
Q1: What are clinical manifestations of organophosphorus poisoning and what antidote will you use in this poisoning (1994)?
Q2: Enumerate insecticides used in agriculture. Describe toxic effects of organ phosphorus poison in human beings (2001).
Q3: Classify the 'Organ phosphorus compounds' Describe the signs, symptoms, diagnosis and management of acute Malathion poisoning.' (2003)
Q4: Classify the organ phosphorous compounds. Describe the signs, symptoms and management of acute organ phosphorus poisoning (2007).
Q5: Describe the signs, symptoms and treatment of acute parathion poisoning. (2010)
Q6: A Young woman presented to the emergency department with a history of pesticide intake. She has massive frothing from the mouth and nose. Which is the pesticide she is likely to have consumed? State What would be the clinical features and management in this patient. Define the "Intermediate Syndrome" which may occur in this setting and its management. (2018)
|
7 videos|219 docs
|
FAQs on OP Poisoning - Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What are organophosphorus compounds and how are they classified? |  |
| 2. What are the clinical manifestations of organophosphorus compound poisoning? |  |
| 3. How should organophosphorus compound poisoning be managed? |  |
| 4. What is the intermediate syndrome associated with organophosphorus compound poisoning? |  |
| 5. How can organophosphorus compound poisoning be prevented? |  |

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
















