Pedestrian Injuries | Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Pedestrian injuries
Three types of injuries are observed:
i. Primary impact injuries
ii. Injuries from secondary impact
iii. Secondary injuries
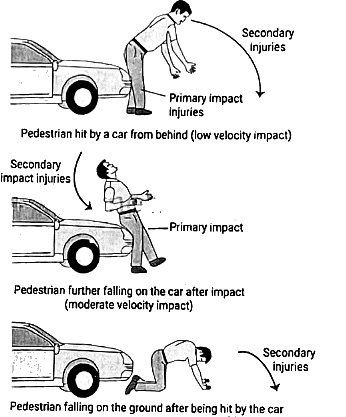

Primary impact injuries
- Owing to the initial collision
- The body part affected is contingent upon the person's positioning relative to the vehicle
- Facilitates the identification of the vehicle responsible
- Fracture of the bumper
Bonnet injury-Waddell's triad
Waddell's triad represents a characteristic injury pattern observed in children pedestrians who are hit by motor vehicles. It includes:
- Fracture of the femoral shaft
- Intra-thoracic or intra-abdominal injuries
- Contralateral head injury.
The mechanism of injury involves an initial impact that results in harm to the pelvis and femur (bumper injury) instead of the knees and tibias. Subsequently, the chest and abdomen are affected (by the grill, fender, or hood). Finally, the child is propelled onto the ground, sustaining an injury to the opposite side of the head.

Injuries from secondary impact
- Resulting from subsequent impacts
- Occur on the same side as the primary impact injuries
- Include injuries from rolling or being run over
Secondary injuries
- Caused by a person violently falling on the ground or colliding with other stationary objects
- Typically found on body parts opposite to the primary impact or on the head
- Lacerations are often observed on bony prominences, marked by traces of dirt.

Blast injuries
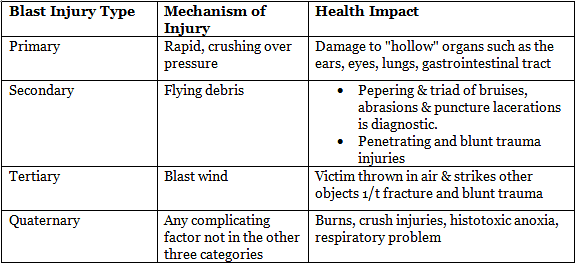
Primary blast injuries
- Resulting from a sudden and significant alteration in barometric pressure, radiating outward in concentric waves from the explosion site at approximately the speed of sound.
- Air blast: The most prevalent form of primary blast injury.
- Order of susceptibility: Tympanic membrane > Lung > Middle ear and cochlea > Eyes > Bowels > Brain.
- Underwater blast: The gastrointestinal (GI) tract is frequently affected, with minimal external injury but potentially severe internal damage.
- Solid blast (e.g., from a warship or tank): Primary impact on the skeleton, particularly the legs and vertebral column.
Injuries by sharp weapon
- Stab (top): Characterized by a depth greater than their length, these injuries typically result from knife wounds; however, implements like scissors, screwdrivers, and barbecue forks are also commonly used to inflict stab wounds.
- Incised (middle): Distinguished by a length greater than their depth, incised wounds are often caused by knives. Generally non-fatal, except in cases where they intersect a major artery, these injuries are typically less severe.
- Chop (bottom): Injuries from chopping are inflicted by objects that are both sharp and heavy, such as axes and hatchets. These wounds exhibit smooth edges similar to stab and incised wounds but also involve abrading and crushing of the surrounding tissue.

Lacerations?
Lacerations fall under the category of blunt force injuries rather than sharp force injuries, as they occur when the skin tears instead of being pierced by a sharp object. A key distinguishing feature is the existence of tissue bridging in lacerations, which is absent in injuries caused by sharp force.
Tissue bridging occurs when the skin is forcibly torn, revealing underlying structures like blood vessels that create "bridges" between the edges of the wound. This phenomenon is not observed in sharp force injuries, where the sharp implement cleanly severs these structures.


Suicidal vs homicidal wound

|
7 videos|219 docs
|
FAQs on Pedestrian Injuries - Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What are the common causes of pedestrian injuries? |  |
| 2. How can pedestrian injuries be prevented? |  |
| 3. What are the most common types of blast injuries? |  |
| 4. How can blast injuries be treated? |  |
| 5. What are some common sharp weapons that can cause injuries? |  |

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|


















