Class 6 Exam > Class 6 Notes > Science Olympiad Class 6 > Olympiad Notes: Electricity and Circuits
Olympiad Notes: Electricity and Circuits | Science Olympiad Class 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Electricity |

|
| Electric Cell |

|
| Electric Bulb |

|
| Electric Bulb connected to Electric Cell |

|
| Electric Circuit |

|
| Electric Switch |

|
| Conductors and Insulators |

|
Electricity
- Electricity is the movement of electric charge, providing energy to operate electrical and electronic devices.
- It powers various electrical appliances such as fans, tube lights, and water pumps, as well as electronic gadgets like TVs, computers, washing machines, and radios.
- Different methods are employed to generate electricity, including thermal power stations, windmills, batteries, and other sources.
Question for Olympiad Notes: Electricity and Circuits
Try yourself:
What is electricity?View Solution
Electric Cell
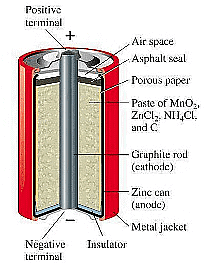
- An electric cell is a device that generates electricity suitable for powering smaller appliances such as torches, clocks, cameras, and radios.
- It consists of two terminals: positive (+) and negative (-).
- The positive side of an electric cell typically features a metal cap, while the negative side comprises a flat metal disc.
- Electricity is produced within the cell through chemical reactions occurring among stored chemicals. As these chemicals are depleted, the cell's capacity to produce electricity diminishes.
Electric Bulb

- An electric bulb is a device that emits light when an electric current flows through its terminals.
- It comprises two thick contact wires positioned at the center, with a thin wire known as the filament bridging them.
- The bulb's terminals are formed by one thick wire connected to the metal case at the base and the other to the metal tip at the base's center.
- Passage of electricity through the bulb's terminals heats up the filament, resulting in light production.
- A bulb is considered fused when its filament breaks, causing it to stop emitting light.
- To prevent a short circuit, the two terminals of the bulb are designed not to make direct contact with each other.
Question for Olympiad Notes: Electricity and Circuits
Try yourself:
What are the two terminals present in an electric cell?View Solution
Electric Bulb connected to Electric Cell
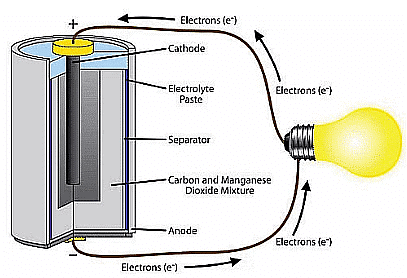
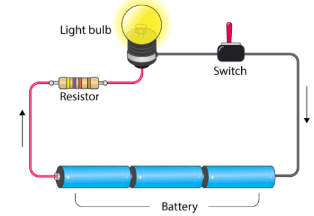
- An electric cell generates sufficient electricity to illuminate a bulb.
- To light up a bulb using a cell, it requires connecting a wire from one terminal of the cell to one terminal of the bulb. Simultaneously, the other terminal of the cell should be linked to the second terminal of the bulb.
- Failure to adhere to this connection sequence and improper wiring will result in the bulb not glowing.
Electric Circuit
- An electric circuit forms a full route for electricity (current) to travel between two terminals of an electric cell.
- The illumination of a bulb occurs when electric current passes through its terminals.
- In conventional terms, current moves from the positive terminal to the negative terminal of the battery.
- A fused bulb, characterized by a broken filament, creates an interrupted path, resulting in the bulb not emitting light.
 |
Download the notes
Olympiad Notes: Electricity and Circuits
|
Download as PDF |
Download as PDF
Electric Switch
- An electric switch serves as an electrical apparatus capable of establishing or interrupting an electric circuit.
- In the 'ON' position, a switch closes or completes the circuit, enabling the flow of current through it.
- Conversely, when in the 'OFF' position, the switch opens or breaks the circuit, preventing the passage of current.
Conductors and Insulators

- Materials that facilitate the passage of electric current are known as conductors of electricity, such as iron nails, keys, safety pins, water, and the human body.
- In contrast, materials that impede the flow of electric current are termed insulators of electricity, including rubber, plastic, glass, air, and cloth.
- Conductors primarily consist of metallic elements, while insulators predominantly comprise non-metallic substances.
- Electrical devices are constructed using conductors. However, to prevent accidental electric shocks or current flow through human contact, these devices are often enveloped in insulating materials like plastic, wood, or aluminum coverings.
The document Olympiad Notes: Electricity and Circuits | Science Olympiad Class 6 is a part of the Class 6 Course Science Olympiad Class 6.
All you need of Class 6 at this link: Class 6
|
49 videos|108 docs|105 tests
|
Related Searches























