UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC > Chemistry of Boranes
Chemistry of Boranes | Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Boranes |

|
| Structure and Bonding in diborane |

|
| Borazine |

|
| Boron Halides |

|
Boranes
Preparation
- Diborane can also be obtained in small quantities by the reaction of iodine with sodium borohydride in diglyme.

- On heating magnesium boride with HCl a mixture of volatile boranes are obtained.

Physical Properties
- Colourless and highly inflammable gas at room temperature.
- At high concentrations, it ignites rapidly in the presence of moist air at room temperature.
- It smells sweet.
- It has boiling point of about 180 K.
- It is toxic gas.
- It releases huge amount of energy when burnt in the presence of O2.
- It readily hydrolysed in the water to give hydrogen gas and boric acid.
Chemical Properties
- Diboranes reacts with water and alkali to give boric acid and metaborates respectively.

- Action of air: At room temperature pure diborane does not react with air or oxygen but in impure form it gives B2O3 along with large amount of heat.

ΔH = -2165 KJ mol-1 - Diborane reacts with methyl alcohol to give trimethyl Borate.

- Hydroboration: Diborane adds on to alkenes and alkynes in ether solvent at room temperature. This reaction is called hydroboration and is highly used in synthetic organic chemistry, especially for anti Markovnikov addition.

- Reaction with ionic hydrides: When treated with metal hydrides it forms metal borohydrides

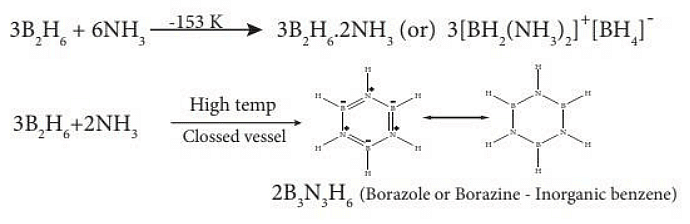
- Reaction with ammonia: When treated with excess ammonia at low temperatures diborane gives diboranediammonate. On heating at higher temperatures it gives borazole.

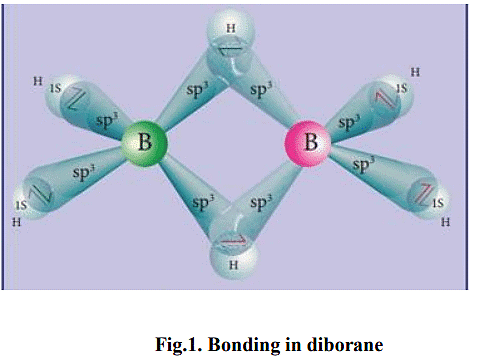
Structure and Bonding in diborane
- In diborane two BH2 units are linked by two bridged hydrogens. Therefore, it has eight B-H bonds. However, diborane has only 12 valance electrons and are not sufficient to form normal covalent bonds. The four terminal B-H bonds are normal covalent bonds (two centre - two electron bond or 2c-2e bond).
- The remaining four electrons have to be used for the bridged bonds. i.e. two three centred B-H-B bonds utilise two electrons each. Hence, these bonds are three centre- two electron bonds (3c-2e). The bridging hydrogen atoms are in a plane as shown in the figure 2.3. In diborne, the boron is sp3 hybridised.

- Three of the four sp3 hybridised orbitals contains single electron and the fourth orbital is empty. Two of the half filled hybridised orbitals of each boron overlap with the two hydrogens to form four terminal 2c-2e bonds, leaving one empty and one half filled hybridised orbitals on each boron. The Three centre - two electron bonds), B-H-B bond formation involves overlapping the half filled hybridised orbital of one boron, the empty hybridised orbital of the other boron and the half filled 1s orbital of hydrogen.
Uses of diborane
- Diborane is used as a high energy fuel for propellant
- It is used as a reducing agent in organic chemist
- It is used in welding torches
Question for Chemistry of BoranesTry yourself: What is the boiling point of diborane?View Solution
Borazine
- Borazine, also known as borazole.
- It is a polar inorganic compound with the chemical formula B3H6N3.
- In this cyclic compound, three BH units and three NH units alternate.
- The compound is isoelectronic and isostructural with benzene.
- Borazine has polar hexagonal structure containing 6 membered ring, in which B and N atoms are arranged alternately.
- Because the similarity between the structures of borazine and benzene that borazine is called inorganic benzene.
- In borazine, both Boron and Nitrogen are sp2 hybridized.
- Each N-atom has an empty p-orbital.
- B-N bond in borazine is dative bond, while arises from the sidewise overlap between the filled porbitals of N-atom and empty p-orbitals of B-atom.
- Since borazine is isoelectronic with benzene, both the compounds have aromatic electron cloud.
- Due to greater difference in electronegativity values of B and N - atoms, the electron cloud in B3N3 ring of the borazine molecule is partially delocalized. While in the case of benzene ring, the electron cloud is completely delocalized.
- MO calculations have indicated that electron drift from N to B is less than the electron drift from B to N due to the greater electronegativity of the N-atom.
- In benzene molecules, C=C bonds are non-polar, while in case of B3H6N3, due to difference in electronegativities between B and N atoms, the B-N bond is polar.
- It is due to the partial delocalization of electron clouds that bonding in the B3N3 ring is weakened.
- N-atoms retain its basicity and B-atoms retain its acidity.
- In borazine, B-N bond length is equal to 1.44 Ao, which is between calculated single B-N bonds (1.54 Ao).
- B=N bond length is 1.36 Ao.
- The angles are equal to 120o.
Preparation

Properties
- Colorless liquid
- Volatile liquid
- Boiling point 84.5 0C
- Melting point -58 0C
- Decomposes at -80 0C
Structure

Chemical properties

Uses
- Borazines are also starting materials for other potential ceramics such as boron carbonides.
- Borazine can also be used as precursor to growing boron nitride thin films on surfaces, such as nanomesh structure which is formed on rhodium.
Question for Chemistry of BoranesTry yourself: Which statement best describes the structure of borazine?View Solution
Boron Halides
It is represented as BX3 where X = F, Cl, Br, I
Synthesis
- When B2O3 is treated with halogens in presence of carbon, Boron halides are formed.

- It is synthesized by reactions of CaF2 and boric oxide in the presence of H2SO4

Properties
- They are small in size with high charge density.
- They are covalent in nature.
- They act as non- electrolytes in liquid state.
- The boiling point is ranging from 13-300°C and it decreases when the atomic number increases.
- Boron halides are electron deficient because B atom has an incomplete octet structure.
- Boron atom accepts 6 electrons from 3 BX bonds and 2 more electrons from the donor compound.
Chemical Properties
- BCl3 hydrolyzes readily to give hydrochloric acid and boric acid:

- Reduction of BCl3 to elemental boron is conduct commercially (see below). In the laboratory, when boron trichloride can be converted to diboron tetrachloride by heating with copper metal:

Question for Chemistry of BoranesTry yourself: What is the general formula for boron halides?View Solution
The document Chemistry of Boranes | Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
FAQs on Chemistry of Boranes - Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is the structure and bonding in diborane? |  |
Ans. Diborane (B2H6) has a unique structure and bonding. It consists of two boron atoms connected by two bridging hydrogen atoms and four terminal hydrogen atoms. The boron atoms form a planar structure with a bond angle of approximately 120 degrees. The bonding in diborane involves three-center, two-electron bonds known as banana bonds. These bonds arise from the overlap of the boron and hydrogen orbitals, resulting in a delocalization of the bonding electrons.
| 2. What is borazine and its structure? |  |
Ans. Borazine (B3N3H6) is an inorganic compound that resembles benzene in its structure. It consists of a six-membered ring composed of alternating boron and nitrogen atoms, with each boron atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms. The boron and nitrogen atoms are sp2 hybridized and form sigma bonds with each other, while the hydrogen atoms occupy the remaining p orbitals. The structure of borazine is often described as an inorganic analogue of benzene.
| 3. What are boranes and their chemistry? |  |
Ans. Boranes are chemical compounds that contain boron and hydrogen atoms. They are known for their unique structures and reactivity. Boranes exhibit a wide range of chemical properties, including their ability to act as Lewis acids and their reactivity towards nucleophiles. Boranes can also form complexes with various ligands, making them valuable in coordination chemistry. Additionally, the synthesis and study of boranes have contributed to our understanding of chemical bonding and molecular structure.
| 4. Can you provide examples of boron halides? |  |
Ans. Yes, some examples of boron halides include boron trifluoride (BF3), boron trichloride (BCl3), and boron tribromide (BBr3). These compounds are formed by the reaction of boron with the corresponding halogen gases. Boron halides are volatile and often used as Lewis acids in various chemical reactions. They are also important precursors in the synthesis of other boron-containing compounds.
| 5. How is the chemistry of boranes relevant to the UPSC exam? |  |
Ans. The chemistry of boranes is relevant to the UPSC exam as it encompasses various concepts in inorganic chemistry. Understanding the structure and bonding in boranes helps in comprehending the principles of chemical bonding and molecular geometry. Furthermore, the reactivity of boranes and their applications in coordination chemistry are important topics in the study of transition metal complexes. Familiarity with the chemistry of boranes can aid in answering questions related to inorganic chemistry on the UPSC exam.

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches